一、类拓展(匿名分类/匿名类别)
1.定义
什么是类拓展,可以查看苹果官方文档
A class extension bears some similarity to a category, but it can only be added to a class for which you have the source code at compile time (the class is compiled at the same time as the class extension).
类拓展和分类很相似,但是前提是你拥有原始类的源码,并且是在 编译时被附加到类上的。(类和类扩展同时编译) 因此您不能在框架类(如Cocoa或NSString之类的Cocoa Touch类)上声明类扩展。
@interface ClassName ()
@end
Because no name is given in the parentheses, class extensions are often referred to as anonymous categories.
因为括号中没有填写任何内容,所以类扩展也被称为匿名的分类。
2.类拓展的两种形式
- 直接在.m文件中新增类拓展
@interface LGPerson ()
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *mName;
@end
@implementation LGPerson
@end
- 新建类拓展的.h文件
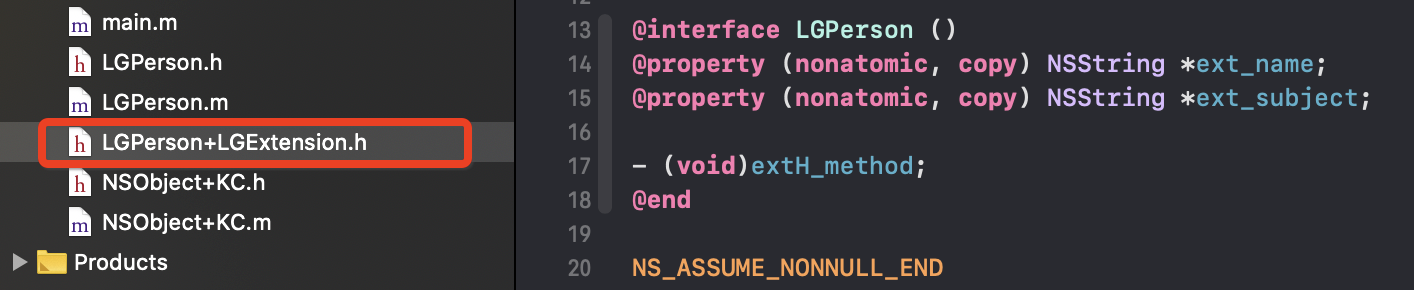
3.何时附加到类上的
上面官方文档说是编译是附加到类上面的,如何验证呢?数据很早就会来到_read_images上,这时还在读取Mach-O里面的数据,我们在Discover classes处打断点,查看ro中是否有mName的setter和getter方法
LGPerson.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface LGPerson : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
LGPerson.m
#import "LGPerson.h"
#import "LGPerson+LGExtension.h"
@interface LGPerson ()
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *mName;
- (void)extM_method;
@end
@implementation LGPerson
+ (void)load{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
}
- (void)extM_method{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
}
- (void)extH_method{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
}
@end
LGPerson+LGExtension.h
#import <AppKit/AppKit.h>
#import "LGPerson.h"
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface LGPerson ()
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *ext_name;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *ext_subject;
- (void)extH_method;
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
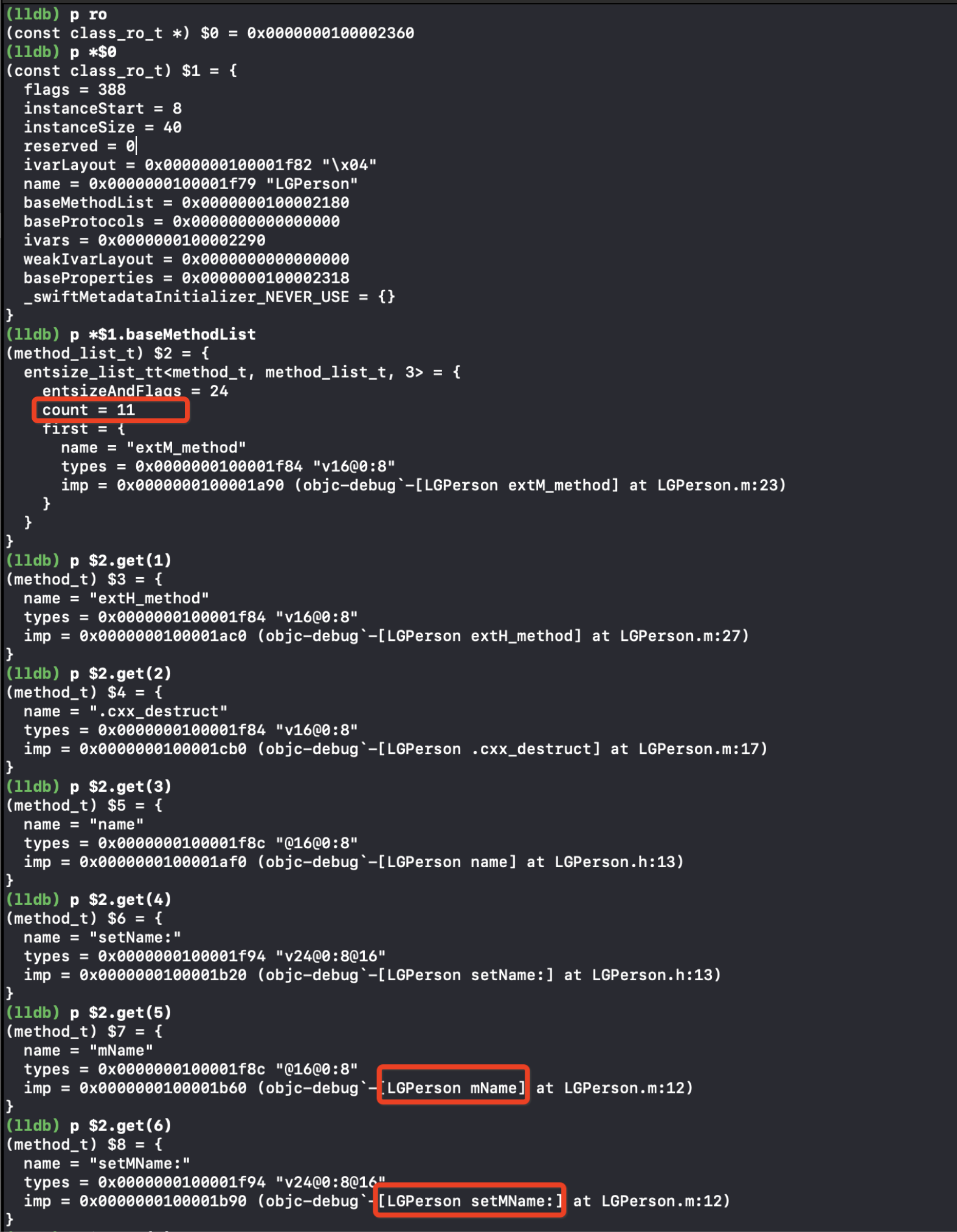
可以看到是有mName的setter和getter方法的,验证的类拓展是在编译时附加在类上的,
我们把LGPerson.m中的#import "LGPerson+LGExtension.h"去掉,在试一次
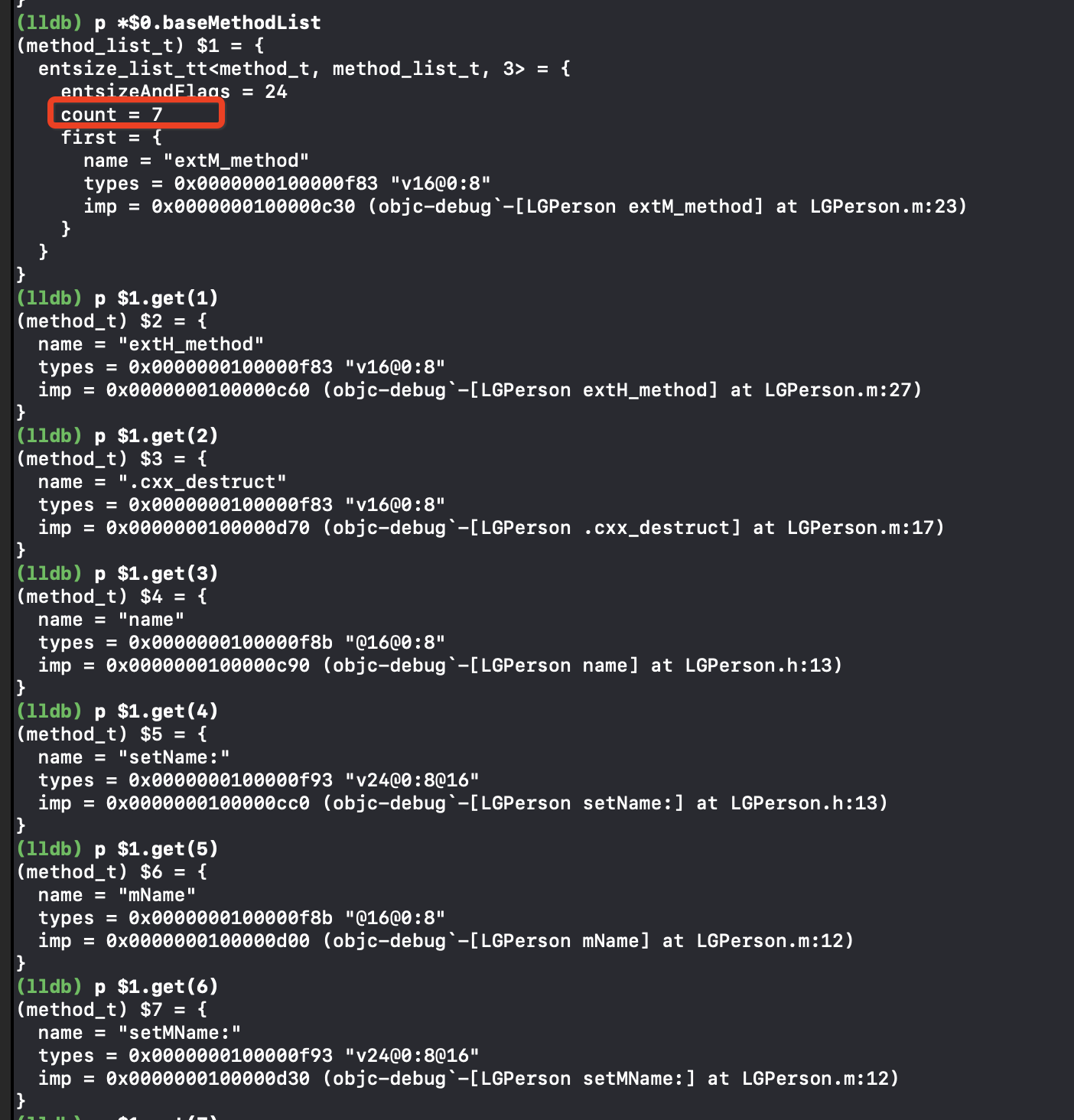
LGPerson+LGExtension.h中的方法并没有编译进来
类拓展没有被引用(#import)就不会编译到到内存
4.类拓展和分类区别
| 研究对象 | 加载时机 | 操作对象 | 能否通过@property声明属性生成 getter 和 setter |
|---|---|---|---|
分类(实现了+load方法) |
运行时 | rw |
不能,需要借助关联对象来实现 |
分类(没实现+load方法) |
编译时 | ro |
不能,需要借助关联对象来实现 |
| 类拓展 | 编译时 | ro |
可以 |
// Attach method lists and properties and protocols from categories to a class.
// Assumes the categories in cats are all loaded and sorted by load order,
// oldest categories first.
static void attachCategories(Class cls, category_list *cats, bool flush_caches) {
...
/// 🌹 🌹 🌹直接操作rw
auto rw = cls->data();
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle);
rw->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);
free(mlists);
if (flush_caches && mcount > 0) flushCaches(cls);
rw->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount);
free(proplists);
rw->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount);
free(protolists);
}
二、关联对象
类拓展中可以声明属性,编译器会帮我们自动生成属性对应的 getter 和 setter 方法,但是分类通过@property 的方式来声明属性却不能生成 getter 和 setter 方法,但我们可以通过关联对象 Associated Objects来添加。
1.定义
这是官方定义
Associative references, available starting in OS X v10.6, simulate the addition of object instance variables to an existing class. Using associative references, you can add storage to an object without modifying the class declaration. This may be useful if you do not have access to the source code for the class, or if for binary-compatibility reasons you cannot alter the layout of the object.
关联引用,是从OS X 10.6开始启用的,模拟了将对象实例变量添加到已经存在的类中。通过使用关联引用,你可以在不修改类声明的前提下为对象添加内容。如果你无权访问该类的源代码,或者由于二进制兼容性原因而无法更改该对象的布局,则这可能很有用。
关联引用使用起来很简单,不外乎两个方法:
// 设置关联对象
objc_setAssociatedObject()
// 获取关联对象
objc_getAssociatedObject()
关联对象内存管理策略如下所示:
| 关联策略 | 等同的 @property |
描述 |
|---|---|---|
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN |
@property (assign) 或@property (unsafe_unretained) |
指定一个关联对象的弱引用。 |
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC |
@property (nonatomic, strong) |
指定一个关联对象的强引用,不能被原子化使用。 |
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC |
@property (nonatomic, copy) |
指定一个关联对象的copy引用,不能被原子化使用。 |
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN |
@property (atomic, strong) |
指定一个关联对象的强引用,能被原子化使用。 |
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY |
@property (atomic, copy) |
指定一个关联对象的copy引用,能被原子化使用。 |
2.objc_setAssociatedObject
void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy) {
_object_set_associative_reference(object, (void *)key, value, policy);
}
void _object_set_associative_reference(id object, void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy) {
// This code used to work when nil was passed for object and key. Some code
// probably relies on that to not crash. Check and handle it explicitly.
// rdar://problem/44094390
/// 🌹当传入的 object 和 key 同时为 nil 的时候,直接返回。这样的处理是为了避免传入空值时而导致崩溃
if (!object && !value) return;
assert(object);
/// 🌹判断要进行关联的对象是否禁用了关联引用
if (object->getIsa()->forbidsAssociatedObjects())
_objc_fatal("objc_setAssociatedObject called on instance (%p) of class %s which does not allow associated objects", object, object_getClassName(object));
// retain the new value (if any) outside the lock.
// 在锁之外保留新值(如果有)。
/// 🌹初始化一个 ObjcAssociation 对象,用于持有原有的关联对象
ObjcAssociation old_association(0, nil);
/// 🌹判断传入的关联对象值是否存在,如果存在就调用 acquireValue(根据关联策略来进行 retain 或 copy 消息的发送) 方法来获取值
id new_value = value ? acquireValue(value, policy) : nil;
{
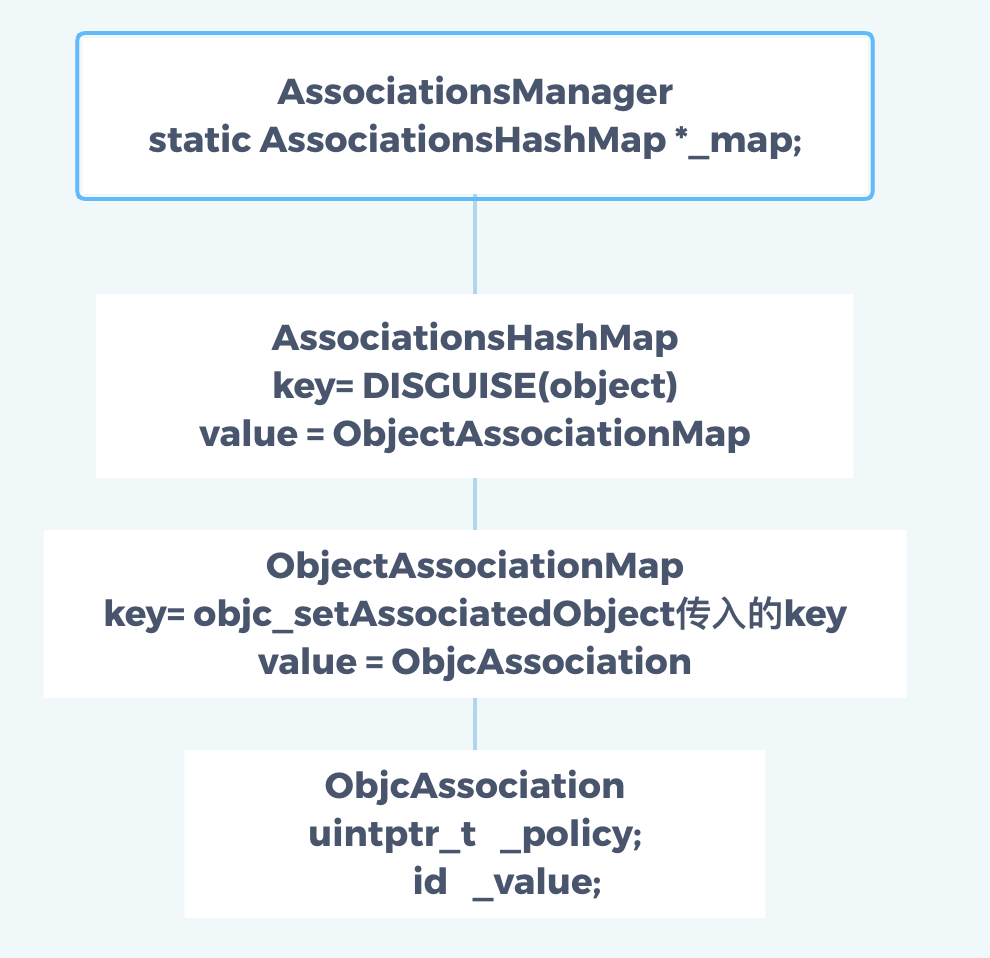
// 关联对象的管理类
AssociationsManager manager;
// 获取关联的 HashMap -> 存储当前关联对象
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations());
// 🌹DISGUISE函数对当前的对象的地址做按位去反操作 - 返回的disguised_object就是 HashMap 的key (哈希函数)
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
///如果传入的关联对象值存在,进行赋值操作
if (new_value) {
// break any existing association.
// 获取 AssociationsHashMap 的迭代器 - (对象的) 进行遍历
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
// secondary table exists
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
// 根据key去获取关联属性的迭代器
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
old_association = j->second;
// 替换设置新值
j->second = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
} else {
// 到最后了 - 直接设置新值 新增一个
(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
}
} else {
// create the new association (first time).
// 如果AssociationsHashMap从没有对象的关联信息表,
// 那么就创建一个map并通过传入的key把value存进去
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = new ObjectAssociationMap;
/// 🌹总表AssociationsHashMap: disguised_object为key, refs即对象表ObjectAssociationMap为值
associations[disguised_object] = refs;
/// 🌹对象表refs: 传入的key为key, ObjcAssociation对象为值
(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
/// 🌹设置当前对象的 isa 的 has_assoc 属性为 true
object->setHasAssociatedObjects();
}
} else {
/// 如果传入的关联对象值不存在,说明是进行置空操作
// setting the association to nil breaks the association.
// 如果传入的value是nil,并且之前使用相同的key存储过关联对象,
// 那么就把这个关联的value移除(这也是为什么传入nil对象能够把对象的关联value移除)
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
old_association = j->second;
refs->erase(j);
}
}
}
}
// release the old value (outside of the lock).
// 最后把之前使用传入的这个key存储的关联的value释放(OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_RETAIN策略存储的)
if (old_association.hasValue()) ReleaseValue()(old_association);
}
-
如果传入的关联对象值存在
- 1.则以上一步按位取反之后的结果
disguised_object为key,在AssociationsHashMap哈希表中查询,这里是通过迭代器的方式进行查询,查询的结果是ObjectAssociationMap对象,也是一个哈希表,其内部存储的是_object_set_associative_reference方法传入的key为键,ObjcAssociation为值的键值对 - 2.如果没有查询到,说明之前在当前类上没有设置过关联对象。则需要初始化一个
ObjectAssociationMap出来,associations[disguised_object] = refs;给总表赋值,(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);给对象表赋值,通过setHasAssociatedObjects设置当前对象的isa的has_assoc属性为true - 3.如果查询到了,说明之前在当前类上设置过关联对象,接着需要看
key是否存在,如果key存在,那么就需要更新原有的关联对象;如果key不存在,则需要新增一个关联对象
- 1.则以上一步按位取反之后的结果
-
如果传入的关联对象值为nil
- 通过
erase擦除key对应的节点,即把对象的关联value移除
- 通过
-
最后会判断
old_association是否有值,如果有的话就释放掉,当然前提是旧的关联对象的策略是OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_RETAIN
struct ReleaseValue {
void operator() (ObjcAssociation &association) {
releaseValue(association.value(), association.policy());
}
};
static void releaseValue(id value, uintptr_t policy) {
if (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_RETAIN) {
return objc_release(value);
}
}
3.objc_getAssociatedObject
id objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key) {
return _object_get_associative_reference(object, (void *)key);
}
id _object_get_associative_reference(id object, void *key) {
id value = nil;
uintptr_t policy = OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN;
{
// 关联对象的管理类
AssociationsManager manager;
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations());
// 生成伪装地址。处理参数 object 地址
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
// 所有对象的额迭代器
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
// 内部对象的迭代器
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
// 找到 - 把值和策略读取出来
ObjcAssociation &entry = j->second;
/// 🌹找到了,赋值给一开始的value和policy
value = entry.value();
policy = entry.policy();
// 🌹policy是OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_RETAIN - 就会持有一下
if (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_RETAIN) {
objc_retain(value);
}
}
}
}
if (value && (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_AUTORELEASE)) {
objc_autorelease(value);
}
return value;
}
- 1.先初始化一个空的
value,以及一个策略为OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN的policy - 2.初始化一个
AssociationsManager关联对象管理类,接着拿到AssociationsHashMap对象,这个对象在AssociationsManager底层是静态的 - 3.然后以
DISGUISE按位取反之后的结果为键去查询AssociationsHashMap - 4.如果在
AssociationsHashMap中找到了,接着以key为键去ObjectAssociationMap中查询ObjcAssociation,如果查询到了,则把值和策略赋值给方法入口声明的两个临时变量,然后判断获取到的关联对象的策略是否为OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_RETAIN,如果是的话,需要对关联值进行retain操作 - 5.最后判断如果关联值是否存在且策略为
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_AUTORELEASE,是的话就需要调用objc_autorelease来释放关联值 - 6.最后返回关联值
三、load_images
我们在load_images处打断点,发现类和分类的+load方法都没有执行,可见load_images先于+load方法
void load_images(const char *path __unused, const struct mach_header *mh) {
// Return without taking locks if there are no +load methods here.
if (!hasLoadMethods((const headerType *)mh)) return;
recursive_mutex_locker_t lock(loadMethodLock);
// Discover load methods
/// 🌹 准备load方法调用所需要的数据
{
mutex_locker_t lock2(runtimeLock);
prepare_load_methods((const headerType *)mh);
}
// Call +load methods (without runtimeLock - re-entrant)
/// 🌹调用+load方法
call_load_methods();
}
1.prepare_load_methods
主要是创建了非懒加载类和非懒加载分类的数据表
void prepare_load_methods(const headerType *mhdr)
{
size_t count, i;
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
/// 🌸🌸🌸非懒加载类相关处理
classref_t *classlist =
_getObjc2NonlazyClassList(mhdr, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
///🌹遍历非懒加载类
schedule_class_load(remapClass(classlist[i]));
}
/// 🌸🌸🌸非懒加载分类相关处理
category_t **categorylist = _getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList(mhdr, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
category_t *cat = categorylist[i];
Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
if (!cls) continue; // category for ignored weak-linked class
if (cls->isSwiftStable()) {
_objc_fatal("Swift class extensions and categories on Swift "
"classes are not allowed to have +load methods");
}
/// 🌹加载相关类
realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls);
/// 🌹添加分类到非懒加载分类列表中
assert(cls->ISA()->isRealized());
add_category_to_loadable_list(cat);
}
}
-
非来加载类
- 通过
_getObjc2NonlazyClassList获取非懒加载类列表 - 通过
schedule_class_load遍历这些类,递归遍历父类,确保父类的+load方法顺序排在子类的前面 - 调用
add_class_to_loadable_list把类的+load方法存在loadable_classes里面
- 通过
-
非来加载分类
- 调用
_getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList取出非懒加载分类列表 - 遍历分类列表
- 通过
realizeClassWithoutSwift来防止类没有初始化(若已经初始化了则不影响) - 调用
add_category_to_loadable_list加载分类中的+load方法到loadable_categories
- 调用
static void schedule_class_load(Class cls)
{
if (!cls) return;
assert(cls->isRealized()); // _read_images should realize
if (cls->data()->flags & RW_LOADED) return;
// Ensure superclass-first ordering
/// 🌹递归父类
schedule_class_load(cls->superclass);
/// 🌹添加类到列表中
add_class_to_loadable_list(cls);
cls->setInfo(RW_LOADED);
}
在添加到列表中时,会先申请空间,可以看到类的+load方法存储在loadable_class中,结构为16字节,所以申请现有空间2倍+16字节,并赋值对应的cls和method。
分类添加到列表中的逻辑和这个基本一样,只不过存储的列表和model的名字不同
// List of classes that need +load called (pending superclass +load)
// This list always has superclasses first because of the way it is constructed
static struct loadable_class *loadable_classes = nil;
// List of categories that need +load called (pending parent class +load)
static struct loadable_category *loadable_categories = nil;
struct loadable_class {
Class cls; // may be nil
IMP method;
};
/***********************************************************************
* add_class_to_loadable_list
* Class cls has just become connected. Schedule it for +load if
* it implements a +load method.
**********************************************************************/
void add_class_to_loadable_list(Class cls)
{
IMP method;
loadMethodLock.assertLocked();
method = cls->getLoadMethod();
if (!method) return; // Don't bother if cls has no +load method
if (PrintLoading) {
_objc_inform("LOAD: class '%s' scheduled for +load",
cls->nameForLogging());
}
if (loadable_classes_used == loadable_classes_allocated) {
// 🌹申请空间
loadable_classes_allocated = loadable_classes_allocated*2 + 16;
loadable_classes = (struct loadable_class *)
realloc(loadable_classes,
loadable_classes_allocated *
sizeof(struct loadable_class));
}
//🌹赋值操作
loadable_classes[loadable_classes_used].cls = cls;
loadable_classes[loadable_classes_used].method = method;
loadable_classes_used++;
}
下面是分类的+load方法添加到另一张表的具体实现
/***********************************************************************
* add_category_to_loadable_list
* Category cat's parent class exists and the category has been attached
* to its class. Schedule this category for +load after its parent class
* becomes connected and has its own +load method called.
**********************************************************************/
void add_category_to_loadable_list(Category cat)
{
IMP method;
loadMethodLock.assertLocked();
method = _category_getLoadMethod(cat);
// Don't bother if cat has no +load method
if (!method) return;
if (PrintLoading) {
_objc_inform("LOAD: category '%s(%s)' scheduled for +load",
_category_getClassName(cat), _category_getName(cat));
}
if (loadable_categories_used == loadable_categories_allocated) {
loadable_categories_allocated = loadable_categories_allocated*2 + 16;
loadable_categories = (struct loadable_category *)
realloc(loadable_categories,
loadable_categories_allocated *
sizeof(struct loadable_category));
}
loadable_categories[loadable_categories_used].cat = cat;
loadable_categories[loadable_categories_used].method = method;
loadable_categories_used++;
}
2.call_load_methods
根据调用顺序可知,类的+load方法比分类的+load方法先调用
void call_load_methods(void)
{
static bool loading = NO;
bool more_categories;
loadMethodLock.assertLocked();
// Re-entrant calls do nothing; the outermost call will finish the job.
if (loading) return;
loading = YES;
压栈自动释放池
void *pool = objc_autoreleasePoolPush();
do {
// 1. Repeatedly call class +loads until there aren't any more
while (loadable_classes_used > 0) {
/// 🌹调用类的load方法
call_class_loads();
}
// 2. Call category +loads ONCE
/// 🌹循环调用分类load方法,仅一次
more_categories = call_category_loads();
// 3. Run more +loads if there are classes OR more untried categories
} while (loadable_classes_used > 0 || more_categories);
/// 🌹出栈自动释放池,保证调用一次
objc_autoreleasePoolPop(pool);
loading = NO;
}
类具体调用+load方法是在call_class_loads中,主要的操作为遍历非懒加载类列表,直接获取到IMP,强转为load_method_t,并直接调用函数实现,没有走消息发送流程
/***********************************************************************
* call_class_loads
* Call all pending class +load methods.
* If new classes become loadable, +load is NOT called for them.
*
* Called only by call_load_methods().
**********************************************************************/
static void call_class_loads(void)
{
int i;
// Detach current loadable list.
struct loadable_class *classes = loadable_classes;
int used = loadable_classes_used;
loadable_classes = nil;
loadable_classes_allocated = 0;
loadable_classes_used = 0;
// Call all +loads for the detached list.
for (i = 0; i < used; i++) {
Class cls = classes[i].cls;
///🌹 遍历列表,得到IMP强转为load_method_t
load_method_t load_method = (load_method_t)classes[i].method;
if (!cls) continue;
if (PrintLoading) {
_objc_inform("LOAD: +[%s load]\n", cls->nameForLogging());
}
///🌹 直接调用函数 +load的调用
(*load_method)(cls, SEL_load);
}
// Destroy the detached list.
if (classes) free(classes);
}
分类的+load调用和类的调用差不多,只不过是从loadable_categories列表中获取数据,分类的+load方法调用完成之后,会一个个依次销毁,保证调用一次
static bool call_category_loads(void)
{
...
// Call all +loads for the detached list.
for (i = 0; i < used; i++) {
Category cat = cats[i].cat;
///🌹 遍历列表,得到IMP强转为load_method_t
load_method_t load_method = (load_method_t)cats[i].method;
Class cls;
if (!cat) continue;
cls = _category_getClass(cat);
if (cls && cls->isLoadable()) {
if (PrintLoading) {
_objc_inform("LOAD: +[%s(%s) load]\n",
cls->nameForLogging(),
_category_getName(cat));
}
///🌹 直接调用函数 +load的调用
(*load_method)(cls, SEL_load);
cats[i].cat = nil;
}
}
...
// Compact detached list (order-preserving)
shift = 0;
for (i = 0; i < used; i++) {
if (cats[i].cat) {
cats[i-shift] = cats[i];
} else {
shift++;
}
}
used -= shift;
// Copy any new +load candidates from the new list to the detached list.
new_categories_added = (loadable_categories_used > 0);
for (i = 0; i < loadable_categories_used; i++) {
if (used == allocated) {
allocated = allocated*2 + 16;
cats = (struct loadable_category *)
realloc(cats, allocated *
sizeof(struct loadable_category));
}
cats[used++] = loadable_categories[i];
}
}
四、initialize
Xcode中command+shift+0搜索initialize,查看官方定义
Initializes the class before it receives its first message.
在这个类接收第一条消息之前调用。
Superclasses receive this message before their subclasses.
父类的调用一定在子类之前
Because initialize is called in a blocking manner, it’s important to limit method implementations to the minimum amount of work necessary possible. Therefore, you should not rely on initialize for complex initialization, and should instead limit it to straightforward, class local initialization.
因为initialize是以阻塞的方式调用的,所以将方法实现限制在尽可能少的工作量是很重要的。因此,对于复杂的初始化,不应该依赖于initialize,而应该将其限制为简单的类本地初始化。
initialize is invoked only once per class. If you want to perform independent initialization for the class and for categories of the class, you should implement load methods.
每个类只调用一次initialize,如果希望对类和类的分类执行独立的初始化,应该实现+load方法。
我们在objc源码中 lookUpImpOrForward 找到了它的踪迹
lookUpImpOrForward->initializeAndLeaveLocked->initializeAndMaybeRelock->initializeNonMetaClass
在 initializeNonMetaClass 方法,递归调用父类,然后真正的调用callInitialize
/***********************************************************************
* class_initialize. Send the '+initialize' message on demand to any
* uninitialized class. Force initialization of superclasses first.
**********************************************************************/
void initializeNonMetaClass(Class cls)
{
...
///🌹 递归调用父类
supercls = cls->superclass;
if (supercls && !supercls->isInitialized()) {
initializeNonMetaClass(supercls);
}
...
///🌹 调用用Initialize方法
callInitialize(cls);
...
}
callInitialize 就是普通的消息发送
void callInitialize(Class cls)
{
((void(*)(Class, SEL))objc_msgSend)(cls, SEL_initialize);
asm("");
}
五、总结
load_image主要调用类和分类的+load方法,并储存在不同的表中- 根据调用顺序,类的
+load比分类的先调用。其他方法,由于分类最后处理,attachCategories->attachLists时,把分类方法插入到已有方法的前面,所以分类比类的方法先调用,但是并没有与覆盖 - 类和多个分类方法同名时(非
+load方法)- 如果分类没实现
load方法,就响应Compile Sources最后一个分类 - 如果其中一个实现
load,响应非懒加载分类(因为懒加载分类在编译时就已经加载到内存,而非懒加载分类运行时才加载)
- 如果都实现
load,响应Compile Sources最后一个分类
- 如果分类没实现
initialize在消息发送时调用
参考
NSHipster - Associated Objects
Draveness - 关联对象 AssociatedObject 完全解析