什么是跨域?
浏览器的同源策略
在解释跨域的概念之前,先让我们来了解下浏览器的同源策略,这也是为什么会有跨域的由来。
同源策略是一项约定,是浏览器的行为,限制了从同一个源下的文档或脚本如何与来自另一个源的资源进行交互。这是一个用于隔离潜在恶意文件的重要安全机制。
所谓同源是指 协议+域名+端口 三者都相同,不满足这个条件即为非同源,即使两个不同域名指向同一IP地址。 当协议、子域名、主域名、端口号中任意一个不相同时,都算作不同域。 不同域之间相互请求资源,就算作跨域。
| 协议 | 子域名 | 主域名 | 端口号 | 资源地址 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| http:// | www. | abc.com | :8080 | /scripts/jquery.js |
| https:// | cdn. | abc.com | :3000 | /b.js |
同源策略限制的内容:
- Cookie、LocalStorage、IndexedDB 等存储性内容
- DOM 节点
- AJAX 请求发送后,响应结果被浏览器拦截(即请求发送了,服务器响应了)
注意:有三个标签是允许跨域加载资源的:
<img src=XXX><link href=XXX><script src=XXX>
总结一下就是: 同源策略是浏览器的一种安全行为,是为了阻止一个域下的文档或脚本读取另一个域下的资源污染自身,所以拦截了响应。 这也是为什么表单提交可以跨域(因为没有获取新的内容)。
常用的解决方案
1.JSONP (json with padding)
1) 原理
利用<script>标签不受跨域限制,将回调函数名作为参数附带在请求中,服务器接受到请求后,进行特殊处理:把接收到的函数名和需要给它的数据拼接成一个字符串返回,客户端会调用相应声明的函数,对返回的数据进行处理。
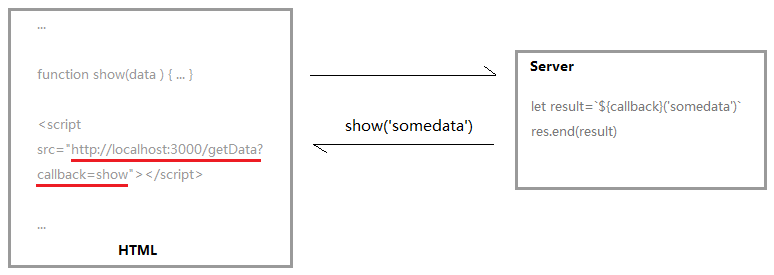
2) 示例
封装jsonp请求
<script>
function jsonp({
url,
params,
cb
}) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let script = document.createElement('script')
window[cb] = function (data) {
resolve(data)
document.body.removeChild(script);
}
params = {
...params,
cb
}
let arrs = []
for (let key in params) {
arrs.push(`${key}=${params[key]}`)
}
script.src = `${url}?${arrs.join('&')}`
document.body.appendChild(script)
})
}
jsonp({
url: 'http://localhost:3000/say',
params: {
wd: 'Iloveyou'
},
cb: 'show'
}).then(data => {
console.log(data)
})
</script>
上述代码向http://localhost:3000/say?wd=Iloveyou&cb=show发起请求,服务器返回show('我不爱你'),因而前台将会调用show方法。
let express = require('express')
let app = express()
app.get('/say', function (req, res) {
let { wd, cb } = req.query
console.log(wd)
console.log(cb)
res.end(`${cb}('我不爱你')`)
})
var server = app.listen(3000, function () {
var host = server.address().address
var port = server.address().port
console.log("应用实例,访问地址为 http://%s:%s", host, port)
})
3) 优缺点
简单兼容性好,解决主流浏览器跨域数据访问。缺点是仅支持GET方法,且需要服务器做支持才能实现。
2.CORS
CORS(cross-origin resource share)跨域资源共享 只是在 HTTP 协议内部,新增了若干个 header字段 ,来制定 跨域资源共享 的实现规则。
目前所有浏览器都支持该功能(IE8+:IE8/9需要使用XDomainRequest对象来支持CORS)),CORS也已经成为主流的跨域解决方案。浏览器会自动进行 CORS 通信,实现 CORS 通信的关键在于后端。只要后端实现了 CORS,就实现了跨域。根据浏览器发送的请求可以分为两种情况。
1) 简单请求
若请求满足所有下述条件,则该请求可视为“简单请求”:
- 使用下列方法之一:
- GET
- HEAD
- POST
- Fetch 规范定义了对 CORS 安全的首部字段集合,不得人为设置该集合之外的其他首部字段。该集合为:
- Accept
- Accept-Language
- Content-Language
- Content-Type (需要注意额外的限制)
- DPR
- Downlink
- Save-Data
- Viewport-Width
- Width
- Content-Type 的值仅限于下列三者之一:
- text/plain
- multipart/form-data
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 请求中的任意XMLHttpRequestUpload 对象均没有注册任何事件监听器;XMLHttpRequestUpload 对象可以使用 XMLHttpRequest.upload 属性访问。
- 请求中没有使用 ReadableStream 对象。
对于简单请求,只服务端设置Access-Control-Allow-Origin即可,前端无须设置,若要带cookie请求:前后端都需要设置。
需注意的是:由于同源策略的限制,所读取的cookie为跨域请求接口所在域的cookie,而非当前页。如果想实现当前页cookie的写入,可参考nginx反向代理中设置proxy_cookie_domain 和 NodeJs中间件代理中cookieDomainRewrite参数的设置。
<script>
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
document.cookie = 'name=chen';
xhr.withCredentials = true
xhr.open('POST', 'http://localhost:4000', true)
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.response)
}
}
}
xhr.send();
</script>
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
if (request.url === '/') {
if (request.method === 'GET') {
response.writeHead(200, { 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': 'http://localhost:3000' })
response.end("{name:'chen',password:'test'}")
}
if (request.method === 'POST') {
response.writeHead(200, {
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': 'http://localhost:3000',
'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials': true,
// 此处设置的cookie还是http://localhost:4000的而非http://localhost:3000,因为后端也不能跨域写cookie(nginx反向代理可以实现),
// 但只要http://localhost:4000中写入一次cookie认证,后面的跨域接口都能从http://localhost:4000中获取cookie,从而实现所有的接口都能跨域访问
'Set-Cookie': 'l=a123456;Path=/;Domain=http://localhost:3000;HttpOnly' // HttpOnly的作用是让js无法读取cookie
})
response.end('true')
}
}
response.end('false')
})
server.listen(4000, () => {
console.log('the server is running at http://localhost:4000')
})
2) 复杂请求
不符合以上条件的请求就肯定是复杂请求了。
复杂请求的CORS请求,会在正式通信之前,增加一次HTTP查询请求,称为 预检 请求,该请求是 option 方法的,通过该请求来知道服务端是否允许跨域请求。
复杂请求例子:
// index.html
<script>
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
document.cookie = 'name=chen';
xhr.withCredentials = true;
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:4000/getData', true)
xhr.setRequestHeader('name', 'chen')
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300 || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.response);
console.log(xhr.getResponseHeader('name'))
}
}
}
xhr.send();
</script>
let express = require('express')
let app = express();
let whiteList = ['http://localhost:3000']
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
let origin = req.headers.origin
if (whiteList.includes(origin)) {
// 设置哪个源可以访问我
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', origin)
// 允许携带哪个头访问我
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'name')
// 允许哪个方法访问我
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'PUT')
// 允许携带cookie
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', true)
// 预检的存活时间
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Max-Age', 6)
// 允许返回的头
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Expose-Headers', 'name')
if (req.method === 'OPTIONS') {
// res.end();
}
}
next();
})
app.put('/getData', function (req, res) {
console.log(req.headers)
res.setHeader('name', 'jw')
res.end('i don\'t love you')
})
app.get('/getData', function (req, res) {
console.log(req.headers)
res.end('i love u')
})
app.use(express.static(__dirname))
app.listen(4000, () => {
console.log('serve at 4000')
})
上述代码由http://localhost:3000/index.html向http://localhost:4000/跨域请求,正如我们上面所说的,后端是实现 CORS 通信的关键,需要对引起跨域的因素在OPTION中进行相应的处理。
3.nginx反向代理
1) 跨域原理
同源策略是浏览器的安全策略,不是HTTP协议的一部分。而服务器端调用HTTP接口只是使用HTTP协议,不会执行JS脚本,不需要同源策略,因此也就不存在跨越问题。
2) 实现思路
通过nginx配置一个代理服务器(域名与domain1相同,端口不同)做跳板机,反向代理访问domain2接口,并且可以顺便修改cookie中domain信息,方便当前域cookie写入,实现跨域登录。
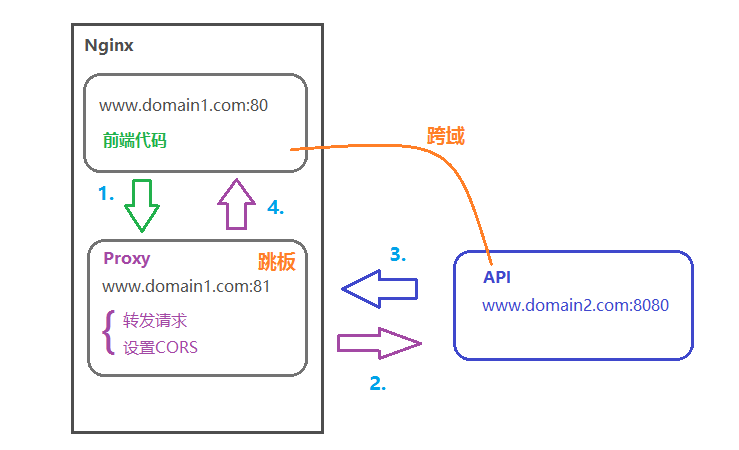
3) 示例代码
nginx相关配置:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.domain1.com;
location / {
root [前端代码路径];
index index.html;
}
}
server {
listen 81;
server_name www.domain1.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://www.domain2.com:8080; #反向代理
proxy_cookie_domain www.domain2.com www.domain1.com; #修改cookie里的domain
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin http://www.domain1.com;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials true;
}
}
前端代码:
// index.html
<script>
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 前端开关:浏览器是否读写cookie
xhr.withCredentials = true;
// 访问nginx中的代理服务器
xhr.open('get', 'http://www.domain1.com:81/?user=admin', true);
xhr.send();
</script>
Nodejs后台:
// server.js
var http = require('http');
var server = http.createServer();
var qs = require('querystring');
server.on('request', function(req, res) {
var params = qs.parse(req.url.substring(2));
// 向前台写cookie
res.writeHead(200, {
'Set-Cookie': 'l=a123456;Path=/;Domain=www.domain2.com;HttpOnly' // HttpOnly:脚本无法读取
});
res.write(JSON.stringify(params));
res.end();
});
server.listen('8080');
console.log('Server is running at port 8080...');
4.Nodejs中间件代理
1)原理
原理和上面的nginx大致相同,都是利用服务器之间无需遵守同源策略,通过一个代理服务器,实现请求的转发以及设置CORS。
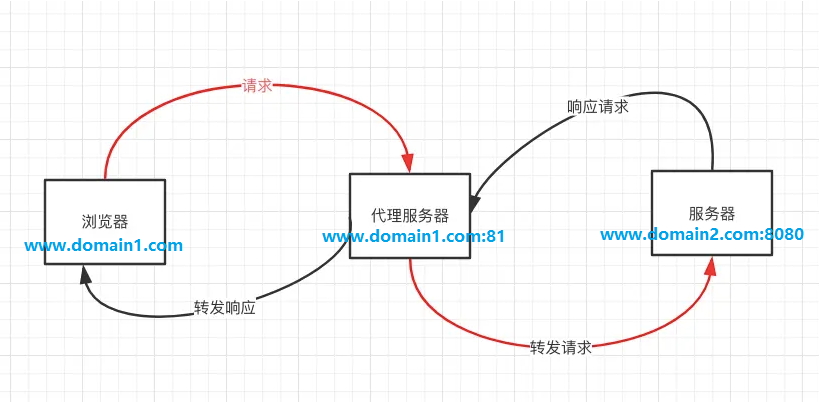
2) 实现思路
node + express + http-proxy-middleware 搭建proxy服务器
3) 示例代码
前端代码:
<script>
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 前端开关:浏览器是否读写cookie
xhr.withCredentials = true;
// 访问nginx中的代理服务器
xhr.open('get', 'http://www.domain1.com:4000/?user=admin', true);
xhr.send();
</script>
中间件:
var express = require('express')
var proxy = require('http-proxy-middleware')
var app = express();
app.use('/', proxy({
target: 'http://www.domain2.com:8080',
changeOrigin: true,
// 修改响应头信息,实现跨域并允许带cookie
onProxyReq: function (proxyRes, req, res) {
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', 'http://www.domain1.com');
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', 'true');
},
// 修改响应中的cookie域
cookieDomainRewrite: 'www.domain1.com' // false 为不修改
}))
app.listen(81, () => {
console.log('Proxy server is running at port 81...')
})
后台接口:
var express = require('express')
var app = express();
var qs = require('querystring')
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
var params = qs.parse(req.url.substring(2));
res.setHeader('Set-Cookie', 'l=a123456;Path=/;Domain=www.domain2.com;HttpOnly')
res.write(JSON.stringify(params));
res.end();
})
app.listen(8080, () => {
console.log('Server is running at port 8080...')
})