出发点:在new Vue()方法,会调用_init()方法,那么这个方法在什么时候被定义的?
在src/core/instance/index.js文件中,定义了Vue构造函数和一些mixin方法。通过打断点调试。
先执行initMixin(Vue) stateMixin(Vue) eventsMixin(Vue) lifecycleMixin(Vue) renderMixin(Vue)等方法,那么我们先从此地方研究Vue的整体流程。
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
import { warn } from '../util/index'
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
先执行initMixin/stateMixin/eventsMixin/lifecycleMixin/renderMixin 方法 -- 主要定义Vue原型上方法
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
- initMixin(Vue):主要定义Vue.prototype._init
- stateMixin(Vue):定义一些state相关的方法 props /delete/$watch
- eventsMixin(Vue):定义和事件相关的方法 off,once
- lifecycleMixin(Vue):定义生命周期的更新和销毁的方法 _update,destroy
- renderMixin(Vue):定义 $nextTick,_render;还通过installRenderHelpers方法定义了一些和渲染函数相关的方法 比如:_v
export function installRenderHelpers (target: any) {
target._o = markOnce
target._n = toNumber
target._s = toString
target._l = renderList
target._t = renderSlot
target._q = looseEqual
target._i = looseIndexOf
target._m = renderStatic
target._f = resolveFilter
target._k = checkKeyCodes
target._b = bindObjectProps
target._v = createTextVNode
target._e = createEmptyVNode
target._u = resolveScopedSlots
target._g = bindObjectListeners
target._d = bindDynamicKeys
target._p = prependModifier
}
initGlobalAPI 方法
此方法是定义了Vue全局方法 在new Vue 之前执行
export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// config
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
//exposed util methods.
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
}
Vue.set = set
Vue.delete = del
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
// 2.6 新增的api --使对象为响应式 -- 使用这个代替Vuex
Vue.observable = <T>(obj: T): T => {
observe(obj)
return obj
}
/*
设置
Vue.options.components={
}
Vue.options.directives={
}
Vue.options.filters={
}
*/
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
// this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object
// components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios.
Vue.options._base = Vue
// 扩展Vue 就是注册 全局组件KeepAlive是abstract组件,还有三个钩子(created/destroyed/mounted)
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)
//定义Vue.extend方法
initUse(Vue)
//定义Vue.mixin
initMixin(Vue)
//定义Vue.extend
initExtend(Vue)
//定义 Vue.component/Vue.directive/Vue.filter 方法
//根据definition判断是获取还是注册操作
// Vue.component 就是执行Vue.extend
//
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
}
// 注册Vue.component/Vue.directive/Vue.filter 全局方法
export function initAssetRegisters (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
/**
* Create asset registration methods.
*/
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue[type] = function (
id: string,
definition: Function | Object
): Function | Object | void {
if (!definition) {//获取操作
return this.options[type + 's'][id]
} else {//注册操作
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && type === 'component') {
validateComponentName(id)
}
if (type === 'component' && isPlainObject(definition)) {
definition.name = definition.name || id
//this.options._base 就是Vue
definition = this.options._base.extend(definition)
}
if (type === 'directive' && typeof definition === 'function') {
definition = { bind: definition, update: definition }
}
this.options[type + 's'][id] = definition
return definition
}
}
})
/** Class 继承
* Class inheritance
就是生成 VueComponent
返回VueComponent构造函数
options 就是extendOptions 和 Vue的options 合并的结构
superOptions 指向super的options
*/
Vue.extend = function (extendOptions: Object): Function {
extendOptions = extendOptions || {}
const Super = this //Vue 每个Vue都有cid
const SuperId = Super.cid
// 配置项的_Ctor 如果不存在 创建并赋值{}
const cachedCtors = extendOptions._Ctor || (extendOptions._Ctor = {})
//缓存
if (cachedCtors[SuperId]) {
return cachedCtors[SuperId]
}
const name = extendOptions.name || Super.options.name
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && name) {
validateComponentName(name)
}
const Sub = function VueComponent (options) {
this._init(options)
}
//继承
Sub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype)
Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub
Sub.cid = cid++
//合并options
Sub.options = mergeOptions(
Super.options,
extendOptions
)
//定义super 指向Vue
Sub['super'] = Super
// For props and computed properties, we define the proxy getters on
// the Vue instances at extension time, on the extended prototype. This
// avoids Object.defineProperty calls for each instance created.
if (Sub.options.props) {
initProps(Sub)
}
if (Sub.options.computed) {
initComputed(Sub)
}
// allow further extension/mixin/plugin usage
Sub.extend = Super.extend
Sub.mixin = Super.mixin
Sub.use = Super.use
// create asset registers, so extended classes
// can have their private assets too.
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) {
Sub[type] = Super[type]
})
// enable recursive self-lookup
if (name) {
Sub.options.components[name] = Sub
}
// keep a reference to the super options at extension time.
// later at instantiation we can check if Super's options have
// been updated.
Sub.superOptions = Super.options
Sub.extendOptions = extendOptions
Sub.sealedOptions = extend({}, Sub.options)
// cache constructor
cachedCtors[SuperId] = Sub
return Sub
}
}
- Vue.extend(options);
- options | Object
- 是利用了Vue构造器 创建一个子类-VueComponent
- 返回VueComponent 构造函数
- use/component/directive/filter/extend/mixin/super --指向Vue
- options/extendOptions/superOptions
- new的时候执行_init()方法 就是Vue构造函数的_init()方法
const Sub = function VueComponent (options) { this._init(options) //this -> super }
initGlobalAPI:
- Vue的全局Api:
-
config
-
util
-
set
-
delete
-
nextTick
-
observable(2.6新增)
-
Vue.options.components,Vue.options.directives,Vue.options.filters 创建空对象
-
use
-
mixin
-
extend
-
定义Vue.component的方法
-
定义Vue.directive的方法
-
定义Vue.filter 的方法 Vue.component/Vue.directive/Vue.filter 判断definition 是否传递(第二个参数),如果传递了第二个参数就直接返回(就是获取操作)this.options.components,this.options.directives,this.options.filters [id] 获取; 就是全局组件/指令/过滤器 全部放在
this.options内部 -
version
-
cid
-
创建不同平台的patch函数
进入html页面开始执行代码
- 执行代码
Vue.component('comp',{
template:'<div>i am comp</div>'
})
-
调用Vue.component方法 返回 VueComponent构造函数 并且挂在this.options.components内,此项就是挂载全局组件的。
- 其实就是执行extend()方法,将definition 配置项转化成构造函数;
- 再执行new Vue方法;
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
foo:1
}
});
其实就是执行_init方法 (Vue.prototype_init)
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
-
在_init方法内部
- 合并 options --> 全局的和new Vue()时传人的options
{el:'#app',data:{foo:1}} - 一系列初始化操作
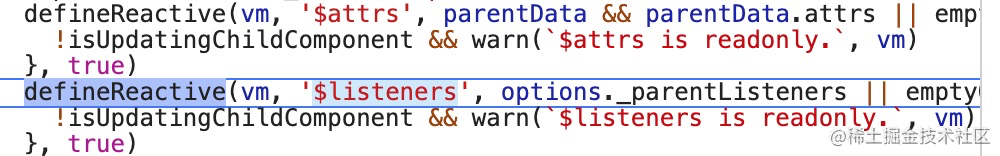
initLifecycle(vm) -- 定义实例vm的 $parent /$root / $children/$refs 等属性 初始化工作 initEvents(vm) -- 定义实例 _events={} initRender(vm) -- 定义实例的 $slots / $scopedSlots /_c / $createElement /定义$attrs/$listeners 响应式属性export function initEvents (vm: Component) { vm._events = Object.create(null) vm._hasHookEvent = false // init parent attached events const listeners = vm.$options._parentListeners if (listeners) { updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners) } } - 合并 options --> 全局的和new Vue()时传人的options
```js
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)