前言
雷达图是以相同点开始的轴上表示的三个或更多个定量变量的二维图形的形式显示多变量数据的图形方法。效果图如下:
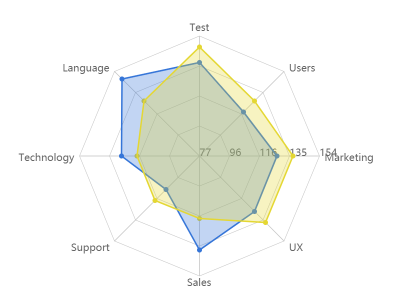
[
{ label: 'Marketing', a: 50, b: 60 },
{ label: 'Users', a: 40, b: 50 },
{ label: 'Test', a: 60, b: 70 },
{ label: 'Language', a: 70, b: 50 },
{ label: 'Technology', a: 50, b: 40 },
{ label: 'Support', a: 30, b: 40 },
{ label: 'Sales', a: 60, b: 40 },
{ label: 'UX', a: 50, b: 60 },
]
雷达图通过传入数据对象数组,数据对象label为雷达图坐标系标签,其余属性为该坐标系上该属性的数值。
接下来,我们看一下雷达图React组件的使用
render() {
return (
<Radar
className="chart"
data={[
{ label: 'Marketing', a: 50, b: 60 },
{ label: 'Users', a: 40, b: 50 },
{ label: 'Test', a: 60, b: 70 },
{ label: 'Language', a: 70, b: 50 },
{ label: 'Technology', a: 50, b: 40 },
{ label: 'Support', a: 30, b: 40 },
{ label: 'Sales', a: 60, b: 40 },
{ label: 'UX', a: 50, b: 60 },
]}
style={{
color: '#C3C3C3', // 背景坐标系颜色
fontColor: '#666666', // 标签字体颜色
enob: 0, // 坐标系有效位数
colors: {
a: '#3575D8', // 对应a属性数据的颜色
b: '#E4D733' // 对应b属性数据的颜色
},
lineWidth: 1, // 坐标系线框的线宽
}}
/>)
}
雷达图层
从效果图上看,我们可以把雷达图分成两部分:坐标系与数据层。
坐标层由不同径长的的正N边形组成,其中N表示数据对象数组的长度。数据层则由依据数值计算的不规则N边型组成。
坐标系构建算法如下:
- 根据图层长宽确定多变形径长(长宽中较小值);
- 根据数据数组长度确定正N边形内角angle = 360 / N;
- 根据角度与不通径长计算正多边形顶点坐标,并绘制多边形;
- 计算数据最大值与最小值,确定不同径长刻度值并绘制刻度值; 代码如下:
let max = -999999999; // 最大值
let min = 999999999; // 最小值
// 计算最大值与最小值
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
const item = this.data[i];
for (let key in item) {
if (key !== 'label') {
if (item[key] > max) {
max = item[key];
}
if (item[key] < min) {
min = item[key];
}
}
}
}
// 根据数据量计算步进角度
const angle = 360 / this.data.length; // 步进角度
// 根据图层大小计算坐标半径
const radius = 0.4 * (this.width > this.height ? this.height : this.width);
// 绘制标签及坐标
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
// 坐标角度
const axisAngle = angle * i / 180 * Math.PI;
// 坐标线
const line = new Line(this.canvas, {
position: new Point(this.position.x + this.width / 2, this.position.y + this.height / 2),
to: new Point(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle),
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle),
),
color: this.color,
lineWidth: this.lineWidth
});
// 标签
let text = new Text(this.canvas, {
text: this.data[i].label,
size: this.fontSize,
font: this.fontFamily,
color: this.fontColor
});
// 根据旋转的角度设置字体的位置
if ( angle * i === 0) {
text.setPosition(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle) + 10,
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle) - text.height / 2,
);
} else if (angle * i === 90) {
text.setPosition(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle) - text.width / 2,
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle) + 10,
);
} else if (angle * i < 90) {
text.setPosition(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle) + 10,
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle),
);
} else if (angle * i === 180) {
text.setPosition(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle) - text.width - 10,
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle) - text.height / 2,
);
} else if (angle * i > 90 && angle * i < 180) {
text.setPosition(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle) - text.width - 10,
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle),
);
} else if (angle * i > 180 && angle * i < 270) {
text.setPosition(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle) - text.width - 10,
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle) - text.height,
);
} else if (angle * i === 270) {
text.setPosition(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle) - text.width / 2,
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle) - text.height,
);
} else if (angle * i > 270) {
text.setPosition(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + radius * Math.cos(axisAngle) + 10,
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + radius * Math.sin(axisAngle) - text.height,
);
}
this.addChild(line, text);
}
let axisMin = 0; // 刻度的最小值
let axisMax = 0; // 刻度的最大值
// 这里我们确保我们的数据不会充盈整个坐标,也不会缩小到0点情况
if (min < 0 && max > 0) {
axisMin = Math.abs(min) > Math.abs(max) ? - Math.abs(min) * 1.1 : - Math.abs(max) * 1.1;
axisMax = max * 1.1;
} else if (min < 0 && max < 0) {
axisMin = min * 1.1;
axisMax = 0;
} else if (min > 0) {
axisMin = 0;
axisMax = max * 1.1;
}
// 单位数值的单位长度
let radiusStep = radius / (axisMax - axisMin);
// 单位刻度的长度
let graduationStep = radius / this.graduationNum;
// 绘制刻度多边形
for (let i = 0; i <= this.graduationNum; i++) {
if (this.shape === RadarLayer.SHAPE.BLOCK) {
// 刻度为多边形
// 多边形的点数组
let polygonPoints = [];
for (let j = 0; j < this.data.length; j++) {
polygonPoints.push(
new Point(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + i * graduationStep * Math.cos(angle * j / 180 * Math.PI),
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + i * graduationStep * Math.sin(angle * j / 180 * Math.PI)
)
)
}
console.log(this.lineWidth)
let polygon = new Polygon(this.canvas, {
lineWidth: this.lineWidth,
color: this.color,
type: Polygon.TYPE.STROKE,
}, polygonPoints);
this.addChild(polygon);
} else {
// 刻度为圆
let circle = new Circle(this.canvas, {
type: Circle.TYPE.STROKE,
radius: i * graduationStep,
position: new Point(this.position.x + this.width / 2, this.position.y + this.height / 2),
lineWidth: 1,
});
this.addChild(circle);
}
// 刻度值
let txtValue = (i * graduationStep / radiusStep + axisMax).toFixed(this.enob);
let text = new Text(this.canvas, {
text: txtValue,
font: this.fontFamily,
size: this.fontSize,
color: this.fontColor,
position: new Point(this.position.x + this.width / 2 + i * graduationStep, this.position.y + this.height / 2)
});
this.addChild(text);
}
数据层的算法如下:
- 遍历数据计算某个属性在坐标轴上的坐标点,构建某个属性的多边形数组;
- 根据多边形点数组,构建多边形,如果为填充类型。 代码如下:
// 绘制数据
// 数据多边形对象
let dataPolygons = {};
// 遍历数据构建数据多变形对象
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
const item = this.data[i];
for(let key in item) {
if (key !== 'label') {
if (dataPolygons[key] === undefined) {
dataPolygons[key] = [];
}
let distance = (item[key] - axisMin) * radiusStep;
let p = new Point(
this.position.x + this.width / 2 + distance * Math.cos(angle * i / 180 * Math.PI),
this.position.y + this.height / 2 + distance * Math.sin(angle * i / 180 * Math.PI)
);
dataPolygons[key].push(p);
// 数值点
let circle = new Circle(this.canvas, {
radius: this.lineWidth * 5,
position: p,
type: Circle.TYPE.FILL,
color: this.colorMap[key]
});
this.addChild(circle);
}
}
}
// 遍历数据多边形对象,绘制多边形
for(let key in dataPolygons) {
let polygon = new Polygon(this.canvas, {
type: Polygon.TYPE.STROKE,
color: this.colorMap[key],
lineWidth: this.lineWidth * 3,
}, dataPolygons[key]);
this.addChild(polygon);
if (this.type === RadarLayer.TYPE.FILL) {
let fillPolygon = new Polygon(this.canvas, {
type: Polygon.TYPE.FILL,
color: this.colorMap[key],
alpha: 0.3,
}, dataPolygons[key]);
this.addChild(fillPolygon);
}
}
// 绘制结束
雷达图层的构造函数如下:
constructor(canvas, style, data = []) {
super(canvas, style);
this.width = style.width || this.canvas.width;
this.height = style.height || this.canvas.height;
this.data = data || [];
this.shape = style.shape || RadarLayer.SHAPE.BLOCK; // 坐标类型
this.type = style.type || RadarLayer.TYPE.STROKE; // 数值多边形为线框或填充型
this.colorMap = style.colors || {}; // 对应数据的颜色
this.graduationNum = style.graduationNum || 4; // 刻度数量
this.enob = style.enob === undefined ? 2 : style.enob; // 坐标系有效位数
}
React封装
React封装需要DOM的挂载完成,所以我们在生命周期componentDidMount函数中构建我们的图层。代码如下:
componentDidMount () {
const { style = {}, data = [] } = this.props;
this.canvas = new Canvas({
ele: this.ref.current,
canAction: false,
});
this.radar = new RadarLayer(this.canvas, {
shape: style.shape || RadarLayer.SHAPE.BLOCK,
type: style.type || RadarLayer.TYPE.FILL,
colors: style.colors,
color: style.color,
lineWidth: style.lineWidth,
graduationNum: style.graduationNum,
enob: style.enob,
fontColor: style.fontColor,
}, data);
this.canvas.addChild(this.radar);
this.radar.make();
this.canvas.paint();
}
目录
【实现自己的可视化引擎01】认识Canvas
【实现自己的可视化框架引擎02】抽象图像元素
【实现自己的可视化引擎03】构建基础图元库
【实现自己的可视化引擎04】图像元素动画
【实现自己的可视化引擎05】交互与事件
【实现自己的可视化引擎06】折线图
【实现自己的可视化引擎07】柱状图
【实现自己的可视化引擎08】条形图
【实现自己的可视化引擎09】饼图
【实现自己的可视化引擎10】散点图
【实现自己的可视化引擎11】雷达图
【实现自己的可视化引擎12】K线图
【实现自己的可视化引擎13】仪表盘
【实现自己的可视化引擎14】地图
【实现自己的可视化引擎15】关系图