在Object-C中,方法调用后会被缓存起来,在下一次调用的时候就会去缓存中拿取,方法缓存在cache_t中,-号方法存在类中,+号方法以实例方法的形式存在元类中。
一、cache_t内部结构
// 类的结构
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA; //8
Class superclass; //8
cache_t cache; //16
class_data_bits_t bits;
...
}
// cache_t结构
struct cache_t {
struct bucket_t *_buckets; //8
mask_t _mask; //4
mask_t _occupied; //4
...
};
typedef uint32_t mask_t;
这是cache_t的源码。
struct bucket_t {
private:
// IMP-first is better for arm64e ptrauth and no worse for arm64.
// IMP-first 对 arm64e 的效果更好,对 arm64 不会有坏的影响。
// SEL-first is better for armv7* and i386 and x86_64.
// SEL-first 适用于 armv7 * 和 i386 和 x86_64
#if __arm64__
MethodCacheIMP _imp; //MethodCacheIMP 为对应的函数的内存地址
cache_key_t _key; //cache_key_t 为方法的SEL,也就是方法名
#else
cache_key_t _key;
MethodCacheIMP _imp;
#endif
public:
inline cache_key_t key() const { return _key; }
inline IMP imp() const { return (IMP)_imp; }
inline void setKey(cache_key_t newKey) { _key = newKey; }
inline void setImp(IMP newImp) { _imp = newImp; }
void set(cache_key_t newKey, IMP newImp);
};
_buckets是一个bucket_t结构体的数组,bucket_t里面存放_imp和_key。_mask的大小等于总大小-1。_occupied表示的是已经存取的方法的个数。- 这里有一个注意点,就是
IMP-first和SEL-first,上面源码已说明。
二、方法缓存
方法在调用的时候,先去缓存中查找,如果缓存中已经存在了该方法,则直接返回,否则就会把方法缓存取来。
static void cache_fill_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver)
{
cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked();
// Never cache before +initialize is done
if (!cls->isInitialized()) return;
// Make sure the entry wasn't added to the cache by some other thread
// before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock.
if (cache_getImp(cls, sel)) return;
cache_t *cache = getCache(cls);//拿到类中的cache
cache_key_t key = getKey(sel);//将sel转换为key
// Use the cache as-is if it is less than 3/4 full
mask_t newOccupied = cache->occupied() + 1;
mask_t capacity = cache->capacity();
//判断cache是否初始化
if (cache->isConstantEmptyCache()) {
// Cache is read-only. Replace it.
//没有缓存过内容,重新开辟空间,最少4字节
cache->reallocate(capacity, capacity ?: INIT_CACHE_SIZE);
}
else if (newOccupied <= capacity / 4 * 3) {
// Cache is less than 3/4 full. Use it as-is.
}
else {
// Cache is too full. Expand it.
cache->expand();//cache扩容
}
// Scan for the first unused slot and insert there.
// There is guaranteed to be an empty slot because the
// minimum size is 4 and we resized at 3/4 full.
bucket_t *bucket = cache->find(key, receiver);//根据key查找
if (bucket->key() == 0) cache->incrementOccupied();
bucket->set(key, imp);//添加方法到缓存
}
enum {
INIT_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2 = 2,
INIT_CACHE_SIZE = (1 << INIT_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2)
};
//可知 INIT_CACHE_SIZE 初始值为 4
if (!cls->isInitialized()) return;类没有初始化,直接returnif (cache_getImp(cls, sel)) return;找到缓存,则直接返回cache_t *cache = getCache(cls);和cache_key_t key = getKey(sel);分别为获取到类的cache_t对象和根据方法名获取到cache_key_t对象mask_t newOccupied = cache->occupied() + 1;和mask_t capacity = cache->capacity();分别为cache对象的Occupied和mask对象在原基础上+1if (cache->isConstantEmptyCache())缓存为空,需要执行cache->reallocate(capacity, capacity ?: INIT_CACHE_SIZE);方法进行申请内存else if (newOccupied <= capacity / 4 * 3)没有超出哈希表3/4容量时,跳过直接进行下面缓存的操作- 如果超出哈希表3/4容量时,需要执行
cache->expand();进行哈希表扩容 bucket_t *bucket = cache->find(key, receiver);根据key进行方法存储cache->incrementOccupied()Occupied++bucket->set(key, imp);写入哈希表
三 、cache的初始化
void cache_t::reallocate(mask_t oldCapacity, mask_t newCapacity)
{
bool freeOld = canBeFreed();
bucket_t *oldBuckets = buckets();//获取现有的buckets
bucket_t *newBuckets = allocateBuckets(newCapacity);//开辟一个新的buckets
// Cache's old contents are not propagated.
// This is thought to save cache memory at the cost of extra cache fills.
// fixme re-measure this
assert(newCapacity > 0);
assert((uintptr_t)(mask_t)(newCapacity-1) == newCapacity-1);
//重新设置buckets和mask
setBucketsAndMask(newBuckets, newCapacity - 1);
//回收旧的buckets
if (freeOld) {
cache_collect_free(oldBuckets, oldCapacity);
cache_collect(false);
}
}
在cache尚未初始化的时候会调用reallocate方法进行初始化,分配一个大小为4的数组
四、expand扩容
缓存的方法数量超过了当前容量的四分之三时,进行扩容,扩容为当前容量的2倍。
void cache_t::expand()
{
cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked();
// 拿到当前的容量
uint32_t oldCapacity = capacity();
// 扩容当前容量的2倍
uint32_t newCapacity = oldCapacity ? oldCapacity*2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
if ((uint32_t)(mask_t)newCapacity != newCapacity) {
// mask overflow - can't grow further
// fixme this wastes one bit of mask
newCapacity = oldCapacity;
}
//重新开辟内存
reallocate(oldCapacity, newCapacity);
}
五、 _buckets查找
bucket_t * cache_t::find(cache_key_t k, id receiver)
{
assert(k != 0);
bucket_t *b = buckets();
mask_t m = mask();
// 通过cache_hash函数【begin = k & m】计算出key值 k 对应的 index值 begin,用来记录查询起始索引
mask_t begin = cache_hash(k, m);
// begin 赋值给 i,用于切换索引
mask_t i = begin;
do {
if (b[i].key() == 0 || b[i].key() == k) {
//用这个i从散列表取值,如果取出来的bucket_t的 key = k,则查询成功,返回该bucket_t,
//如果key = 0,说明在索引i的位置上还没有缓存过方法,同样需要返回该bucket_t,用于中止缓存查询。
return &b[I];
}
} while ((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin);
// hack
Class cls = (Class)((uintptr_t)this - offsetof(objc_class, cache));
cache_t::bad_cache(receiver, (SEL)k, cls);
}
cache_next方法其实就是i= i-1,回到do循环里面,相当于查找数据的上一个元素。当i=0的时候,i指向的是数组的首元素位置,重新将mask赋值给i,使其指向散列表最后一个元素,重新开始反向遍历数组。
#if __arm__ || __x86_64__ || __i386__
// objc_msgSend has few registers available.
// Cache scan increments and wraps at special end-marking bucket.
#define CACHE_END_MARKER 1
static inline mask_t cache_next(mask_t i, mask_t mask) {
return (i+1) & mask;
}
#elif __arm64__
// objc_msgSend has lots of registers available.
// Cache scan decrements. No end marker needed.
#define CACHE_END_MARKER 0
static inline mask_t cache_next(mask_t i, mask_t mask) {
return i ? i-1 : mask;
六、setBucketsAndMask() 设置buckets和mask
//重新设置buckets和mask
setBucketsAndMask(newBuckets, newCapacity - 1);
void cache_t::setBucketsAndMask(struct bucket_t *newBuckets, mask_t newMask)
{
// objc_msgSend uses mask and buckets with no locks.
// It is safe for objc_msgSend to see new buckets but old mask.
// (It will get a cache miss but not overrun the buckets' bounds).
// It is unsafe for objc_msgSend to see old buckets and new mask.
// Therefore we write new buckets, wait a lot, then write new mask.
// objc_msgSend reads mask first, then buckets.
// ensure other threads see buckets contents before buckets pointer
mega_barrier();//添加线程安全,确保其他线程查看到新的存储单元
_buckets = newBuckets;
// ensure other threads see new buckets before new mask
mega_barrier();//添加线程安全,确保其他线程设置新的mask之后,查看新的存储单元
// _mask为总容量-1
_mask = newMask;
_occupied = 0;//清空旧的缓存,已占用容量为0
}
七、cache流程
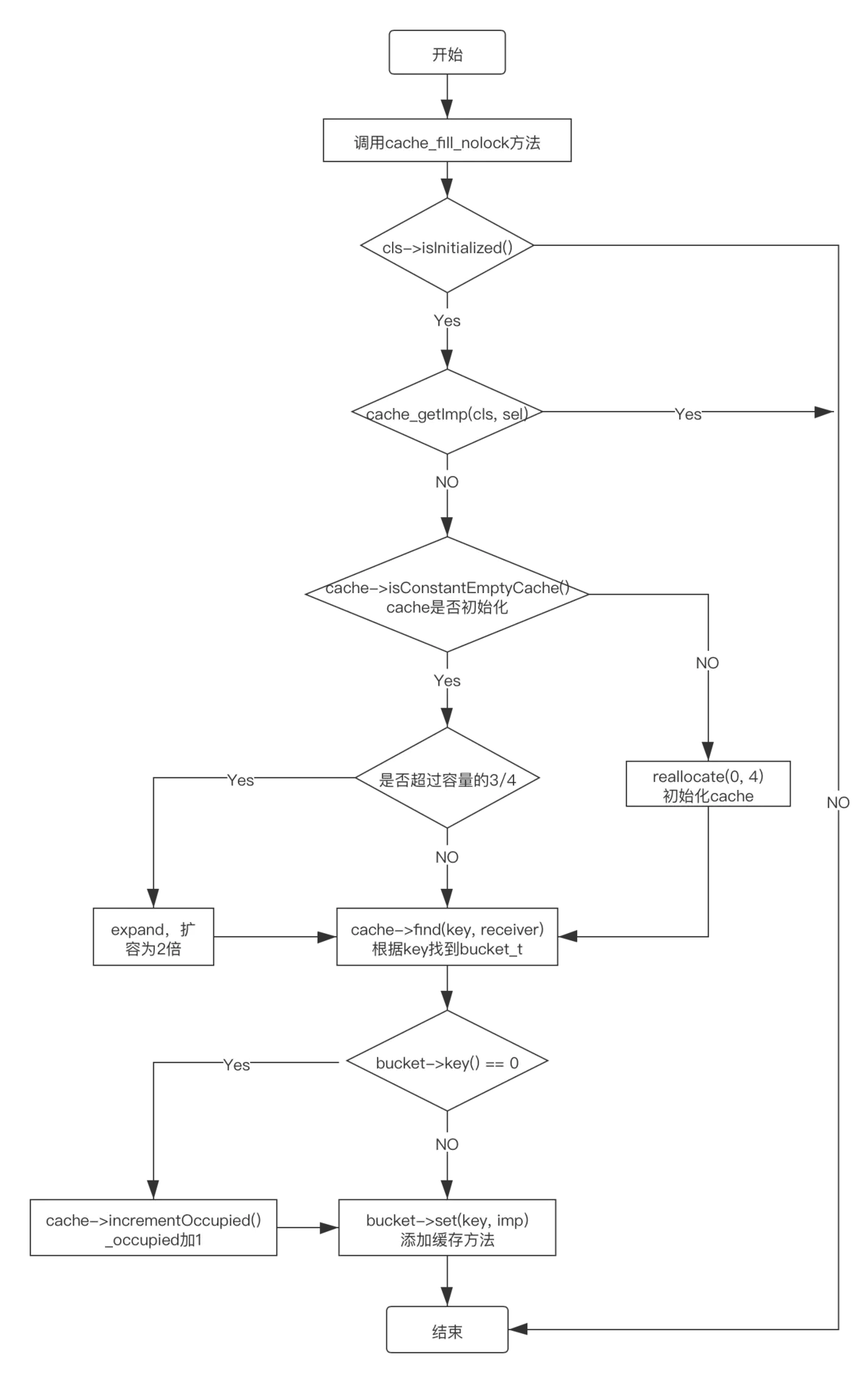
八、总结
Class中的Cache主要是为了在消息发送的过程中,进行方法的缓存,加快调用效率,使用了动态扩容的技术,当容量达到总容量的3/4时,开始2倍扩容,扩容时会完全抹除旧的buckets,并且创建新的buckets代替,之后把最近一次临界的imp和key缓存进来,经典的LRU算法。