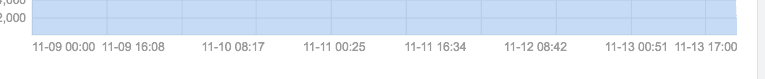
1 AxisBottom 使用
// left, top 是距离左边的距离和顶部的距离
// scale 传入的计算函数
// tickformat 显示格式
// numTicks 显示多少个坐标
// 因为ui的标准是左对齐和右边对齐,所以可以设置tickValues,tickValues 必须在xScale 的定义域之内,tickValues 函数把数组均分成几份
const xScale = scaleTime({
rangeRound: [0, width],
domain: d3.extent(data, x)
});
<AxisBottom
top={height}
scale={xScale}
tickFormat={d => d3.timeFormat("%m-%d %H:%M")(d)}
tickValues={tickValues(8, d3.extent(data, x))}
/>
效果图如下
bar 使用
在使用柱形图的时候,经常需要根据数据的大小来动态的调整柱子的宽度,于是可以设置一个最大宽度,然后其它的可以根据d3.scaleBand的padding来动态的设置。
render() {
let { width, height, data } = this.props;
// const data = appleStock;
data = data.slice(0, 4);
return (
<div>
<Container
padding={padding}
x={x}
y={y}
// 定义tooltip格式
tooltip={data => (
<div>
{String(x(data))}: {y(data)}
</div>
)}
>
{({
width,
height,
showBasicTooltip,
showLineTooltip,
hideTooltip
}) => {
const xScale = scaleBand({
rangeRound: [0, width],
// domain: d3.extent(data, x)
domain: data.map(x)
}).padding(0.5);
const yScale = scaleLinear({
rangeRound: [height, 0],
domain: d3.extent(data, y)
});
const xAxisScale = scaleLinear({
rangeRound: [0, width],
domain: d3.extent(data, x)
});
return (
<Group>
{/* <Grid
width={width}
height={height}
xScale={xScale}
yScale={yScale}
/> */}
<AxisBottom
top={height}
scale={xAxisScale}
tickFormat={d => d3.timeFormat("%m-%d %H:%M")(d)}
tickValues={tickValues(8, d3.extent(data, x))}
/>
<AxisLeft scale={yScale} />
<Group className="line-graph">
{/* <AreaClosed
data={data}
xScale={xScale}
yScale={yScale}
x={x}
y={y}
/> */}
{/* 定义整个图形触发区间 */}
{data.map(d => (
<Bar
key={`bar-${x(d)}`}
width={xScale.bandwidth() > 20 ? 20 : xScale.bandwidth()}
height={height - yScale(y(d))}
data={d}
fill="#2d84e5"
x={xScale(x(d))}
y={yScale(y(d))}
/>
))}
</Group>
</Group>
);
}}
</Container>
{/* <div styleName="sd" />
<div styleName="sd" /> */}
</div>
);
}
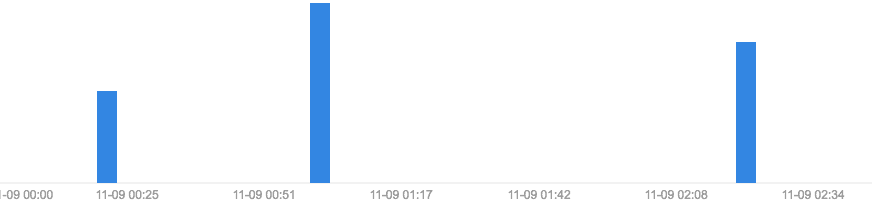
当数据很小的时候,表现如下图:
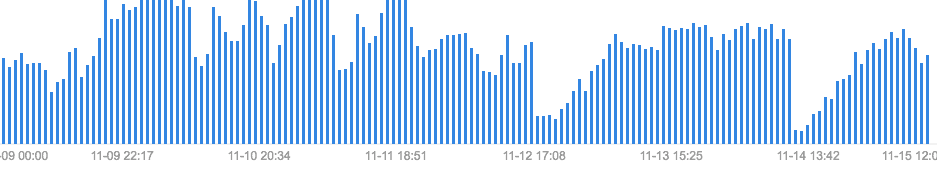
当数据很大的时候,表现如下图:
tooltip
当需要tooltip的时候,可以使用传入tooltip,
<div>
<Container
padding={padding}
x={x}
y={y}
// 定义tooltip格式
tooltip={data => {
return (
<div>
{String(x(data))}: {y(data)}
</div>
);
}}
>
{({
width,
height,
showBasicTooltip,
showLineTooltip,
hideTooltip
}) => {
// const xScale = scaleBand({
// rangeRound: [0, width],
// // domain: d3.extent(data, x)
// domain: data.map(x)
// }).padding(0.5);
// const yScale = scaleLinear({
// rangeRound: [height, 0],
// domain: d3.extent(data, y)
// });
const xScale = scaleTime({
rangeRound: [0, width],
domain: d3.extent(data, x)
});
const yScale = scaleLinear({
rangeRound: [height, 0],
domain: d3.extent(data, y)
});
const xAxisScale = scaleLinear({
rangeRound: [0, width],
domain: d3.extent(data, x)
});
return (
<Group>
{/* <Grid
width={width}
height={height}
xScale={xScale}
yScale={yScale}
/> */}
<AxisBottom
top={height}
scale={xAxisScale}
tickFormat={d => d3.timeFormat("%m-%d %H:%M")(d)}
tickValues={tickValues(8, d3.extent(data, x))}
/>
<AxisLeft scale={yScale} />
<Group className="line-graph">
<AreaClosed
data={data}
xScale={xAxisScale}
yScale={yScale}
x={x}
y={y}
/>
<Bar
x={0}
y={0}
width={width}
height={height}
fill="transparent"
data={data}
onMouseMove={d => e => {
showLineTooltip({
event: e,
data: d,
xScale,
yScale
});
// showBasicTooltip({
// event: e,
// data: d
// });
}}
onMouseLeave={d => e => hideTooltip()}
/>
</Group>
</Group>
);
}}
</Container>
</div>
showLineTooltip 是指带有线的tooltip,showBasicTooltip不带线 效果如下
两个tooltip
因为在ui图中经常会出现很多次一个图中出现两个tooltip, 这样可以通过样式让下一个tooltip,像是出现在下方。
render() {
const data = appleStock.slice(0, 20);
return (
<div style={{ position: "relative" }}>
<h2>默认配置,坐标轴为category, value</h2>
<Container
padding={padding}
x={x}
y={y}
tooltip={data => (
<Fragment>
<div>
{String(x(data))}: {y(data)}
</div>
<div
style={{
position: "absolute",
backgroundColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)",
color: "#fff",
padding: "10px",
borderRadius: "3px",
border: "none",
fontSize: "12px",
fontWeight: "normal",
lineHeight: "1",
pointerEvents: "none",
zIndex: 10,
top: "100px",
left: 0
}}
>
sddw
</div>
</Fragment>
)}
>
效果如下图:
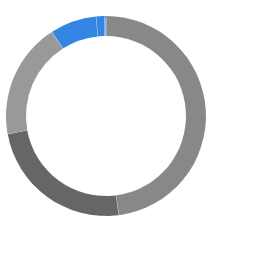
基本圆环图
构建基本的圆环图,圆环图比较简单,
const letters = letterFrequency.slice(0, 4);
const browsers = Object.keys(browserUsage[0])
.filter(k => k !== "date")
.map(k => ({ label: k, usage: browserUsage[0][k] }));
const x = d => new Date(d.date);
const y = d => +d.close;
const y2 = d => +d.close - 10;
// console.log(appleStock);
const padding = {
top: 150,
left: 140,
bottom: 20,
right: 20
};
const radius = 200;
console.log(letters);
const circleColor = ["#888", "#666", "#999"];
class PieTest extends Component {
render() {
// const data = appleStock.slice(0, 20);
return (
<div style={{ position: "relative" }}>
<Container
padding={padding}
// x={x}
// y={y}
tooltip={data => (
<Fragment>
<div>{JSON.stringify(data.data.label)}</div>
</Fragment>
)}
height={300}
style={{}}
>
{({
width,
height,
showBasicTooltip,
showLineTooltip,
hideTooltip
}) => {
return (
<Group className="bar-group">
<Pie
data={browsers}
pieValue={d => d.usage}
outerRadius={radius - 100}
innerRadius={radius - 120}
fill={d => circleColor[d.index] || "#2d84e5"}
// fillOpacity={d => 1 / (d.index + 2)}
// cornerRadius={3}
padAngle={0.002}
onMouseMove={d => e =>
showBasicTooltip({
event: e,
data: d
})}
onMouseLeave={d => e => hideTooltip()}
// centroid={(centroid, arc) => {
// const [x, y] = centroid;
// const { startAngle, endAngle } = arc;
// if (endAngle - startAngle < 0.1) return null;
// return arc.data.label;
// }}
/>
</Group>
);
}}
</Container>
</div>
);
}
}
export default PieTest;
基本效果图如下: