转换模型格式
- 使用官网提供的
tools/deploy/coffe2_converter.py进行转换. - 需要修改
setup_cfg(args)适配自己的数据集,以及模型情况.
def setup_cfg(args):
cfg = get_cfg()
# cuda context is initialized before creating dataloader, so we don't fork anymore
cfg.DATALOADER.NUM_WORKERS = 0
register_coco_instances("name", {},
"../../val.json",
"image_path")
metadata = MetadataCatalog.get("name")
print(metadata)
cfg.merge_from_file(
"../../configs/COCO-Detection/faster_rcnn_X_101_32x8d_FPN_3x.yaml"
)
cfg.DATASETS.TEST = ("name") # no metrics implemented for this dataset
cfg.DATALOADER.NUM_WORKERS = 4
cfg.SOLVER.IMS_PER_BATCH = 1
cfg.SOLVER.BASE_LR = 0.02
cfg.SOLVER.MAX_ITER = (
300
) # 300 iterations seems good enough, but you can certainly train longer
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.BATCH_SIZE_PER_IMAGE = (
128
) # faster, and good enough for this toy dataset
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.NUM_CLASSES = 20
cfg.OUTPUT_DIR = '../../name/output_20/'
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = os.path.join(cfg.OUTPUT_DIR, "model_final.pth")
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST = 0.5 # set the testing threshold for this model
cfg = add_export_config(cfg)
# cfg.merge_from_file(args.config_file)
# cfg.merge_from_list(args.opts)
cfg.DATASETS.TEST = ("name",)
cfg.freeze()
if cfg.MODEL.DEVICE != "cpu":
TORCH_VERSION = tuple(int(x) for x in torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
assert TORCH_VERSION >= (1, 5), "PyTorch>=1.5 required for GPU conversion!"
return cfg
- 转换命令行:
python caffe2_converter.py --format torchscript --output ./caffe2_model/ts-gpu2 MODEL.DEVICE gpu
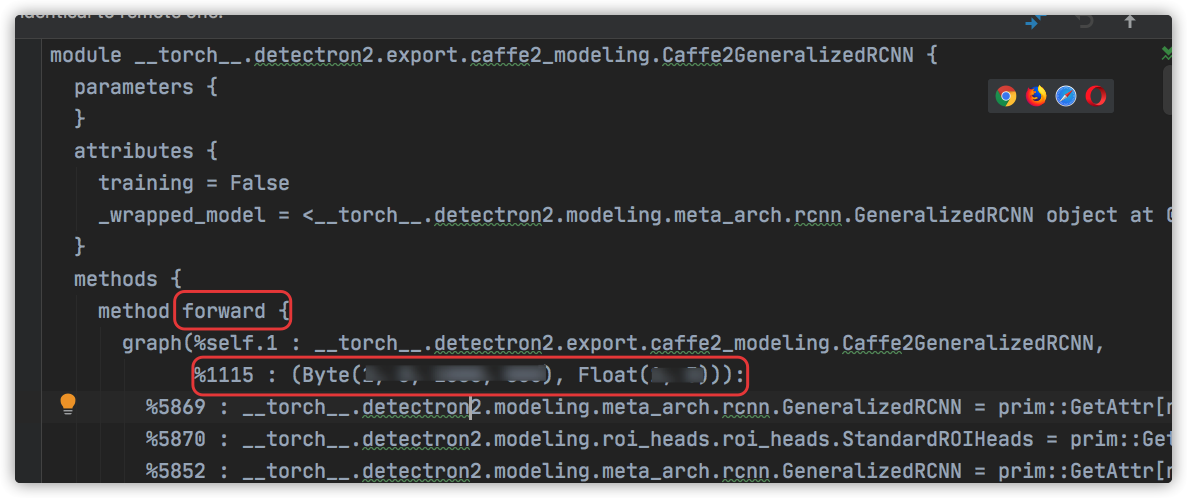
更详细说明:deployment
- 测试导出模型
forward是否正常:
model_path = "../tools/deploy/caffe2_model/ts-gpu2/model.ts"
print(model_path)
model_local = torch.jit.load(model_path)
# 具体数值可查看导出的model_ts_IR.txt
input_1 = torch.ones(x, x, xx, xx).cuda()
input_2 = torch.ones(x, x).cuda()
y = model_local((input_1, input_2))
print(y)
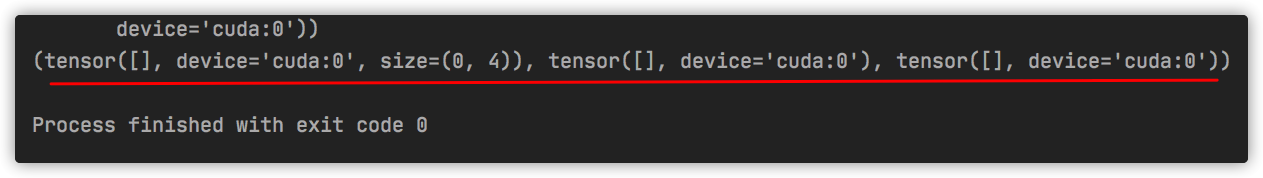
如果不顺利,看到类似这样的报错信息:
RuntimeError: forward() Expected a value of type 'Tensor' for argument 'data' but instead found type 'tuple'.
Position: 1
Value: (tensor([[[[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
...,
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.]]]], device='cuda:0'), tensor([[1., 1., 1.]], device='cuda:0'))
Declaration: forward(__torch__.detectron2.export.caffe2_modeling.Caffe2GeneralizedRCNN self, Tensor data, Tensor im_info) -> ((Tensor, Tensor, Tensor))
Cast error details: Unable to cast Python instance to C++ type (compile in debug mode for details)
那就是输入 没设置正确,要么输入不是规定格式的tensor,要么就是 size 不对.这时候,再检查一下model_ts_IR.txt的信息,填正确即可
- 进一步测试导出模型是否与训练的
pth模型预测结果是否一致. 这一步和 第四步 很类似,不过输入是一张真实的图片,拿到预测结果和pth模型的结果作对比.
import os
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import cv2
import detectron2.data.transforms as T
from detectron2.checkpoint import DetectionCheckpointer
from detectron2.config import get_cfg
from detectron2.data import MetadataCatalog, build_detection_test_loader
from detectron2.data.datasets import register_coco_instances
from detectron2.data.transforms import transform_gen
from detectron2.export import add_export_config, Caffe2Tracer
from detectron2.modeling import build_model
def setup_cfg():
cfg = get_cfg()
# cuda context is initialized before creating dataloader, so we don't fork anymore
cfg.DATALOADER.NUM_WORKERS = 0
register_coco_instances("name", {},
"./json/val.json",
"/image_path/")
metadata = MetadataCatalog.get("name")
print(metadata)
cfg.merge_from_file(
"../configs/COCO-Detection/faster_rcnn_X_101_32x8d_FPN_3x.yaml"
)
# cfg.DATASETS.TRAIN = ("name",)
cfg.DATASETS.TEST = ("name") # no metrics implemented for this dataset
cfg.DATALOADER.NUM_WORKERS = 4
cfg.SOLVER.IMS_PER_BATCH = 1
cfg.SOLVER.BASE_LR = 0.02
cfg.SOLVER.MAX_ITER = (
300
) # 300 iterations seems good enough, but you can certainly train longer
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.BATCH_SIZE_PER_IMAGE = (
128
) # faster, and good enough for this toy dataset
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.NUM_CLASSES = xx
cfg.OUTPUT_DIR = './xxx/'
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = os.path.join(cfg.OUTPUT_DIR, "model_final.pth")
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST = 0.5 # set the testing threshold for this model
cfg = add_export_config(cfg)
# cfg.merge_from_file(args.config_file)
# cfg.merge_from_list(args.opts)
cfg.DATASETS.TEST = ("name",)
cfg.freeze()
if cfg.MODEL.DEVICE != "cpu":
TORCH_VERSION = tuple(int(x) for x in torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
assert TORCH_VERSION >= (1, 5), "PyTorch>=1.5 required for GPU conversion!"
return cfg
cfg = setup_cfg()
torch_model = build_model(cfg)
DetectionCheckpointer(torch_model).resume_or_load(cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS)
data_loader = build_detection_test_loader(cfg, cfg.DATASETS.TEST[0])
first_batch = next(iter(data_loader))
tracer = Caffe2Tracer(cfg, torch_model, first_batch)
model_path = "../tools/deploy/caffe2_model/ts-gpu2/model.ts"
print(model_path)
model_local = torch.jit.load(model_path)
model, inputs = tracer._get_traceable()
data, im_info = inputs
y = model(inputs)
print('y1:', y)
y = model(inputs)
print('y2:', y)
y_local1 = model_local(inputs)
y_local2 = model_local(inputs)
print('y_local1:', y_local1)
print('y_local2:', y_local2)
特别注意的是:
要对比 y2 和y_local2的结果.
y1结果并不是真实的结果,其原因也未知
同时最好再作进一步确认,拿预测图出来,对比一下 数量和置信度这些是否能对号入座.
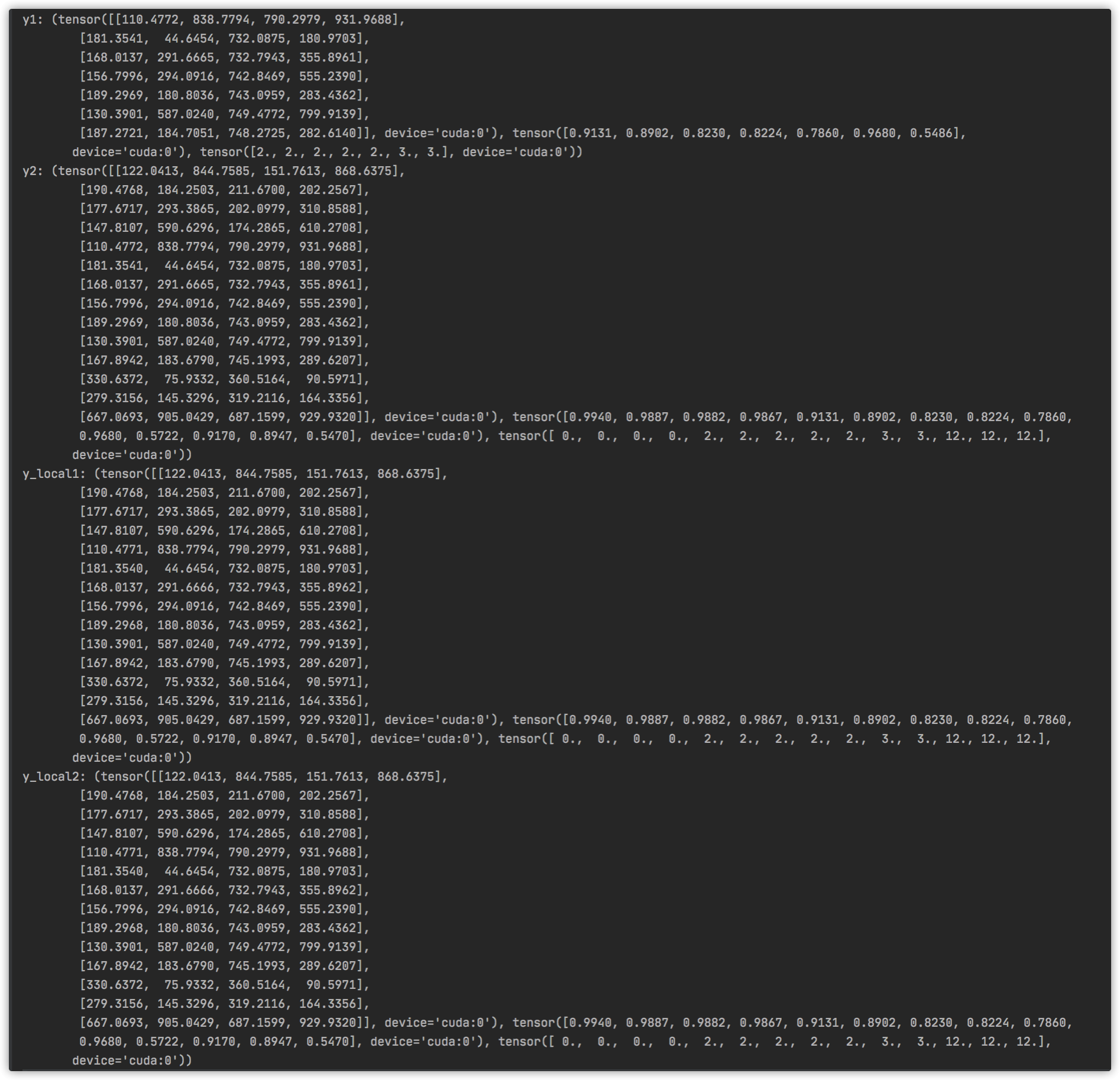
两次模型推理结果不一致?
y_local1: (tensor([[110.4771, 838.7794, 790.2979, 931.9688],
[193.6403, 41.6621, 721.1300, 179.5269],
[168.0137, 291.6666, 732.7943, 355.8962],
[156.7996, 294.0916, 742.8469, 555.2390],
[189.2968, 180.8036, 743.0959, 283.4362],
[130.3901, 587.0240, 749.4772, 799.9139],
[187.2721, 184.7051, 748.2725, 282.6140]], device='cuda:0'), tensor([0.9131, 0.8459, 0.8230, 0.8224, 0.7860, 0.9680, 0.5486],
device='cuda:0'), tensor([2., 2., 2., 2., 2., 3., 3.], device='cuda:0'))
y_local2: (tensor([[122.0413, 844.7585, 151.7613, 868.6375],
[190.4768, 184.2503, 211.6700, 202.2567],
[177.6717, 293.3865, 202.0979, 310.8588],
[147.8107, 590.6296, 174.2865, 610.2708],
[110.4771, 838.7794, 790.2979, 931.9688],
[181.3540, 44.6454, 732.0875, 180.9703],
[168.0137, 291.6666, 732.7943, 355.8962],
[156.7996, 294.0916, 742.8469, 555.2390],
[189.2968, 180.8036, 743.0959, 283.4362],
[130.3901, 587.0240, 749.4772, 799.9139],
[167.8942, 183.6790, 745.1993, 289.6207],
[330.6372, 75.9332, 360.5164, 90.5971],
[279.3156, 145.3296, 319.2116, 164.3356],
[667.0693, 905.0429, 687.1599, 929.9320]], device='cuda:0'), tensor([0.9940, 0.9887, 0.9882, 0.9867, 0.9131, 0.8902, 0.8230, 0.8224, 0.7860,
0.9680, 0.5722, 0.9170, 0.8947, 0.5470], device='cuda:0'), tensor([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 2., 2., 2., 2., 2., 3., 3., 12., 12., 12.],
device='cuda:0'))
相同模型,相同的数据,却有不同的结果.
搞了好久,还以为导出模型,瞎搞搞出问题了,观察了一回儿,发现现象:只有第一次的y是不正常的,之后都是正常的.
推测: 可能是模型第一次初始化的时候有问题.
其他特别注意事项:
detectron2/export/api.py
def export_torchscript(self):
"""
Export the model to a `torch.jit.TracedModule` by tracing.
The returned object can be saved to a file by ".save()".
Returns:
torch.jit.TracedModule: a torch TracedModule
"""
model, inputs = self._get_traceable()
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.info("Tracing the model with torch.jit.trace ...")
with torch.no_grad():
return torch.jit.trace(model, (inputs,), optimize=True)
可以看到 模型的输入实际是一个tuple,确切来说,是一个 含有两个tensor的 tuple.在部署的时候,tuple并不一定方便.可以去除之后,重新导出torch.jit.trace(model, inputs, optimize=True)这样模型输入就变成了两个 tensor
- 训练模型的输入和导出模型的输入是不一样的,这点需要特别注意,搞清楚.我是阅读追踪了不少源码才搞清楚情况的.