百分比很好理解,就是摆放的 view 占父 view 宽的百分之几,高占父 view 的百分之几。假定父 view 的宽高跟屏幕大小一致,比如 1080 * 1920 分辨率的手机屏幕, 有一个子 view 的高占屏幕高的50% ,即 1920 * 0.5 = 960px, 宽占屏幕宽的30%,即 1080 * 0.3 = 324px。
什么场景下会使用
笔者在开发中曾经遇到设计师将一张图片作为背景,在背景图片上某些位置需要摆放控件,又不能写死,因为控件内容会改变。这种恶心的布局如果通过写死 dp, 基本上适配其他机型绝对 gg。所以这种场景就非常适合用百分比适配。其思想也是非常简单,首先我们必须保证背景图片的缩放比例一定不能改变,然后得到每个摆放控件与图片背景的比例,这样我们就可以通过计算得出。那如果改变了缩放比例会怎样? 答案就是再怎么计算都没*用。
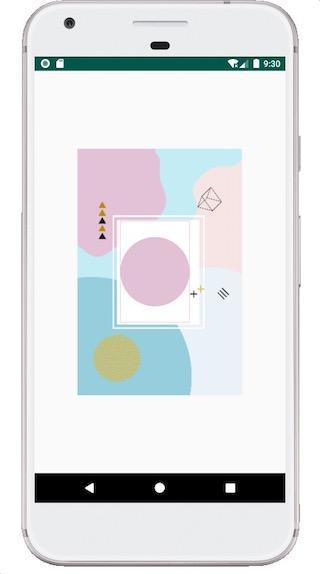
举个例子,现在我们看下如下背景图片,如果现在告诉你需要在白色的填写内容,注意:白色区域并非在布局居中对齐,并且内部还有 “+” 符号,要求如图 1-2 所示,我们只在可编辑区域(填充粉红色的区域)填写内容。


适配计算
首先需要找到可编辑区域在原图(即背景图)的到左上角的绝对位置,由于这张背景图从网上找来的,因此它的点是我通过尺子测量而来。这里大致测量得到: mOldLeft = 282; mOldTop = 476; mOldRight = 736; mOldBottom = 1140; mOldWidth = 1080; mOldHeight = 1619; 这几个值依次是左上右下以及宽高的值。得到这几个值后那就很简单了,我们只需要在不同设备的设备上,按着比例缩放图片,然后根据公式: mOldLeft / mOldWidth = mLleft / mBitmapWidth。 其中 mBitmapWidth 为缩放后的图片宽度, mLleft 为所求真实屏幕的left 的值。其代码如下:
private Bitmap mBackgroundImage;
/**
* 背景图片的宽度
*/
private int mBitmapWidth;
/**
* 背景图片的高度
*/
private int mBitmapHeight;
/**
* 原始图片,白色输入框在原图的绝对位置
*/
private int mOldTop = 476;
/**
* 原始图片,白色输入框在原图的绝对位置
*/
private int mOldLeft = 282;
/**
* 原始图片,白色输入框在原图的绝对位置
*/
private int mOldRight = 736;
/**
* 原始图片,白色输入框在原图的绝对位置
*/
private int mOldBottom = 1140;
/**
* 原始图片的宽
*/
private int mOldWidth = 1080;
/**
* 原始图片的高
*/
private int mOldHeight = 1619;
private int mleft;
private int mTop;
private int mRight;
private int mBottom;
private Paint mPaint;
public PercentView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public PercentView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public PercentView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init() {
// 对图片缩放处理.
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.background, options);
options.inSampleSize = 4;
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
mBackgroundImage = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.background, options);
mBitmapWidth = mBackgroundImage.getWidth();
mBitmapHeight = mBackgroundImage.getHeight();
// 根据背景图片空白框的比列计算位置.
mleft = mBitmapWidth * mOldLeft / mOldWidth;
mTop = mBitmapHeight * mOldTop / mOldHeight;
mRight = mBitmapWidth * mOldRight / mOldWidth;
mBottom = mBitmapHeight * mOldBottom / mOldHeight;
// 初始化画笔.
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG | Paint.DITHER_FLAG);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(mBitmapWidth, mBitmapHeight);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
// 绘制背景图片.
canvas.drawBitmap(mBackgroundImage, 0, 0, null);
// 绘制红色输入框边界.
canvas.drawRect(mleft, mTop, mRight, mBottom, mPaint);
// 绘制白色输入框中的圆
mPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#E2C0D6"));
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
canvas.drawCircle( (float) (mRight - mleft) / 2 + mleft,
(float) (mBottom - mTop) / 2 + mTop,
(float) (mRight - mleft) / 2,
mPaint);
}
效果图如下:

布局中写比例
上面是针对手写代码来进行适配,一般场景下如果我们可以在布局中愉快的编写,就不要通过计算来适配。下面我将通过继承自 RelativeLayout 来实现,其原理就是在 onMeasure 测量的时候注入我们的比例设置,所谓比例是根据屏幕的实际宽高尺寸进行比例计算得到。代码如下:
当然最合适的方式肯定是在 attrs 中进行配置,这样用起来也就爽了
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="PercentRelativeLayout">
<!-- 宽的比例 -->
<attr name="layout_widthPercent" format="float"/>
<!-- 高的比例-->
<attr name="layout_heightPercent" format="float"/>
<!-- 距离父控件左边距离比例 -->
<attr name="layout_marginLeftPercent" format="float"/>
<!-- 距离父控件上边距离比例 -->
<attr name="layout_marginTopPercent" format="float"/>
<!-- 距离父控件右边距离比例 -->
<attr name="layout_marginRightPercent" format="float"/>
<!-- 距离父控件下边距离比例 -->
<attr name="layout_marginBottomPercent" format="float"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
// 继承自 RelativeLayout, 在 onMeasure 注入计算过程.
public class PercentRelativeLayout extends RelativeLayout {
public PercentRelativeLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public PercentRelativeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public PercentRelativeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams childLayoutParams = child.getLayoutParams();
// 检查当前控件的 layoutParams 是否是 PercentRelativeLayoutParams 或者其子类
if (checkLayoutParams(childLayoutParams)) {
float widthPercent = ((PercentRelativeLayoutParams) childLayoutParams).mWidthPercent;
// 在布局中填写的宽度占屏幕宽的比例. 比如 0.5 占屏幕宽一半
if (widthPercent > 0) {
// 屏幕的宽度按着指定的比例缩放得到控件的宽度.
childLayoutParams.width = (int) (widthSize * widthPercent);
}
// 余下的步骤原理同上
float heightPercent = ((PercentRelativeLayoutParams) childLayoutParams).mHeightPercent;
if (heightPercent > 0) {
childLayoutParams.height = (int) (heightSize * heightPercent);
}
float marginLeftPercent = ((PercentRelativeLayoutParams) childLayoutParams).mMarginLeftPercent;
if (marginLeftPercent > 0) {
((MarginLayoutParams)childLayoutParams).leftMargin = (int) (widthSize * marginLeftPercent);
}
float marginTopPercent = ((PercentRelativeLayoutParams) childLayoutParams).mMarginTopPercent;
if (marginTopPercent > 0) {
((MarginLayoutParams)childLayoutParams).topMargin = (int) (heightSize * marginTopPercent);
}
float marginRightPercent = ((PercentRelativeLayoutParams) childLayoutParams).mMarginRightPercent;
if (marginRightPercent > 0) {
((MarginLayoutParams)childLayoutParams).rightMargin = (int) (widthSize * marginRightPercent);
}
float marginBottomPercent = ((PercentRelativeLayoutParams) childLayoutParams).mMarginBottomPercent;
if (marginBottomPercent > 0) {
((MarginLayoutParams)childLayoutParams).bottomMargin = (int) (heightSize * marginBottomPercent);
}
}
}
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof PercentRelativeLayoutParams;
}
@Override
public PercentRelativeLayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new PercentRelativeLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
public static class PercentRelativeLayoutParams extends LayoutParams {
public float mWidthPercent;
public float mHeightPercent;
public float mMarginLeftPercent;
public float mMarginTopPercent;
public float mMarginRightPercent;
public float mMarginBottomPercent;
public PercentRelativeLayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
// 获取自定义属性.
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.PercentRelativeLayout);
try {
mWidthPercent = a.getFloat(R.styleable.PercentRelativeLayout_layout_widthPercent, 0.0f);
mHeightPercent = a.getFloat(R.styleable.PercentRelativeLayout_layout_heightPercent, 0.0f);
mMarginLeftPercent = a.getFloat(R.styleable.PercentRelativeLayout_layout_marginLeftPercent, 0.0f);
mMarginTopPercent = a.getFloat(R.styleable.PercentRelativeLayout_layout_marginTopPercent, 0.0f);
mMarginRightPercent = a.getFloat(R.styleable.PercentRelativeLayout_layout_marginRightPercent, 0.0f);
mMarginBottomPercent = a.getFloat(R.styleable.PercentRelativeLayout_layout_marginBottomPercent, 0.0f);
} finally {
a.recycle();
}
}
}
}
使用如下,将根布局设置为我们自定义的布局 PercentRelativeLayout。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.hxj.enjoyandroid.ui.PercentRelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".UIAdapter2Activity">
<!-- 为屏幕宽高的 80%,-->
<com.hxj.enjoyandroid.ui.PercentRelativeLayout
app:layout_widthPercent="0.8"
app:layout_heightPercent="0.8"
android:background="#ff22ff"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!-- 为父控件宽高的 100%,但是有外边距,为父控件的 20% -->
<TextView
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="百分比适配"
app:layout_widthPercent="1.0"
app:layout_heightPercent="1.0"
app:layout_marginTopPercent="0.2"
app:layout_marginRightPercent="0.2"
app:layout_marginLeftPercent="0.2"
app:layout_marginBottomPercent="0.2"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</com.hxj.enjoyandroid.ui.PercentRelativeLayout>
</com.hxj.enjoyandroid.ui.PercentRelativeLayout>
效果如下:

如果有疑惑为什么继承自 RelativeLayout ? 为什么要继承 LayoutParams 来加载我们的自定义属性?请看源码分析篇 Android 布局属性加载过程