【实现自己的可视化引擎01】认识Canvas
【实现自己的可视化框架引擎02】抽象图像元素
【实现自己的可视化引擎03】构建基础图元库
【实现自己的可视化引擎04】图像元素动画
【实现自己的可视化引擎05】交互与事件
【实现自己的可视化引擎06】折线图
【实现自己的可视化引擎07】柱状图
【实现自己的可视化引擎08】条形图
【实现自己的可视化引擎09】饼图
【实现自己的可视化引擎10】散点图
【实现自己的可视化引擎11】雷达图
【实现自己的可视化引擎12】K线图
【实现自己的可视化引擎13】仪表盘
【实现自己的可视化引擎14】地图
【实现自己的可视化引擎15】关系图
前言
柱形图,又称长条图,是一种以长方形的长度为变量的统计图表。长条图用来比较两个或以上的价值(不同时间或者不同条件),只有一个变量,通常利用于较小的数据集分析。效果图如下:
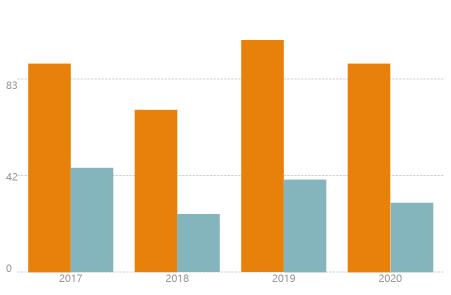
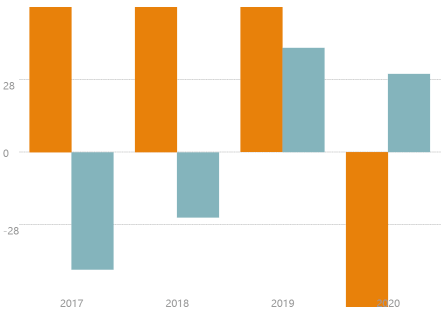
[{
label: '2017',
data: [
{ color: '#D78521', value: 90 },
{ color: '#90B3BB', value: -45 }
]
}, {
label: '2018',
data: [
{ color: '#D78521', value: 70 },
{ color: '#90B3BB', value: -25 }
]
}, {
label: '2019',
data: [
{ color: '#D78521', value: 100 },
{ color: '#90B3BB', value: 40 }
]
}, {
label: '2020',
data: [
{ color: '#D78521', value: -90 },
{ color: '#90B3BB', value: 30 }
]
}]
组件使用代码:
render() {
return (
<Histogram
data={data}
className="chart"
style={{
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
fontSize: 20,
fontColor:'#999999',
xFontSize: 20,
yFontSize: 20,
}}
/>
)
}
柱状图层
由上面效果图可以看出,我们柱状图有两种类型,一种是所有数据数值都大于0,另一种数据中有大于0同时存在小于0的数据。
当所有数据都大于0的情况,我们柱状图的坐标0轴位于底部,算法如下:
- 计算数据最大值,并根据最大Y坐标值计算单位数值占用的高度yStep;
- 计算每组数据柱图占用的宽度xStep;
- 遍历数据,根据公式(value - 0) / yStep 计算柱图的高度;
- 根据宽高绘制柱图矩形,并加入柱形图层。 代码实现如下:
// 计算绘图区域的高度
const entityHeight = this.height - this.xFontSize;
// 计算最大Y坐标值, 最大柱形占绘图区域的80%
const maxValue = max / 0.8;
// 根据最大Y坐标值计算单位数值占用的高度
const yStep = maxValue / entityHeight;
// 计算Y坐标线的高度步长
const yAxisStep = entityHeight / this.yAxisGraduations;
// 记录Y坐标值最大宽度
let yFontMaxWidth = 0;
// 绘制Y轴坐标值
for (let i = 0; i < this.yAxisGraduations; i++) {
const value = (i * yAxisStep * yStep).toFixed(this.enob);
const yText = new Text(this.canvas, {
text: value,
font: this.fontFamily,
size: this.yFontSize,
color: this.fontColor,
});
// Y轴坐标值偏移
const yShift = i === 0 ? 0 : i === this.yAxisGraduations - 1 ? yText.height : yText.height / 2;
yText.setPosition(this.position.x, this.position.y + this.xFontSize + i * yAxisStep - yShift);
if (yFontMaxWidth < yText.width) {
yFontMaxWidth = yText.width;
}
this.addChild(yText);
}
// 绘制Y轴坐标线
for (let i = 0; i < this.yAxisGraduations; i++) {
const line = new Line(this.canvas, {
lineWidth: 0.5,
lineDash: [5, 2],
color: '#999999',
position: new Point(this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth, this.position.y + this.xFontSize + i * yAxisStep),
to: new Point(this.position.x + this.width, this.position.y + this.xFontSize + i * yAxisStep),
});
this.addChild(line);
}
// 根据Y轴坐标宽度计算可绘制柱形区域的宽度
const entityWidth = this.width - yFontMaxWidth;
// 计算X轴单位宽度
const xStep = entityWidth / this.data.length;
// 绘制柱体
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
// 计算组内柱体的宽度, 左右边距0.1 * xStep
const xStep1 = xStep * 0.8 / this.data[i].data.length;
// 遍历组内数据,绘制长方形柱体
for (let j = 0; j < this.data[i].data.length; j++) {
// 计算柱体的高度
const height = (this.data[i].data[j].value - 0) / yStep;
console.log('yFontMaxWidth', yFontMaxWidth, this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth + (i + 0.1) * xStep + j * xStep1);
// 绘制长方形
const rect = new Rectangle(this.canvas, {
width: xStep1,
height,
type: Rectangle.TYPE.FILL,
color: this.data[i].data[j].color,
position: new Point(
this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth + (i + 0.1) * xStep + j * xStep1 + xStep1 / 2,
this.position.y + this.xFontSize + height / 2
),
});
this.addChild(rect);
}
// 绘制X轴坐标
let xText = new Text(this.canvas, {
font: this.fontFamily,
size: this.fontSize,
color: this.fontColor,
text: this.data[i].label,
});
xText.setPosition(
this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth + (i + 0.5) * xStep - xText.width / 2,
this.position.y
);
this.addChild(xText);
}
当所有数据同时存在正值与负值的情况,我们柱状图的坐标0轴位于图层的中央。我们计算柱形的高度,柱图的位置起始计算位置为height/2,当数值小于0时,我们需要下移一个柱图的高度,绘制算法如下:
- 计算数据绝对值的最大值,并根据最大Y坐标值计算单位数值占用的高度yStep;
- 计算每组数据柱图占用的宽度xStep;
- 遍历数据,根据公式(value - 0) / yStep 计算柱图的高度;
- 根据宽高绘制柱图矩形,当数值小于0时,我们将矩形的位置下移矩形高度。 实现代码如下:
// 计算绘图区域的高度
const entityHeight = this.height - this.xFontSize;
const yAbsMax = Math.abs(max) > Math.abs(min) ? Math.abs(max) : Math.abs(min);
// 根据最大Y坐标值计算单位数值占用的高度
const yStep = yAbsMax / 0.9 / entityHeight;
const yAxisCount = Math.ceil((this.yAxisGraduations + 1) / 2);
// y轴高度步进
const yAxisStep = entityHeight / yAxisCount / 2;
let yFontMaxWidth = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < yAxisCount; i++) {
const value = (i * yAxisStep * yStep).toFixed(this.enob);
// 正方向坐标值
const yText = new Text(this.canvas, {
text: value,
font: this.fontFamily,
size: this.yFontSize,
color: this.fontColor,
});
// Y轴坐标值偏移
const yShift = i === yAxisCount - 1 ? yText.height : yText.height / 2;
yText.setPosition(
this.position.x,
this.position.y + entityHeight / 2 + this.xFontSize + i * yAxisStep - yShift
);
if (yFontMaxWidth < yText.width) {
yFontMaxWidth = yText.width;
}
// 负方向坐标值
const yText2 = new Text(this.canvas, {
text: `-${value}`,
font: this.fontFamily,
size: this.yFontSize,
color: this.fontColor
});
yText2.setPosition(
this.position.x,
this.position.y + entityHeight / 2 + this.xFontSize - i * yAxisStep - yShift
);
if (yFontMaxWidth < yText2.width) {
yFontMaxWidth = yText2.width;
}
this.addChild(yText, yText2);
}
// 绘制Y轴坐标线
for (let i = 1; i < yAxisCount; i++) {
// 正方向
const line = new Line(this.canvas, {
lineWidth: 0.5,
lineDash: [5, 2],
color: '#999999',
position: new Point(
this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth,
this.position.y + this.xFontSize + i * yAxisStep + entityHeight / 2
),
to: new Point(
this.position.x + this.width,
this.position.y + this.xFontSize + i * yAxisStep + entityHeight / 2
),
});
// 负方向
const line2 = new Line(this.canvas, {
lineWidth: 0.5,
lineDash: [5, 2],
color: '#999999',
position: new Point(
this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth,
this.position.y + this.xFontSize - i * yAxisStep + entityHeight / 2
),
to: new Point(
this.position.x + this.width,
this.position.y + this.xFontSize - i * yAxisStep + entityHeight / 2
),
});
this.addChild(line, line2);
}
// 绘制0轴与0线
let zeroText = new Text(this.canvas, {
text: '0',
font: this.fontFamily,
size: this.yFontSize,
color: this.fontColor
});
zeroText.setPosition(this.position.x, this.position.y + this.xFontSize + entityHeight / 2 - zeroText.height / 2);
let zeroLine = new Line(this.canvas, {
lineWidth: 0.5,
lineDash: [5, 2],
color: '#999999',
position: new Point(
this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth,
this.position.y + this.xFontSize + entityHeight / 2
),
to: new Point(
this.position.x + this.width,
this.position.y + this.xFontSize + entityHeight / 2
),
});
this.addChild(zeroText, zeroLine);
// 根据Y轴坐标宽度计算可绘制柱形区域的宽度
const entityWidth = this.width - yFontMaxWidth;
// 计算X轴单位宽度
const xStep = entityWidth / this.data.length;
// 绘制柱体
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
// 计算组内柱体的宽度, 左右边距0.1 * xStep
const xStep1 = xStep * 0.8 / this.data[i].data.length;
// 遍历组内数据,绘制长方形柱体
for (let j = 0; j < this.data[i].data.length; j++) {
// 计算柱体的高度
const height = (Math.abs(this.data[i].data[j].value) - 0) / yStep;
// 绘制长方形
const rect = new Rectangle(this.canvas, {
width: xStep1,
height,
type: Rectangle.TYPE.FILL,
color: this.data[i].data[j].color,
position: new Point(
this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth + (i + 0.1) * xStep + j * xStep1 + xStep1 / 2,
this.position.y + entityHeight / 2 + height / 2 + this.xFontSize - (this.data[i].data[j].value > 0 ? 0 : height)
),
});
console.log(rect);
this.addChild(rect);
}
// 绘制X轴坐标
let xText = new Text(this.canvas, {
font: this.fontFamily,
size: this.fontSize,
color: this.fontColor,
text: this.data[i].label,
});
xText.setPosition(
this.position.x + yFontMaxWidth + (i + 0.5) * xStep - xText.width / 2,
this.position.y
);
this.addChild(xText);
}
}
React 封装
React封装需要DOM的挂载完成,所以我们在生命周期componentDidMount函数中构建我们的图层。
export default class extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.ref = React.createRef();
}
componentDidMount () {
const { style = {}, data = [] } = this.props;
this.canvas = new Canvas({
ele: this.ref.current,
canAction: false,
});
this.histogram = new Histogram(this.canvas, style, data);
this.canvas.addChild(this.histogram);
this.histogram.make();
this.canvas.paint();
}
render() {
const { className = '' } = this.props;
return (
<div className={className} ref={this.ref} />
)
}
}