from ipywidgets import widgets
from ipywidgets import interact, interactive, fixed, interact_manual
from ipywidgets import FloatSlider
import numpy as np
import io
import pandas as pd
file = widgets.FileUpload()
file

FileUpload(value=(), description='Upload')
data = pd.read_csv(io.BytesIO(file.value[0].content))
data.shape
select_time = widgets.NaiveDatetimePicker(description='Pick a Time')
box = widgets.VBox([select_time])
display(widgets.HBox([box]))

print(select_time.value)
num = widgets.FloatSlider(
value=7.5,
min=0,
max=10.0,
step=0.1,
description='Test:',
disabled=False,
continuous_update=False,
orientation='horizontal',
readout=True,
readout_format='.1f',
)
num

print(num.value)
val = widgets.IntProgress(
value=3,
min=0,
max=10,
description='Loading:',
bar_style='',
style={'bar_color': 'maroon'},
orientation='horizontal'
)
val

print(val.value)
n = widgets.BoundedFloatText(
value=7.5,
min=0,
max=10.0,
step=0.1,
description='Text:',
disabled=False
)
n

print(n.value)
char = widgets.Dropdown(
options=[('One', 1), ('Two', 2), ('Three', 3)],
value=3,
description='Number:',
disabled=False,
)
char

print(char.value)
f = widgets.ToggleButtons(
options=['Slow', 'Regular', 'Fast'],
description='模式:',
disabled=False,
button_style='info',
tooltips=['Description of slow', 'Description of regular', 'Description of fast'],
)
f

print(f.value)
text = widgets.Textarea(
value='Hello World',
placeholder='Type something',
description='String:',
disabled=False
)
text

print(text.value)
password = widgets.Password(
value='password',
placeholder='Enter password',
description='Password:',
disabled=False
)
password

print(password.value)
实时交互 interact
def f1(a):
display(a)
a = widgets.IntSlider(value=5, min=0, max=10)
out1 = widgets.interactive_output(f1, {'a': a})
display(a)
display(out1)
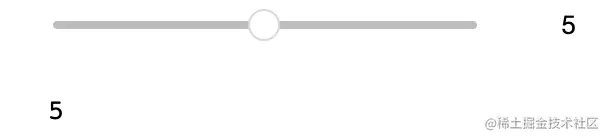
value = int(list(out1.outputs[0]['data'].values())[0])
print(value, "\n", type(value))
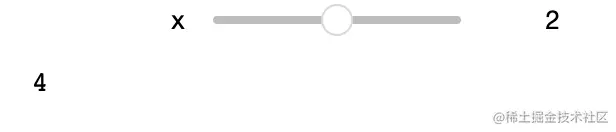
def f(x):
return x * 2
func = interact(f, x=2)
def slow_function(i):
print(int(i))
return
slow = interactive(
slow_function,
i=widgets.FloatSlider(min=1e4, max=1e6, step=1e4, continuous_update=True),
)
slow

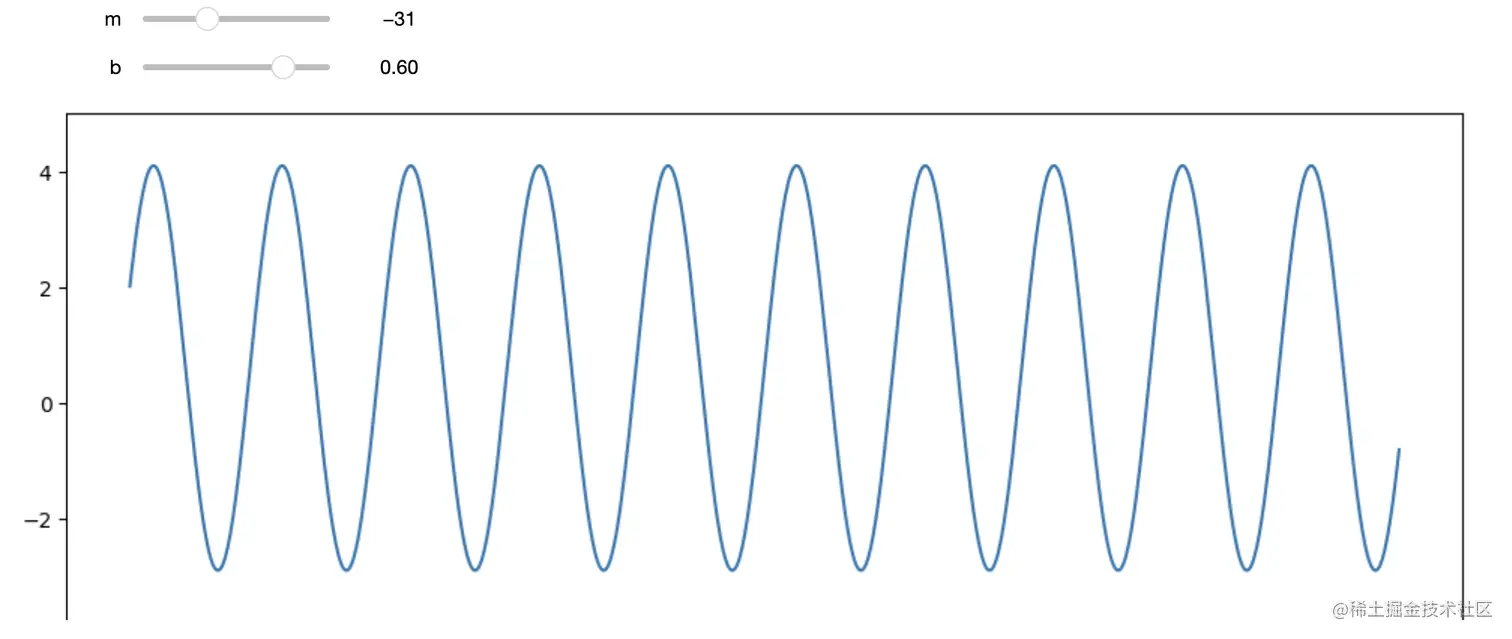
def f(m, b):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
x = np.linspace(-m, m, num=1000)
y = np.sin(x)*3.5 + b
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.ylim(-5, 5)
plt.show()
interactive_plot = interactive(f, m=(-100, 100), b=(-1.2, 1.2))
output = interactive_plot.children[-1]
output.layout.height = '350px'
interactive_plot