本文根据zpao/building-react-from-scratch 和 Implementation Notes - React
逐步讲解react的实现。
hyperscript(configuration -> dom)
浏览器提供了DOM API方便我们生成元素,如通过如下代码即可生成如下的DOM元素
var elem = document.createElement('a');
elem.href= 'http://www.baidu.com'
elem.textContent = 'hyperscript'
一个DOM元素主要由三部分组成nodeType,props,和children组成,因此只需要提供{nodeType,props,children}既可以构建出想要的DOM元素。
这里得区分下attr和prop的区别。angular2文档中有比较好的说明
attribute 是由 HTML 定义的。property 是由 DOM (Document Object Model) 定义的。
1.少量 HTML attribute 和 property 之间有着 1:1 的映射,如id。
2.有些 HTML attribute 没有对应的 property,如colspan。
3.有些 DOM property 没有对应的 attribute,如textContent。
4.大量 HTML attribute看起来映射到了property…… 但却不像我们想的那样!
attribute 初始化 DOM property,然后它们的任务就完成了。property 的值可以改变;attribute 的值不能改变。
因此hyperscript使用property而非attribute来构建DOM节点,其用法如下
const h = require('hyperscript')
const node = h('a', {href: 'http:www.baidu.com'}, 'hyperscript')
console.log(node.outerHTML)// => '<a href="http://www.baidu.com">hyperscript</a>mount (element -> dom)
hyperscript为了提供便利性提供了很多快捷操作,例如h('div#id')等价于h('#id')等价于h('div',{id:'id'}这带来便利的同时,也使得难以精确定义配置的具体类型,为了更加精确定义配置的格式,我们定义其类型为ReactElement其类型定义如下,并把配置对象称为element。
type ReactElement = ReactDOMElement;
type ReactDOMElement = {
type : string,
props : {
children : ReactNodeList,
className : string,
etc.
}
};
type ReactNodeList = ReactNode | ReactEmpty;
type ReactNode = ReactElement | ReactFragment | ReactText;
type ReactFragment = Array<ReactNode | ReactEmpty>;
type ReactText = string | number;
type ReactEmpty = null | undefined | boolean;而根据element生成DOM节点的函数称为mount,其类型定义如下
mount = (ReactElement) => Dom节点我们发现ReactElement的类型定义是递归的,这就意味这mount的实现也是递归的。
mount的简单实现如下。
function mount(element) {
var type = element.type;
var props = element.props;
var children = props.children;
children = children.filter(Boolean); // 对ReactEmpty进行过滤,其不渲染
var node = document.createElement(type);
Object.keys(props).forEach(propName => {
if (propName !== 'children') {
node.setAttribute(propName, props[propName]);
}
});
// 递归mount children
children.forEach(childElement => {
if(typeof childElement === 'string'){
childNode = mountText(childElement); //若子节点为ReactText则渲染文本节点
}else {
childNode = mount(childElement); //若子节点为Reactelement则递归渲染
}
node.appendChild(childNode);
});
return node;
}
function mountText(text){
return document.createTextNode(text);
}
//测试
var element1 = {
type: 'a',
props: {
href: 'http://www.baidu.com',
children: [{
type: 'button',
props: {
class: 'btn',
children: ['this is a button']
},
},
'hyperscript']
}
}
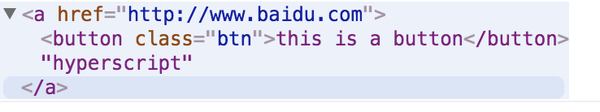
console.log(mount(element1))执行结果如下
组件 (element -> element)
随着dom结构的复杂,配置对象element也变得更加复杂,类似函数提供了数据组合的抽象,组件提供了element组合的抽象机制用于构建更加复杂的element对象。
function Button(props){
return {
type: 'button',
props: {
class: 'btn',
children: [props.text]
}
}
}此时可以这样调用
function Button(props){
return {
type: 'button',
props: {
class: 'btn',
children: [props.text]
}
}
}
var element1 = {
type: 'a',
props: {
href: 'http://www.baidu.com',
children: [
Button({text:'this is a button'}),
Button({text:'this is another button'}),
'hyperscript'
]
}
}
var node = mount(element1);这样需要每次手动调用Button,这种调用需要手动调用Button函数,较为不便,且形式不太统一。为此我们需要修改ReactElement的定义和mount的实现,使得调用处比较简单一致。修改后的调用方式如下。
var element1 = {
type: 'a',
props: {
href: 'http://www.baidu.com',
children: [
{
type: Button,
props: {
text: 'this is a button'
}
},
{
type: Button,
props: {
text: 'this is another button'
}
},
'hyperscript']
}
}
var node = mount(element1);修改后的类型定义如下
type ReactElement = ReactComponentElement | ReactDOMElement;
type ReactComponentElement<TProps> = {
type : ReactFunc<TProps>,
props : TProps
};
type ReactFunc<TProps> = TProps => ReactElementmount的实现需要处理三种情形
- ReactComponentElement
- ReactDomElement
- ReactText
修改实现如下
function mount(element){
if(typeof element === 'string'){
return mountText(element);
}
if(typeof element.type === 'function'){
return mountComposite(element);
}
return mountHost(element);
}
function mountHost(element) {
var type = element.type;
var props = element.props;
var children = props.children;
children = children.filter(Boolean); // 对ReactEmpty进行过滤,其不渲染
var node = document.createElement(type);
Object.keys(props).forEach(propName => {
if (propName !== 'children') {
node.setAttribute(propName, props[propName]);
}
});
// 递归mount children
children.forEach(childElement => {
var childNode = mount(childElement); //若子节点为Reactelement则递归渲染
node.appendChild(childNode);
});
return node;
}
function mountText(text){
return document.createTextNode(text);
}
function mountComposite(element){
element = element.type(element.props);
return mount(element); // delegate to mount
}至此我们的mount已经支持函数组件了,但是element的构建还是略显复杂。接下来通过两种方式简化element的构建。
createElement && JSX (简化element构建)
children虽然作为props的一部分,但是在html中其区别于其他的属性,其支持多种形式,为此通过createElement统一其处理。
function createElement(type,props,...args){
let children = [].concat(...args);
props.children = children;
return { type, props };
}
//一、 createElement构建
var element = createElement(
'a', {
href: 'http://www.baidu.com'
},
createElement(Button, { text: 'this is a button'}),
createElement(Button, { text: 'this is another button'}),
'hyperscript'
)至此我们的element构建已经比较简洁了,假如也能像写html一样构建element多好啊,JSX的作用正是如此。JSX语法类似html,其使得我们可以像写html一样构建element。使用JSX构建element方式如下所示。
//二、 JSX构建
var element = (
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">
<Button text="this is a button"/>
<Button text="this is another button"/>
hyperscript
</a>
)因此只需要使用babel通过如下配置将(二)的语法转换为(一)的语法即可。
{
"presets": ["env", "react"],
"plugins": [
["transform-react-jsx", {
"pragma": "createElement" // default pragma is React.createElement
}]
]
}至此我们的库使用方法已经很像React了。
完整实现如下
function mount(element){
if(typeof element === 'string'){
return mountText(element);
}
if(typeof element.type === 'function'){
return mountComposite(element);
}
return mountHost(element);
}
function mountHost(element) {
var type = element.type;
var props = element.props;
var children = props.children;
children = children.filter(Boolean); // 对ReactEmpty进行过滤,其不渲染
var node = document.createElement(type);
Object.keys(props).forEach(propName => {
if (propName !== 'children') {
node.setAttribute(propName, props[propName]);
}
});
// 递归mount children
children.forEach(childElement => {
var childNode = mount(childElement); //若子节点为Reactelement则递归渲染
node.appendChild(childNode);
});
return node;
}
function mountText(text){
return document.createTextNode(text);
}
function mountComposite(element){
element = element.type(element.props);
return mount(element); // delegate to mount
}
function Button(props){
return (
<button class="btn">{props.text}</button>
)
}
function createElement(type,props,...args){
let children = [].concat(...args);
props.children = children;
return { type, props };
}
var element = (
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">
<Button text="this is a button"/>
<Button text="this is another button"/>
hyperscript
</a>
)
var node = mount(element);
document.body.appendChild(node);