一、消息查找流程
1.1、对象的实例方法查找流程
- 自己有->调用
- 自己没->父类有->调用
- 自己没->父类没->父类的父类(NSObject)有->调用
- 都没有->经典报错(
unrecognized selector sent to instance)
1.2、对象的类方法查找流程
- 自己有->调用
- 自己没->父类有->调用
- 自己没->父类没->父类的父类(NSObject)有->调用
自己没->父类没->父类的父类(NSObject)也没有,但是有相应实例方法->调用实例方法- 都没有->经典报错(
unrecognized selector sent to instance)
注意:类方法中,如果没有对应的类方法,而有对应的实例方法,并不会崩溃,而是会调用相应的实例方法。 因为类方法在底层是以元类的实例方法存在的,而元类的继承关系中有一个关键点,即根元类继承自NSObject。
二、消息查找底层实现
上篇文章 6.iOS底层之方法调用(objc_msgSend) 已经讲了方法的快速查找流程:CacheLookup---> CheckMiss---> __objc_msgSend_uncached---> MethodTableLookup---> __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3,接下来探索慢速查找流程
2.0、_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
/**
查找当前的imp或者转发
cls:如果是实例方法那就是类,如果是类方法那就是元类
sel:方法名
obj:方法调用者
NO/*cache*/ //因为是CheckMiss状态下点用的该方法,所以此处为NO
*/
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
2.1、lookUpImpOrForward 查找IMP或消息转发
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
// ️ initialize = YES , cache = NO , resolver = YES
// 初始化相关参数
IMP imp = nil;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
// 缓存查找, 因为cache传入的为NO,这里不会进行缓存查找
if (cache) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
// 📍1.为查找方法做准备条件,判断类有没有加载好,如果没有加载好,那就先加载一下类信息,
//准备好类、元类、以及父类、父类的元类、直到它的根类、根元类
runtimeLock.read();
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
runtimeLock.write();
realizeClass(cls);
runtimeLock.unlockWrite();
runtimeLock.read();
}
//确定类已经加载完毕
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
runtimeLock.read();
}
retry:
runtimeLock.assertReading();
// Try this class's cache.
// 📍2.查找类缓存 先去类的方法缓存中查找一次,多线程并发调用时可能已经存在之前的调用缓存
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done; ////拿到方法就返回
// Try this class's method lists.
// 📍3.查找类的方法列表
// 大括号是为了形成局部域,避免局部变量命名重复
{
// 根据sel去类对象里面查找方法
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
// 如果方法存在,则缓存方法 log_and_fill_cache->cache_fill->cache_fill_nolock
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
// 方法缓存之后, 拿到imp并返回
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// Try superclass caches and method lists.
// 📍4.如果类方法列表中没有找到, 则去父类的缓存中或方法列表中查找方法
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
//遍历父类,父类的父类等等一系列父类,直到为nil
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
// 📍4.1查找父类的cache_t缓存
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
// 判断是否是消息转发,如果不是消息转发,那么就把找到的 IMP 通过 log_and_fill_cache 缓存到当前类的缓存中;如果是消息转发,就退出循环。
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
//在父类中找到方法, 在本类中缓存方法, 注意这里传入的是cls, 将方法缓存在本类缓存列表中, 而非父类中
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
// 跳出循环, 停止搜索
break;
}
}
// Superclass method list.
// 📍4.2 查找父类的方法列表
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
// 同样拿到方法, 在本类进行缓存
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
//📍5.没有找到方法实现,调用一次方法动态解析
️//首先检查是否已经被标记为动态方法解析,如果没有才会进入动态方法解析
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
/*
实例方法解析:_class_resolveInstanceMethod
类方法解析:_class_resolveClassMethod
*/
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.read();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
//将triedResolver标记为YES,下次就不会再进入动态方法解析
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
//📍6.未能找到方法实现,且方法的动态解析也没,就会走到消息转发流程(下篇文章会讲)
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
//返回方法地址
return imp;
}
下面盗用一幅流程图
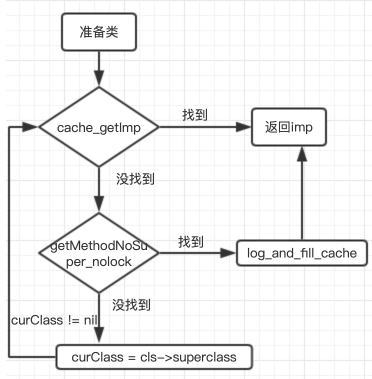
2.2、getMethodNoSuper_nolock 方法列表中查找
static method_t *
getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
assert(cls->isRealized());
// fixme nil cls?
// fixme nil sel?
for (auto mlists = cls->data()->methods.beginLists(),
end = cls->data()->methods.endLists();
mlists != end;
++mlists)
{
//通过二分查找获取m
method_t *m = search_method_list(*mlists, sel);
if (m) return m;
}
return nil;
}
getMethodNoSuper_nolock 就是一个简单的一个遍历方法列表
2.3、search_method_list 二分查找获取m
static method_t *search_method_list(const method_list_t *mlist, SEL sel)
{
int methodListIsFixedUp = mlist->isFixedUp();
int methodListHasExpectedSize = mlist->entsize() == sizeof(method_t);
if (__builtin_expect(methodListIsFixedUp && methodListHasExpectedSize, 1)) {
// 如果方法列表已经排序好了,则通过二分查找法查找方法,以节省时间
return findMethodInSortedMethodList(sel, mlist);
} else {
// Linear search of unsorted method list
//如果方法列表没有排序好就遍历查找
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
if (meth.name == sel) return &meth;
}
}
#if DEBUG
// sanity-check negative results
if (mlist->isFixedUp()) {
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
if (meth.name == sel) {
_objc_fatal("linear search worked when binary search did not");
}
}
}
#endif
return nil;
}
2.4、findMethodInSortedMethodList 二分查找实现
static method_t *findMethodInSortedMethodList(SEL key, const method_list_t *list)
{
assert(list);
const method_t * const first = &list->first;
const method_t *base = first;
const method_t *probe;
uintptr_t keyValue = (uintptr_t)key;
uint32_t count;
// count >>= 1 右移1位,最高位补0
// 如果count为偶数则值变为(count / 2)
// 如果count为奇数则值变为(count-1) / 2
for (count = list->count; count != 0; count >>= 1) {
// probe 指向数组中间的值
probe = base + (count >> 1);
// 取出中间method_t的name,也就是SEL
uintptr_t probeValue = (uintptr_t)probe->name;
if (keyValue == probeValue) {
// `probe` is a match.
// Rewind looking for the *first* occurrence of this value.
// This is required for correct category overrides.
// 向前二分查询
while (probe > first && keyValue == (uintptr_t)probe[-1].name) {
probe--;
}
// 取出 probe
return (method_t *)probe;
}
// 向后二分查询
if (keyValue > probeValue) {
base = probe + 1;
count--;
}
}
return nil;
}
2.5、_class_resolveMethod 动态方法解析
void _class_resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
//判断类不是元类,那sel就是实例方法,那就先转发resolveInstanceMethod方法,判断有没有实现resolveInstanceMethod,没实现就不做处理
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
//如果是元类,那sel就是类方法
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
// 先查找下resolveClassMethod,如果没实现就不做处理
_class_resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst);
//再次查找方法,如果没有的话,就再转发一下resolveInstanceMethod方法
因为根元类继承NSObject, 元类的类方法相当于类的实例方法
if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
}
}
2.6、_objc_msgForward_impcache 未能找到方法实现,且方法的动态解析也没实现,就会调用这个方法,发现又进入了汇编
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
// Method cache version
// THIS IS NOT A CALLABLE C FUNCTION
// Out-of-band condition register is NE for stret, EQ otherwise.
jne __objc_msgForward_stret
jmp __objc_msgForward
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
ENTRY __objc_msgForward
// Non-stret version
movq __objc_forward_handler(%rip), %r11
jmp *%r11
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward
锁定汇编方法__objc_forward_handler,全局搜索找到定义,并且找到了objc_defaultForwardHandler方法
2.7、objc_defaultForwardHandler
objc_defaultForwardHandler(id self, SEL sel)
{
_objc_fatal("%c[%s %s]: unrecognized selector sent to instance %p "
"(no message forward handler is installed)",
class_isMetaClass(object_getClass(self)) ? '+' : '-',
object_getClassName(self), sel_getName(sel), self);
}
void *_objc_forward_handler = (void*)objc_defaultForwardHandler;
如果处理失败那么则报出经典错误unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x88888888
2.8、补充:准备条件 realizeClass
static Class realizeClass(Class cls)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
const class_ro_t *ro; // 方法列表 属性列表等
class_rw_t *rw; // 存储 class_ro_t的结构体
Class supercls; // 父类
Class metacls; // 元类
bool isMeta; // 当前类是否是元类
ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data();// 给ro赋值
isMeta = ro->flags & RO_META; // 是否是元类判断
supercls = realizeClass(remapClass(cls->superclass)); // 初始化父类
metacls = realizeClass(remapClass(cls->ISA())); // 初始化元类
cls->superclass = supercls; //找到当前类的 父类
cls->initClassIsa(metacls); //初始化当前类的元类
// 如果有父类就把当前类关联到父类的子类列表中
if (supercls) {
addSubclass(supercls, cls);
} else {
addRootClass(cls);
}
三、总结
- 方法查找,先是通过汇编快速查找缓存:
objc_msgSend--->CacheLookup---> CheckMiss---> __objc_msgSend_uncached---> MethodTableLookup---> __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3,再通过lookUpImpOrForward对类以及父类的缓存以及方法列表进行慢速查找,找到就缓存起来 - 如果没有找到方法实现,那么先进入动态方法解析,之后进入消息的快速转发和常规转发,消息转发处理失败之后则报经典crash