树简介
- 一种分层数据的抽象模型
- 前端常见的树包括:DOM树、级联选择、树控件
- js中没有树,使用Object和Array模拟树
- 树的常用操作: 深度/广度优先遍历、先中后序遍历(二叉树)
树的深度和广度优先遍历
- 深度优先遍历:尽可能深的搜索树的分支
- 广度优先遍历: 先访问离根节点最近的节点

深度优先遍历算法口诀
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的children挨个进行深度优先遍历
const tree = {
val: "a",
children: [
{
val: "a-1",
children: [
{
val: "a-1-1",
},
{
val: "a-1-2",
},
],
},
{
val: "a-2",
children: [
{
val: "a-2-1",
},
{
val: "a-2-2",
},
],
},
],
};
const dfs = (tree) => {
if (!tree?.val) {
return;
}
console.log(tree.val);
tree?.children?.forEach(dfs);
};
dfs(tree);
广度优先遍历口诀
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队
- 把队头出队并访问
- 把队头的children 挨个入队
- 重复第二、三步,直到队列为空
const tree = {
val: "a",
children: [
{
val: "a-1",
children: [
{
val: "a-1-1",
},
{
val: "a-1-2",
},
],
},
{
val: "a-2",
children: [
{
val: "a-2-1",
},
{
val: "a-2-2",
},
],
},
],
};
module.exports = {
tree,
};
const bfs = (tree) => {
const q = [tree];
while (q.length) {
let n = q.shift();
console.log(n?.val);
n?.children?.forEach((c) => q.push(c));
}
};
bfs(tree);
二叉树的先中序遍历
- 树中的每个节点最多只能有两个子节点
- 在js中通常用Object来模拟二叉树
先序遍历口诀 (根左右)
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历
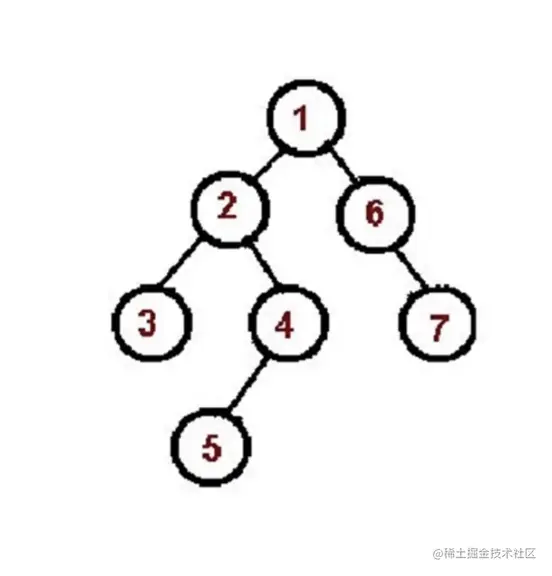
const tree = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
};
const preOrder = (tree) => {
if(!tree) {
return;
}
console.log(tree?.val);
preOrder(tree?.left);
preOrder(tree?.right);
}
preOrder(tree)
const preOrder = (tree) => {
if (!tree) {
return;
}
const stack = [tree];
while (stack?.length) {
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
if (n?.right) stack.push(n.right);
if (n?.left) stack.push(n.left);
}
};
中序遍历口诀 (左 根 右)
- 对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历
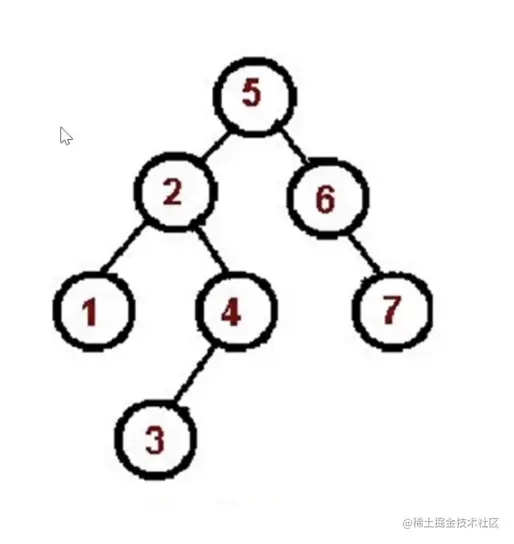
const tree = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
};
const inOrder = (tree) => {
if(!tree) {
return;
}
inOrder(tree?.left);
console.log(tree?.val);
inOrder(tree?.right);
}
inOrder(tree)
const inorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return;
const stack = [];
let p = root;
while (stack.length || p) {
while (p) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
p = n.right;
}
};
后序遍历算法口诀 (左右根)
- 对根节点的左子树进行后序遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行后序遍历
- 访问根节点
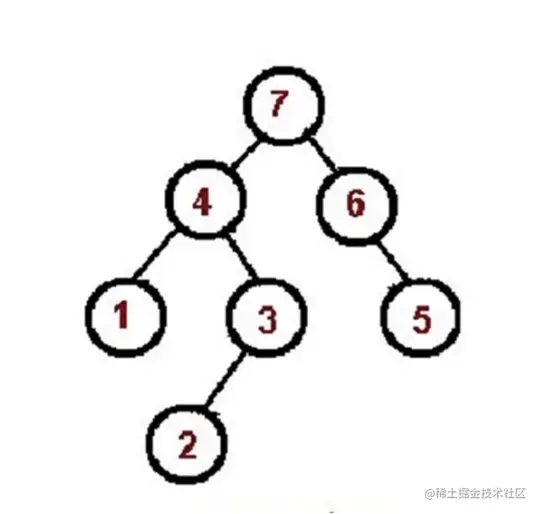
const tree = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
};
const postOrder = (tree) => {
if(!tree) {
return;
}
postOrder(tree?.left);
postOrder(tree?.right);
console.log(tree?.val);
}
postOrder(tree)
const postOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
const stack = [root];
const outPutStack = [];
while (stack.length) {
const c = stack.pop();
outPutStack.push(c);
if (c.left) stack.push(c.left);
if (c.right) stack.push(c.right);
}
while (outPutStack.length) {
const c = outPutStack.pop();
console.log(c.val);
}
};
leetcode-cn.com 算法题实战
完整题目请打开 leetcode
解题思路
- 求最多深度,考虑使用深度优先遍历
- 在深度优先遍历过程中,记录每个节点所在层级,找出最大层级即可
- 新增一个遍历记录最大深度
- 深度优先遍历整棵树,并记录每个节点层级,同时不断刷新最大深度这个变量
var maxDepth = function(root) {
let res = 0;
const dfs = (root, l) => {
if(!root) { return; }
if(!root?.left && !root?.right) {
res = Math.max(res,l);
}
if(root?.left) {
dfs(root?.left,l + 1)
}
if(root?.right) {
dfs(root?.right, l + 1)
}
}
dfs(root,1)
return res;
};
解题思路
- 求最小深度,考虑使用广度优先遍历
- 在广度优先遍历过程中,遇到叶子节点,停止遍历,返回节点层级
- 广度优先遍历整棵树,并记录每个节点层级
- 遇到叶子节点,返回节点层级,停止遍历
var minDepth = function (root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
const q = [[root, 1]];
while (q.length) {
const [n, l] = q.shift();
if (!n?.left && !n?.right) {
return l;
}
if (n?.left) q.push([n?.left, l + 1]);
if (n?.right) q.push([n.right, l + 1]);
}
};
下一站 图