一、什么是Runtime
runtime是由C和C++、汇编实现的一套API,为OC语言加入了面向对象、运行时的功能- 运行时(
runtime)将数据类型的确定由编译时推迟到了运行时 - 平时编写的OC代码,在程序运行过程中,最终会转换成
runtime的C语言代码——runtime是Objective-C的幕后⼯作者
如类结构中的ro和rw属性
ro(read-only)在编译时已经确定rw(read-write)在运行时才确定,因此可以使用runtime进行修改
二、方法的本质是什么
方法的本质是发送消息objc_msgSend,即寻找IMP的过程
发送消息会有以下⼏个流程:
- 1.快速查找流程——通过汇编
objc_msgSend查找缓存cache_t是否有imp实现 - 2.慢速查找流程——通过
C++中lookUpImpOrForward递归查找当前类和父类的rw中methodlist的方法 - 3.动态方法解析——通过调用
resolveInstanceMethod和resolveClassMethod来动态方法决议——实现消息动态处理 - 4.快速转发流程——通过
CoreFoundation来触发消息转发流程,forwardingTargetForSelector实现快速转发,由其他对象来实现处理方法 - 5.慢速转发流程——先调用
methodSignatureForSelector获取到方法的签名,生成对应的invocation;再通过forwardInvocation来进行处理 - 6.以上流程均无法挽救就崩溃并报错
三、SEL和IMP的关系
SEL是方法编号,也是方法名,在dyld加载镜像到内存时,通过_read_image方法加载到内存的表中了
IMP是函数实现指针,找IMP就是找函数实现的过程
SEL和IMP的关系就可以解释为:
SEL就相当于书本的⽬录标题IMP就是书本的⻚码- 函数就是具体页码对应的内容
四、能否向运⾏时创建的类中添加实例变量
具体情况具体分析:
- 编译好的类不能添加实例变量
- 运行时创建的类可以添加实例变量,但若已注册到内存中就不行了
原因:
- 编译好的实例变量存储的位置在
ro,而ro是在编译时就已经确定了的 - ⼀旦编译完成,内存结构就完全确定就⽆法修改
- 只能修改
rw中的方法或者可以通过关联对象的方式来添加属性
五、isKindOfClass 和 isMemberOfClass
#import "DHPerson.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
BOOL re1 = [(id)[NSObject class] isKindOfClass:[NSObject class]];//1
BOOL re2 = [(id)[NSObject class] isMemberOfClass:[NSObject class]];// 0
BOOL re3 = [(id)[DHPerson class] isKindOfClass:[DHPerson class]];//0
BOOL re4 = [(id)[DHPerson class] isMemberOfClass:[DHPerson class]];// 0
NSLog(@" re1 :%hhd\n re2 :%hhd\n re3 :%hhd\n re4 :%hhd\n",re1,re2,re3,re4);
BOOL re5 = [(id)[NSObject alloc] isKindOfClass:[NSObject class]];//1
BOOL re6 = [(id)[NSObject alloc] isMemberOfClass:[NSObject class]];// 1
BOOL re7 = [(id)[DHPerson alloc] isKindOfClass:[DHPerson class]];//1
BOOL re8 = [(id)[DHPerson alloc] isMemberOfClass:[DHPerson class]];// 1
NSLog(@" re5 :%hhd\n re6 :%hhd\n re7 :%hhd\n re8 :%hhd\n",re5,re6,re7,re8);
}
return 0;
}
我们先看一下源码的实现
5.1 +isKindOfClass
+ (Class)class {
return self;
}
// 获取元类
Class object_getClass(id obj) {
if (obj) return obj->getIsa();
else return Nil;
}
+ (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls {
for (Class tcls = object_getClass((id)self); tcls; tcls = tcls->superclass) {
if (tcls == cls) return YES;
}
return NO;
}
+isKindOfClass是元类及其父类 vs 类
5.2 +isMemberOfClass
+ (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls {
return object_getClass((id)self) == cls;
}
相较于+isKindOfClass少了父类的比较,因此+isMemberOfClass为YES时, +isKindOfClass一定为YES
+isMemberOfClass是元类 vs 类
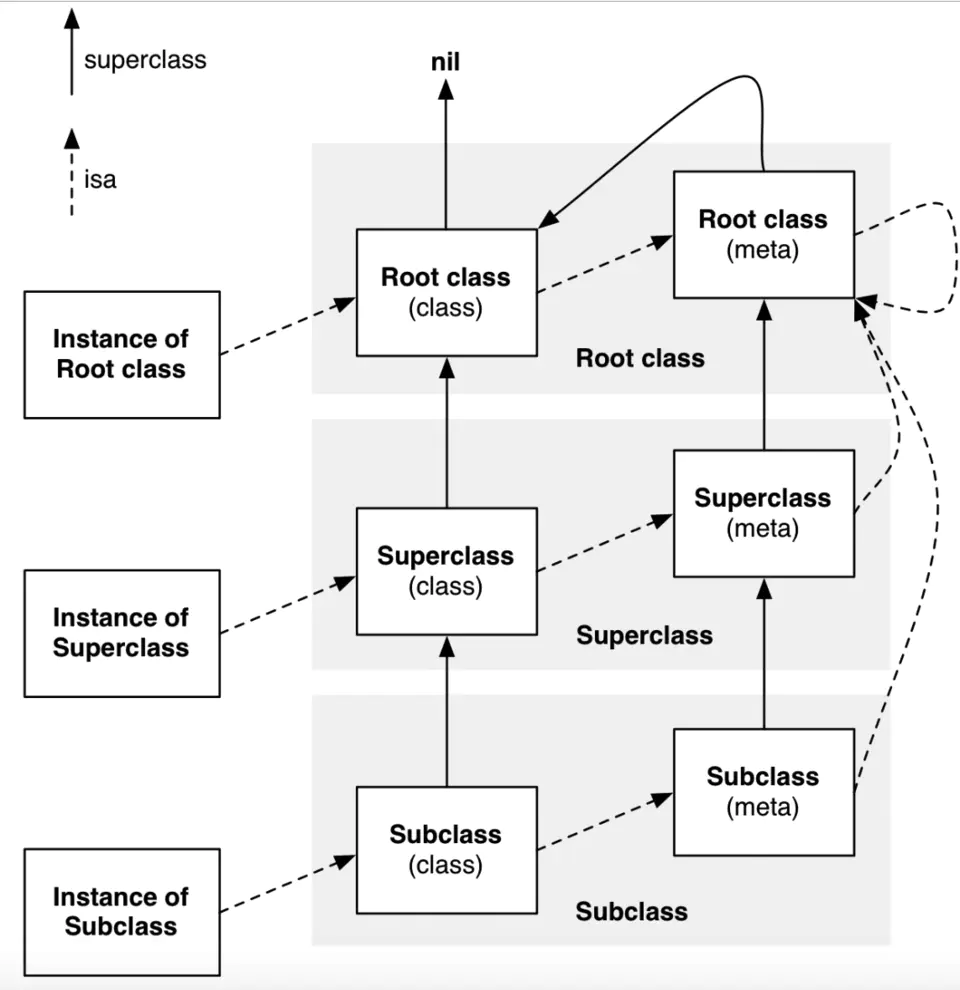
isa走位图 可以得出前面四个打印结果:
NSObject元类与NSObject类不相等,NSObject元类的父类(指向NSObject类)与NSObject类相等——YESNSObject元类与NSObject类不相等——NODHPerson元类与DHPerson类不相等,DHPerson元类的父类与DHPerson类不相等——NODHPerson元类与DHPerson类不相等——NO
5.3 -isKindOfClass
- (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls {
for (Class tcls = [self class]; tcls; tcls = tcls->superclass) {
if (tcls == cls) return YES;
}
return NO;
}
-isKindOfClass是类本身及其父类 vs 类
5.4 -isMemberOfClass
- (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls {
return [self class] == cls;
}
-isMemberOfClass是当前类和cls作比较,-isKindOfClass多了一步for循环类对象的父类
-isMemberOfClass是类本身 vs 类
后面四个结果分析如下:
NSObject类与NSObject类相等——YESNSObject类与NSObject类相等——YESDHPerson类与DHPerson类相等——YESDHPerson类与DHPerson类相等——YES
六、 [self class]和[super class]
DHSon 继承于 DHFather,主程序初始化 DHSon,求问打印内容以及思路
#import "DHSon.h"
@implementation DHSon
- (instancetype)init {
self = [super init];
if (self) {
NSLog(@"[self class] = %@", NSStringFromClass([self class]));//DHSon
NSLog(@"[super class] = %@", NSStringFromClass([super class]));//DHSon
NSLog(@"[self superclass] = %@", NSStringFromClass([self superclass]));//DHFather
NSLog(@"[super superclass] = %@", NSStringFromClass([super superclass]));//DHFather
}
return self;
}
@end
结果有点出乎意料,我们查看一下源码
+ (Class)class {
return self;
}
- (Class)class {
return object_getClass(self);
}
+ (Class)superclass {
return self->superclass;
}
- (Class)superclass {
return [self class]->superclass;
}
从这段代码能解释[self class]和[self superclass],但是另外两个又怎么解释呢?
终端clang编译代码得到super.cpp,就能看到初始化的底层代码了(也可以断点查看汇编)
clang -rewrite-objc DHSon.m -o super.cpp
可见[super class]和[super superclass]底层都是调用的objc_msgSendSuper
objc_msgSendSuper(void /* struct objc_super *super, SEL op, ... */ )
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0, 2.0);
/// Specifies the superclass of an instance.
struct objc_msgSendSuper {
/// Specifies an instance of a class.
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull id receiver;
/// Specifies the particular superclass of the instance to message.
#if !defined(__cplusplus) && !__OBJC2__
/* For compatibility with old objc-runtime.h header */
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull Class class;
#else
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull Class super_class;
#endif
/* super_class is the first class to search */
};
使用objc_msgSendSuper向objc_super发送消息,而objc_super在objc2.0下有两个元素: id类型的receiver和Class类型的super_class
我们仿写一下
struct objc_super lg_super = {
self,
class_getSuperclass([self class]),
};
NSLog(@"%@",NSStringFromClass(objc_msgSendSuper(&lg_super,@selector(class))));
就能得到和以下一样的结果了
NSLog(@"[super class] = %@", NSStringFromClass([super class]));
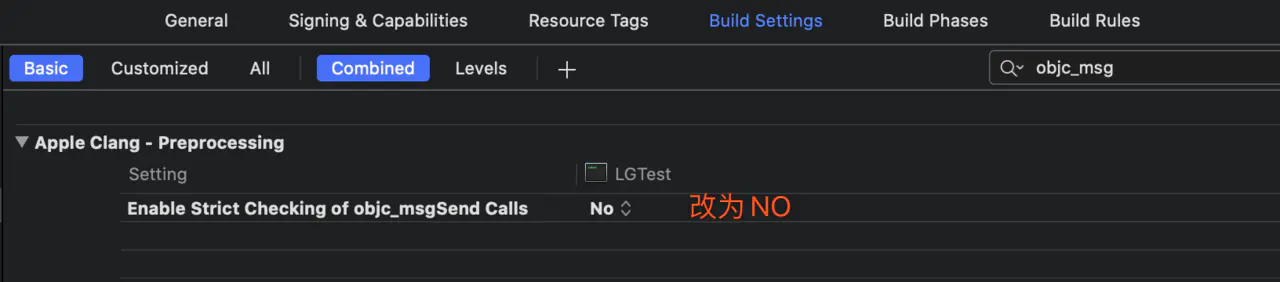
记得导入<objc/message.h>,报错Too many arguments就去修改编译期配置
那苹果为什么要这么设计呢?把消息查找和isa走位图联系起来就明白了!
son实例对象的实例方法存在DHSon类中
-
调用
[self class]就是son照着DHSon->DHFather->NSObject顺序问老爸要-class方法 -
调用
[super class]就是son跳过DHSon,直接通过DHFather->NSObject查找 -
还有比
[super class]更快找到class方法的写法,lg_super结构体中[self class]改为[super class],直接找到NSObjct -
当
lg_super结构体中[self class]改为[DHFather class]时,因为类方法存在元类中,会按DHFather元类->NSObject元类->NSObject根元类找-class方法,最后也是会输出DHSon
结论:
[self class]就是发送消息objc_msgSend,消息接收者是self,方法编号是class[super class]就是发送消息objc_msgSendSuper,消息接收者是self,方法编号是class,只不过objc_msgSendSuper会跳过self的查找
七、 weak置空原理
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
DHPerson *person = [[DHPerson alloc] init];
id __weak person = object;
}
return 0;
}
id __weak一行打断点,Debug->Debug Workflow->Always show Disassembly查看汇编——汇编代码会来到libobjc库的objc_initWeak
7.1objc_initWeak
id objc_initWeak(id *location, id newObj)
{
if (!newObj) {
*location = nil;
return nil;
}
return storeWeak<DontHaveOld, DoHaveNew, DoCrashIfDeallocating>
(location, (objc_object*)newObj);
}
location:表示__weak指针的地址(我们研究的就是__weak指针指向的内容怎么置为nil)
newObj:所引用的对象,即例子中的 person
7.2storeWeak
查看storeWeak源码,根据注释,可以知道如下几点
HaveOld:weak指针之前是否已经指向了一个弱引用HaveNew:weak指针是否需要指向一个新引用CrashIfDeallocating:如果被弱引用的对象正在析构,此时再弱引用该对象,是否应该crash。
// Update a weak variable.
// If HaveOld is true, the variable has an existing value
// that needs to be cleaned up. This value might be nil.
// If HaveNew is true, there is a new value that needs to be
// assigned into the variable. This value might be nil.
// If CrashIfDeallocating is true, the process is halted if newObj is
// deallocating or newObj's class does not support weak references.
// If CrashIfDeallocating is false, nil is stored instead.
enum CrashIfDeallocating {
DontCrashIfDeallocating = false, DoCrashIfDeallocating = true
};
template <HaveOld haveOld, HaveNew haveNew,
CrashIfDeallocating crashIfDeallocating>
static id
storeWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj)
{
assert(haveOld || haveNew);
if (!haveNew) assert(newObj == nil);
Class previouslyInitializedClass = nil;
id oldObj;
SideTable *oldTable;
SideTable *newTable;
// Acquire locks for old and new values.
// Order by lock address to prevent lock ordering problems.
// Retry if the old value changes underneath us.
retry:
///🌹 如果weak指针之前弱引用过一个obj,则将这个obj所对应的SideTable取出,赋值给oldTable
if (haveOld) {
oldObj = *location;
oldTable = &SideTables()[oldObj];
} else {
// 没有弱引用过,则oldTable = nil
oldTable = nil;
}
///🌹 如果weak指针要弱引用一个新的obj,则将该obj对应的SideTable取出,赋值给newTable
if (haveNew) {
newTable = &SideTables()[newObj];
} else {
newTable = nil;
}
//加锁操作,防止多线程中竞争冲突
SideTable::lockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);
// location 应该与 oldObj 保持一致,如果不同,说明当前的 location 已经处理过 oldObj 可是又被其他线程所修改
if (haveOld && *location != oldObj) {
SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);
goto retry;
}
// Prevent a deadlock between the weak reference machinery
// and the +initialize machinery by ensuring that no
// weakly-referenced object has an un-+initialized isa.
if (haveNew && newObj) {
Class cls = newObj->getIsa();
// 如果cls还没有初始化,先初始化,再尝试设置弱引用
if (cls != previouslyInitializedClass &&
!((objc_class *)cls)->isInitialized())
{
SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);
_class_initialize(_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, (id)newObj));
// If this class is finished with +initialize then we're good.
// If this class is still running +initialize on this thread
// (i.e. +initialize called storeWeak on an instance of itself)
// then we may proceed but it will appear initializing and
// not yet initialized to the check above.
// Instead set previouslyInitializedClass to recognize it on retry.
// 完成初始化后进行标记
previouslyInitializedClass = cls;
//newObj 初始化后,重新获取一遍newObj
goto retry;
}
}
// Clean up old value, if any.
///🌹 如果weak指针之前弱引用过别的对象oldObj,则调用weak_unregister_no_lock,在oldObj的weak_entry_t中移除该weak指针地址
if (haveOld) {
weak_unregister_no_lock(&oldTable->weak_table, oldObj, location);
}
// Assign new value, if any.
///🌹 如果weak指针需要弱引用新的对象newObj
if (haveNew) {
///🌹 调用weak_register_no_lock方法,将weak指针的地址记录到newObj对应的weak_entry_t中
newObj = (objc_object *)
weak_register_no_lock(&newTable->weak_table, (id)newObj, location,
crashIfDeallocating);
// weak_register_no_lock returns nil if weak store should be rejected
// Set is-weakly-referenced bit in refcount table.
//更新newObj的isa指针的weakly_referenced bit标志位
if (newObj && !newObj->isTaggedPointer()) {
newObj->setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
}
// Do not set *location anywhere else. That would introduce a race.
//*location 赋值,也就是将weak指针直接指向了newObj,而且没有将newObj的引用计数+1
*location = (id)newObj;
}
else {
// No new value. The storage is not changed.
}
SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);
return (id)newObj;
}
因为我们这里是第一次调用,所以是一个新的对象,也就是haveNew的情况,获取到的是新的散列表SideTable,主要执行了weak_register_no_lock方法来进行插入。
7.3weak_register_no_lock
id weak_register_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id,
id *referrer_id, bool crashIfDeallocating)
{
//先获取需要弱引用对象
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
objc_object **referrer = (objc_object **)referrer_id;
//果被弱引用对象referent为nil 或者被弱引用对象采用了TaggedPointer计数方式,则直接返回
if (!referent || referent->isTaggedPointer()) return referent_id;
// ensure that the referenced object is viable
//确保被引用的对象可用(没有在析构,同时应该支持weak弱引用)
bool deallocating;
if (!referent->ISA()->hasCustomRR()) {
deallocating = referent->rootIsDeallocating();
}
else {
BOOL (*allowsWeakReference)(objc_object *, SEL) =
(BOOL(*)(objc_object *, SEL))
object_getMethodImplementation((id)referent,
SEL_allowsWeakReference);
if ((IMP)allowsWeakReference == _objc_msgForward) {
return nil;
}
deallocating =
! (*allowsWeakReference)(referent, SEL_allowsWeakReference);
}
//如果是正在析构的对象,那么不能够被弱引用
if (deallocating) {
if (crashIfDeallocating) {
_objc_fatal("Cannot form weak reference to instance (%p) of "
"class %s. It is possible that this object was "
"over-released, or is in the process of deallocation.",
(void*)referent, object_getClassName((id)referent));
} else {
return nil;
}
}
// now remember it and where it is being stored
///🌹在 weak_table 中找到被弱引用对象 referent 对应的 weak_entry,并将 referrer 加入到 weak_entry 中
weak_entry_t *entry;
if ((entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent))) {
//如果能找到 weak_entry,则将referrer 插入到 weak_entry 中
append_referrer(entry, referrer);
}
else {
//如果找不到 weak_entry,就新建一个
weak_entry_t new_entry(referent, referrer);
weak_grow_maybe(weak_table);
weak_entry_insert(weak_table, &new_entry);
}
// Do not set *referrer. objc_storeWeak() requires that the
// value not change.
return referent_id;
}
- 如果可以被弱引用,则将被弱引用对象所在的
weak_table中的weak_entries哈希数组中取出对应的weak_entry_t,然后将指向被弱引用对象地址的指针referrer通过函数append_referrer插入到对应的weak_entry_t引用数组。 - 如果
weak_entry_t不存在,则会新建一个。weak_grow_maybe判断要不要扩容,然后weak_entry_insert插入到weak表 - 至此就完成了弱引用。
7.4 append_referrer
主要是找到弱引用对象的对应的weak_entry哈希数组中,基本就是个遍历插入的过程
static void append_referrer(weak_entry_t *entry, objc_object **new_referrer)
{
//果weak_entry 使用静态数组 inline_referrers
if (! entry->out_of_line()) {
// Try to insert inline.
//试将 referrer 插入数组
for (size_t i = 0; i < WEAK_INLINE_COUNT; i++) {
if (entry->inline_referrers[i] == nil) {
entry->inline_referrers[i] = new_referrer;
return;
}
}
// Couldn't insert inline. Allocate out of line.
//如果inline_referrers的位置已经存满了,则要转型为 referrers,动态数组
weak_referrer_t *new_referrers = (weak_referrer_t *)
calloc(WEAK_INLINE_COUNT, sizeof(weak_referrer_t));
// This constructed table is invalid, but grow_refs_and_insert
// will fix it and rehash it.
for (size_t i = 0; i < WEAK_INLINE_COUNT; i++) {
new_referrers[i] = entry->inline_referrers[i];
}
entry->referrers = new_referrers;
entry->num_refs = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT;
entry->out_of_line_ness = REFERRERS_OUT_OF_LINE;
entry->mask = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT-1;
entry->max_hash_displacement = 0;
}
assert(entry->out_of_line());
//如果动态数组中元素个数大于或等于数组总空间的3/4,则扩展数组空间为当前长度的一倍,然后将 referrer 插入数组
if (entry->num_refs >= TABLE_SIZE(entry) * 3/4) {
return grow_refs_and_insert(entry, new_referrer);
}
//如果不需要扩容,直接插入到weak_entry中
//& (entry->mask) 保证 begin 的位置只能大于或等于数组的长度
size_t begin = w_hash_pointer(new_referrer) & (entry->mask);
size_t index = begin;
size_t hash_displacement = 0;
while (entry->referrers[index] != nil) {
hash_displacement++;
index = (index+1) & entry->mask;
if (index == begin) bad_weak_table(entry);
}
if (hash_displacement > entry->max_hash_displacement) {
entry->max_hash_displacement = hash_displacement;
}
weak_referrer_t &ref = entry->referrers[index];
ref = new_referrer;
entry->num_refs++;
}
7.5 weak_unregister_no_lock
如果weak指针在指向obj之前,已经弱引用了其他的对象,则需要先将weak指针从其他对象的weak_entry_t的hash数组中移除。在storeWeak方法中会调用weak_unregister_no_lock函数来做移除操作
weak_unregister_no_lock函数首先会在weak_table中找出以前被弱引用的对象referent对应的weak_entry_t,在weak_entry_t中移除被弱引用的对象referrer。移除元素后,判断此时weak_entry_t中是否还有元素。如果此时weak_entry_t已经没有元素了,则需要将weak_entry_t从weak_table中移除。
void weak_unregister_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id,
id *referrer_id)
{
//拿到以前弱引用的对象和对象的地址
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
objc_object **referrer = (objc_object **)referrer_id;
weak_entry_t *entry;
if (!referent) return;
//查找到以前弱引用的对象 referent 所对应的 weak_entry_t
if ((entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent))) {
//在以前弱引用的对象 referent 所对应的 weak_entry_t 的 hash 数组中,移除弱引用 referrer
remove_referrer(entry, referrer);
//移除元素之后, 要检查一下 weak_entry_t 的 hash 数组是否已经空了
bool empty = true;
if (entry->out_of_line() && entry->num_refs != 0) {
empty = false;
}
else {
for (size_t i = 0; i < WEAK_INLINE_COUNT; i++) {
if (entry->inline_referrers[i]) {
empty = false;
break;
}
}
}
//如果 weak_entry_t 的hash数组已经空了,则需要将 weak_entry_t 从 weak_table 中移除
if (empty) {
weak_entry_remove(weak_table, entry);
}
}
// Do not set *referrer = nil. objc_storeWeak() requires that the
// value not change.
}
7.6 以上是weak的创建,现在看看weak的销毁
- (void)dealloc {
_objc_rootDealloc(self);
}
**********************************
void _objc_rootDealloc(id obj)
{
assert(obj);
obj->rootDealloc();
}
***********************************
inline void objc_object::rootDealloc()
{
//如果是Tagged Pointer,就直接返回
if (isTaggedPointer()) return; // fixme necessary?
/*
如果同时满足
1. 是优化过的isa、
2. 没有被weak指针引用过、
3. 没有关联对象、
4. 没有C++析构函数、
5. 没有sideTable,
就可以直接释放内存free()
*/
if (fastpath(isa.nonpointer &&
!isa.weakly_referenced &&
!isa.has_assoc &&
!isa.has_cxx_dtor &&
!isa.has_sidetable_rc))
{
assert(!sidetable_present());
free(this);
}
else {//否则的话就需要通过下面的函数处理
object_dispose((id)this);
}
}
id
object_dispose(id obj)
{
if (!obj) return nil;
objc_destructInstance(obj);
free(obj);
return nil;
}
void *objc_destructInstance(id obj)
{
if (obj) {
// Read all of the flags at once for performance
bool cxx = obj->hasCxxDtor();
bool assoc = obj->hasAssociatedObjects();
// This order is important.
// 如果有C++析构函数,则从运行相关函数
if (cxx) object_cxxDestruct(obj);
// 如果有关联对象,则移除所有的关联对象,并将其自身从Association Manager的map中移除
if (assoc) _object_remove_assocations(obj);
// 继续清理其它相关的引用
obj->clearDeallocating();
}
return obj;
}
inline void
objc_object::clearDeallocating()
{
if (slowpath(!isa.nonpointer)) {
// Slow path for raw pointer isa.
// 如果要释放的对象没有采用了优化过的isa引用计数
sidetable_clearDeallocating();
}
else if (slowpath(isa.weakly_referenced || isa.has_sidetable_rc)) {
// Slow path for non-pointer isa with weak refs and/or side table data.
// 如果要释放的对象采用了优化过的isa引用计数,并且有弱引用或者使用了sideTable的辅助引用计数
clearDeallocating_slow();
}
assert(!sidetable_present());
}
NEVER_INLINE void
objc_object::clearDeallocating_slow()
{
assert(isa.nonpointer && (isa.weakly_referenced || isa.has_sidetable_rc));
// 在全局的SideTables中,以this指针(要释放的对象)为key,找到对应的SideTable
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
table.lock();
if (isa.weakly_referenced) {
//要释放的对象被弱引用了,通过weak_clear_no_lock函数将指向该对象的弱引用指针置为nil
weak_clear_no_lock(&table.weak_table, (id)this);
}
//使用了sideTable的辅助引用计数,直接在SideTable中擦除该对象的引用计数
if (isa.has_sidetable_rc) {
table.refcnts.erase(this);
}
table.unlock();
}
void
weak_clear_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id)
{
//获取被弱引用对象的地址
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
// 根据对象地址找到被弱引用对象referent在weak_table中对应的weak_entry_t
weak_entry_t *entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent);
if (entry == nil) {
/// XXX shouldn't happen, but does with mismatched CF/objc
//printf("XXX no entry for clear deallocating %p\n", referent);
return;
}
// zero out references
weak_referrer_t *referrers;
size_t count;
// 找出弱引用该对象的所有weak指针地址数组
if (entry->out_of_line()) {
referrers = entry->referrers;
count = TABLE_SIZE(entry);
}
else {
referrers = entry->inline_referrers;
count = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT;
}
// 遍历取出每个weak指针的地址
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
objc_object **referrer = referrers[i];
if (referrer) {
// 如果weak指针确实弱引用了对象 referent,则将weak指针设置为nil
if (*referrer == referent) {
*referrer = nil;
}
// 如果所存储的weak指针没有弱引用对象 referent,这可能是由于runtime代码的逻辑错误引起的,报错
else if (*referrer) {
_objc_inform("__weak variable at %p holds %p instead of %p. "
"This is probably incorrect use of "
"objc_storeWeak() and objc_loadWeak(). "
"Break on objc_weak_error to debug.\n",
referrer, (void*)*referrer, (void*)referent);
objc_weak_error();
}
}
}
weak_entry_remove(weak_table, entry);
}
主要流程是
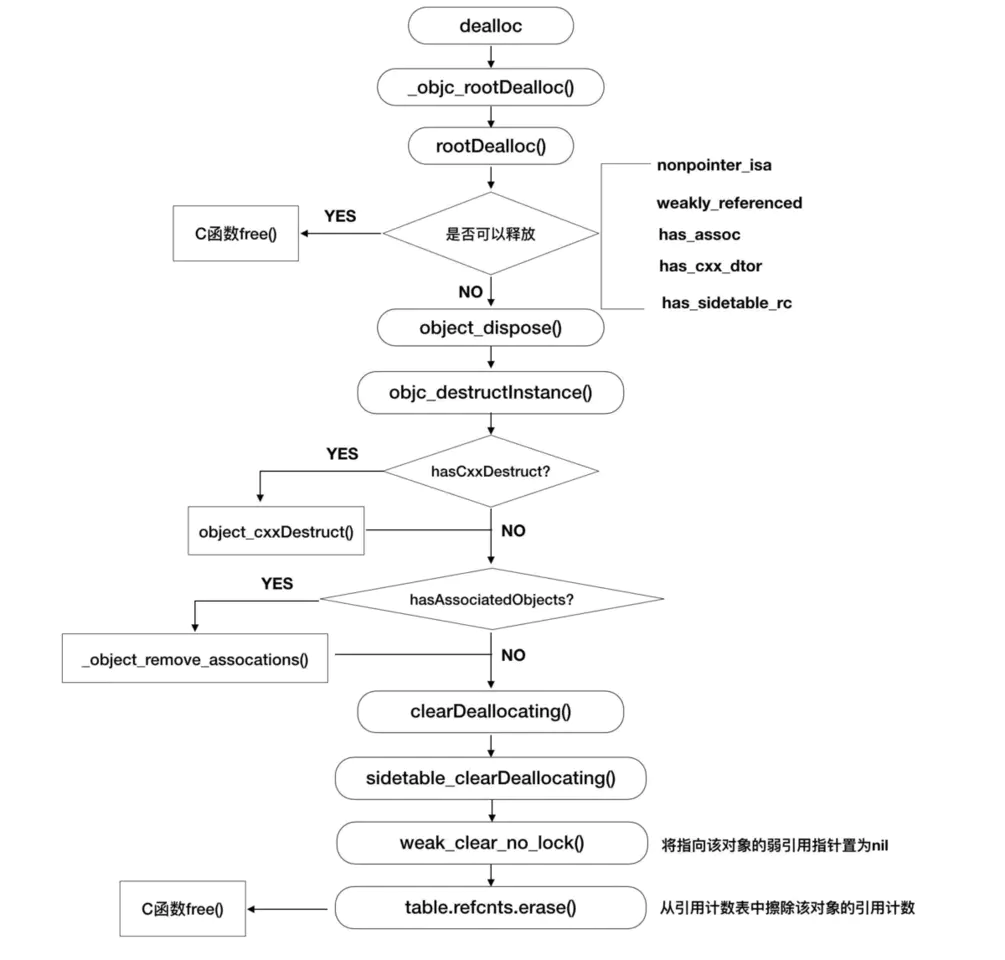
dealloc->_objc_rootDealloc->rootDealloc->object_dispose->objc_destructInstance->clearDeallocating->clearDeallocating_slow->weak_clear_no_lock
7.7 小结
- 当一个对象
obj被weak指针指向时,这个weak指针会以obj作为key,被存储到sideTable中的weak_table这个散列表上对应的一个weak指针数组weak_entries里面。 - 当一个对象
obj的dealloc方法被调用时,Runtime会以obj为key,从sideTable的weak_table散列表中,找出对应的weak指针列表,然后将里面的weak指针逐个置为nil。
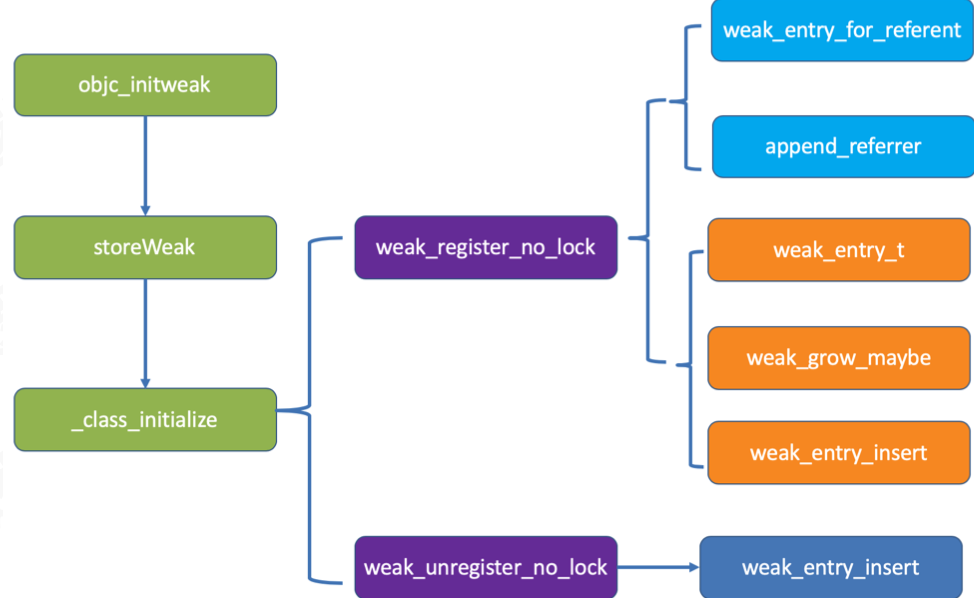
创建流程图
销毁流程图引用
八、 Method Swizzing坑点
坑点一,类簇
比如处理数组越界问题
NSArray *array = @[@"b", @"o", @"o", @"k", @"s"];
NSLog(@"%@", array[5]);
NSLog(@"%@", [array objectAtIndex:5]);
- 新建
NSArray分类 - 导入
runtime头文件——<objc/runtime.h> - 写下新的方法
- 在
+load利用黑魔法交换方法
#import "NSArray+EX.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation NSArray (EX)
+ (void)load {
// 交换objectAtIndex方法
Method oriMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(objectAtIndex:));
Method swiMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(ex_objectAtIndex:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod1, swiMethod1);
// 交换取下标方法
Method oriMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
Method swiMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(ex_objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod2, swiMethod2);
}
- (void)ex_objectAtIndex:(NSInteger)index {
if (index > self.count - 1) {
NSLog(@"objectAtIndex————————数组越界");
return;
}
return [self ex_objectAtIndex:index];
}
- (void)ex_objectAtIndexedSubscript:(NSInteger)index {
if (index > self.count - 1) {
NSLog(@"取下标————————数组越界");
return;
}
return [self ex_objectAtIndexedSubscript:index];
}
@end
然而还是越界崩溃了
其实在iOS中NSNumber、NSArray、NSDictionary等这些类都是类簇(Class Clusters),一个NSArray的实现可能由多个类组成。所以如果想对NSArray进行方法交换,必须获取到其真身进行方法交换,直接对NSArray进行操作是无效的
| 类名 | 真身 |
|---|---|
| NSArray | __NSArrayI |
| NSMutableArray | __NSArrayM |
| NSDictionary | __NSDictionaryI |
| NSMutableDictionary | __NSDictionaryM |
这样就好办了,可以使用runtime取出本类
#import "NSArray+EX.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation NSArray (EX)
+ (void)load {
Class cls = objc_getClass(@"__NSArrayI")
// 交换objectAtIndex方法
Method oriMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, @selector(objectAtIndex:));
Method swiMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, @selector(ex_objectAtIndex:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod1, swiMethod1);
// 交换取下标方法
Method oriMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, @selector(objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
Method swiMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, @selector(ex_objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod2, swiMethod2);
}
- (void)ex_objectAtIndex:(NSInteger)index {
if (index > self.count - 1) {
NSLog(@"objectAtIndex————————数组越界");
return;
}
return [self ex_objectAtIndex:index];
}
- (void)ex_objectAtIndexedSubscript:(NSInteger)index {
if (index > self.count - 1) {
NSLog(@"取下标————————数组越界");
return;
}
return [self ex_objectAtIndexedSubscript:index];
}
@end
坑点二,最好写成单例,避免多次交换
比如说添加了[NSArray load]代码,方法实现又交换回去了导致了崩溃
NSArray *array = @[@"b", @"o", @"o", @"k", @"s"];
[NSArray load];
NSLog(@"%@", array[5]);
将+load方法改写成单例
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
// 交换objectAtIndex方法
Method oriMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(objectAtIndex:));
Method swiMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(fx_objectAtIndex:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod1, swiMethod1);
// 交换取下标方法
Method oriMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
Method swiMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(fx_objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod2, swiMethod2);
});
}
坑点3, 子类没有实现 - 父类实现
Student 继承 Person, Person 继承 NSObject,子类没有实现父类方法personInstanceMethod
Student *s = [[Student alloc] init];
[s personInstanceMethod];
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
[p personInstanceMethod];
子类打印出结果,而父类调用却崩溃了,为什么会这样呢?
因为Student交换方法personInstanceMethod会先在本类查找方法,再在父类里查找,在父类Person中找到了方法实现就把它跟新方法进行交换了。可是新方法是在Student分类中的,Person找不到imp就unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x600002334250
所以这种情况下应该给子类添加方法实现,只交换子类的方法,不动父类的方法
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
// oriSEL personInstanceMethod
// swizzledSEL ex_personInstanceMethod
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(personInstanceMethod));
Method swiMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(ex_personInstanceMethod));
//给原方法添加方法实现,如果之前没实现就能添加成功,如果之前实现了,就会添加失败
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(self, @selector(personInstanceMethod), method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
///如果添加成功 则替换ex_的方法实现,这样也达到了方法交换的效果
/**
添加后:personInstanceMethod(sel) - ex_personInstanceMethod(imp)
替换后:ex_personInstanceMethod (swizzledSEL) - personInstanceMethod(imp,这里因为父类有实现,所以调用的是父类的实现)
*/
class_replaceMethod(self, @selector(ex_personInstanceMethod), method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swiMethod);
}
});
}
- (void)ex_personInstanceMethod{
[self ex_personInstanceMethod];
NSLog(@"Student分类添加的ex对象方法:%s",__func__);
}
这样就没有动父类的方法,相当于子类重写了父类的方法personInstanceMethod
坑点4, 子类没有实现 - 父类也没有实现 会造成死循环
因为都没有实现,导致class_replaceMethod时,获取原方法的实现personInstanceMethod(imp)无效,ex_personInstanceMethod方法中想调用旧的方法实现,可是找不到personInstanceMethod实现,就会死循环
所以我们判断一下,如果原方法没实现,则添加空实现
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(doInstance));
Method swiMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(fx_doInstance));
/// 原方法没实现,添加一个空的实现
if (!oriMethod) {
class_addMethod(self, @selector(doInstance), method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
method_setImplementation(swiMethod, imp_implementationWithBlock(^(id self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"方法未实现");
}));
}
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(self, @selector(doInstance), method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(self, @selector(fx_doInstance), method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swiMethod);
}
});
}
- 尽可能在+load方法中交换方法 使用单例保证只交换一次
- 自定义方法名不能产生冲突
- 对于系统方法要调用原始实现,避免对系统产生影响
- 做好注释(因为方法交换比较绕)
- 迫不得已情况下才去使用方法交换
+ (void)DHMethodSwizzlingWithClass:(Class)cls oriSEL:(SEL)oriSEL swizzledSEL:(SEL)swizzledSEL{
if (!cls) NSLog(@"传入的交换类不能为空");
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, oriSEL);
Method swiMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL);
if (!oriMethod) {
// 在oriMethod为nil时,替换后将swizzledSEL复制一个不做任何事的空实现,代码如下:
class_addMethod(cls, oriSEL, method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
method_setImplementation(swiMethod, imp_implementationWithBlock(^(id self, SEL _cmd){ }));
}
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(cls, oriSEL, method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL, method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
}else{
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swiMethod);
}
}
九、 内存偏移问题
程序能否运行吗?是否正常输出?
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface Person : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@end
@implementation Person
- (void)printMyProperty {
NSLog(@"当前打印内容为%s", __func__);
}
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [Person class];
void *obj= &cls;
[(__bridge id)obj printMyProperty];
Person *p = [Person alloc];
[p printMyProperty];
}
@end
运行结果与普通初始化对象一模一样
正常操作:指针p->实例对象的首地址isa->类对象
指针操作:指针obj->指针cls->类对象
isa不是可以强转位cls吗,所以都能正常打印
拓展一
修改打印方法printMyProperty——不但打印方法,同时打印属性name
- (void)printMyProperty {
NSLog(@"当前打印内容为%s——————%@", __func__, self.name);
}
当前打印内容为 -[Person printMyProperty]——————<ViewController: 0x10472bd50>
为什么属性name还没有赋值,却打印出了ViewController的内存地址?
- 由于栈先入后出,
viewDidLoad入栈先拉伸栈空间,然后依次放入self、_cmd局部变量 - 调用
[super viewDidLoad],继续放入super_class、self - 正常情况下获取
name,本质是p的内存地址往下偏移8字节
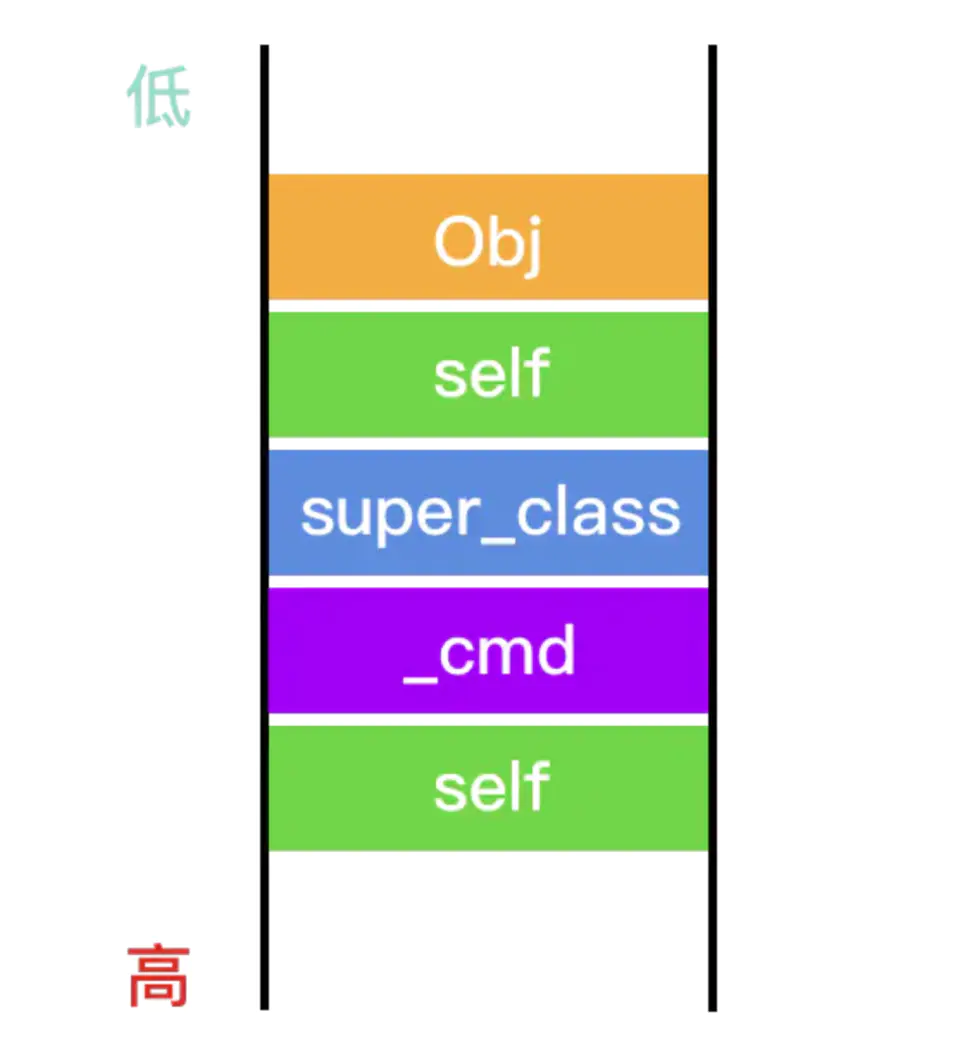
拓展二
修改viewDidLoad——在obj前面加个临时字符串变量
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSString *temp = @"dh";
id cls = [Person class];
void *obj= &cls;
[(__bridge id)obj printMyProperty];
Person *p = [Person alloc];
[p printMyProperty];
}
打印如下:
当前打印内容为 -[Person printMyProperty]——————dh
同理,在obj入栈前已经有了temp变量,此时访问self.name就会访问到temp
拓展三
去掉临时变量,Person类新增字符串属性hobby,打印方法改为打印hobby,运行
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface Person : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *hobby;
@end
@implementation Person
- (void)printMyProperty {
NSLog(@"当前打印内容为%s——————%@", __func__, self.hobby);
}
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [Person class];
void *obj= &cls;
[(__bridge id)obj printMyProperty];
Person *p = [Person alloc];
[p printMyProperty];
}
@end
当前打印内容为 -[Person printMyProperty]——————ViewController
ViewController就是obj偏移16字节拿到的super_class,见上图
拓展四
去掉[super viewDidLoad]
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface Person : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *hobby;
@end
@implementation Person
- (void)printMyProperty {
NSLog(@"当前打印内容为%s——————%@", __func__, self.name);
}
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
//[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [Person class];
void *obj= &cls;
[(__bridge id)obj printMyProperty];
Person *p = [Person alloc];
[p printMyProperty];
}
@end
崩溃保存Thread 1: EXC_BAD_ACCESS (code=1, address=0x477656990)
野指针——指针偏移的offset不正确,获取不到对应变量的首地址
打印改一下
- (void)printMyProperty {
NSLog(@"当前打印内容为%s——————%@", __func__, self.hobby);
}
当前打印内容为-[LGPerson saySomething]——————<ViewController: 0x11fd365c0>
变量的存放顺序,是根据定义的先后顺序,从函数栈底(高地址)开始,一个一个排列