1. 概述
react-redux 类库的意义是将 redux 状态注入到组件中,且在状态更新时驱动组件重绘。在这个类库的设计和实现上,需要面临两个问题:如何将 store 中缓存的状态注入到组件中;在状态更新时,如何驱动组件重绘。
对于第一个问题,react-redux 解决手法也极为简单且常见。通过顶层 Provider 容器接受 store 作为 props,再将 store 作为 context 内容传入子孙组件;在用户端实际消费状态的组件(自定义组件)外层构造直属父级容器(HOC 高阶组件),由直属父级容器将通过 context.store 属性获取的状态数据输入为自定义组件的 props。
对于第二个问题,react-redux 解决手法是:通过 store.subscribe 方法注册状态变更后待执行的回调函数 listener,在该回调函数执行直属父级容器的 forceUpdate 或 setState 方法,重新计算注入自定义组件的 props 数据,由此重绘自定义组件。在这个过程中,无论 store 中的状态数据作何种更新,均会触发 listener 回调的执行,因而实现上有一个优化性能的关键点,即怎样使组件在指定状态更新时启用重绘机制。这一优化点通过重新计算注入自定义组件的 props 实现。在 react-redux 源码中,重新计算 props 数据由 selector 筛选器完成。除此以外,react-redux 还有另一处优化:为减少 listener 的数量,当某个 HOC 组件的重绘机制(在 redux 源码中,表现为该 HOC 组件的 onStateChange 方法)已挂载为 listener 时,其下子孙容器(同样是 HOC 组件)的重绘机制将在这个 listener 的函数体中实现。
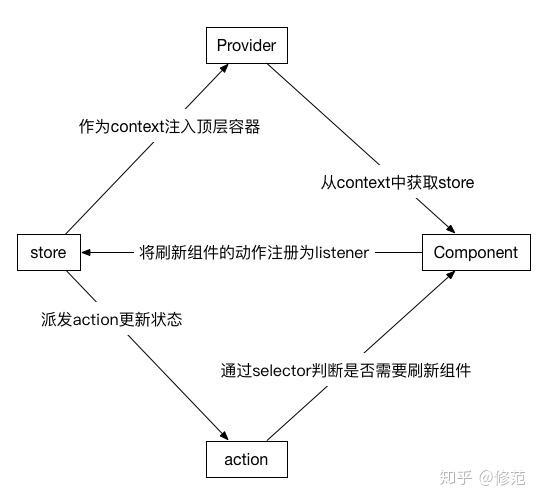
图 1 中,store, action, listener 概念来自于 redux,可参见Redux 源码分析;context 用于为子孙组件传入数据,概念来自于 react;Provider 作为顶层容器,由 react-redux 提供;Component,实际为自定义组件的直属父级容器,由 react-redux 提供;selector 是 react-redux 机制中将state、dispatch 和 boundAction 转化为自定义组件所需的 props 的筛选器。
2. selector
selector 筛选器注入组件的 props 有两种:store 中存储的状态值、驱动状态值变更的方法 boundAction(包含 store.dispatch 方法)。这两份数据分别通过用户配置项 mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps 获得,再由用户配置的 mergeProps = (stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps) => props 获取注入组件的 props(ownProps 是由父组件注入自定义组件的 props)。
主要处理流程为:
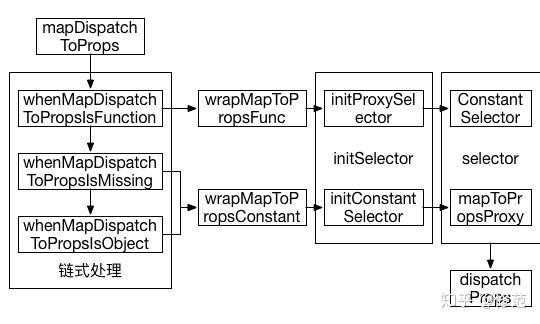
- 采用泛职责链模式处理用户配置项 mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps 的多态特征(配置项类型可能为函数、对象或 undefined),转换成 mapStateToProps = (state, ownProps) => stateProps, mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch, ownProps) => dispatchProps。链式处理参数多态的手法值得借鉴。
- mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps 经由 wrapMapToPropsConstant, wrapMapToPropsFunc 函数封装为 initSelector = (dispatch, options) => sourceSelector 函数(在源码中,initSelector 函数实际表现为 connect/wrapMapToProps 模块中的 initConstantSelector, initProxySelector 函数,作归一化处理需要)。initSelector 的参数 dispatch 由组件传入。sourceSelector 为 (stateOrDispatch, ownProps?) => props 函数形式,返回值为 stateProps, dispatchProps,参数同样由组件注入(与 dispatch 不同的是,参数 state 是动态的),用于获取 stateProps, dispatchProps。封装的意义,就是将 selector 筛选器从组件中独立出来。
- 将前两步的处理逻辑复合为 mapStateToPropsFactory = mapStateToProps => initSelector, mapDispatchToPropsFactory = mapDispatchToProps => initSelector,可在构建父级直属容器时直接使用。返回值 initSelector = (dispatch, options) => stateOrDispatchSelector 通过父级指数容器获得入参 store.dispatch,并生成 stateOrDispatchSelector = (stateOrDispatch, ownProps) => props 。stateOrDispatchSelector 用于获得注入组件的 props,在源码中实际表现为 mapStateToPropsProxy, mapdispatchToPropsSelector。
- stateOrDispatchSelector 由 selectorFctory 函数调用,并在 selectorFctory 函数体内通过 mergeProps 将 stateProps, dispatchProps 复合成待传入组件的 props(mergeProps 的多态特征也经过链式处理)。selectorFctory 函数的特殊意义是,如果 state 或 ownProps 未作更改,沿用缓存的 stateProps, dispatchProps,以提升性能。
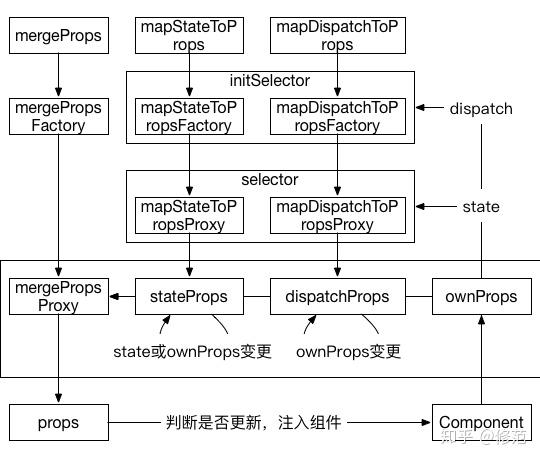
2.1. mapToPropsFactory
mapToPropsFactory 包含 mapStateToPropsFactory, mapDispatchToPropsFactory,这里只概述 mapDispatchToPropsFactory 的处理流程。mapStateToPropsFactory 实现同 mapDispatchToPropsFactory。
// connect/mapDispatchToProps
import { bindActionCreators } from 'redux'
import { wrapMapToPropsConstant, wrapMapToPropsFunc } from './wrapMapToProps'
export function whenMapDispatchToPropsIsFunction(mapDispatchToProps) {
return (typeof mapDispatchToProps === 'function')
? wrapMapToPropsFunc(mapDispatchToProps, 'mapDispatchToProps')
: undefined
}
export function whenMapDispatchToPropsIsMissing(mapDispatchToProps) {
return (!mapDispatchToProps)
? wrapMapToPropsConstant(dispatch => ({ dispatch }))
: undefined
}
export function whenMapDispatchToPropsIsObject(mapDispatchToProps) {
return (mapDispatchToProps && typeof mapDispatchToProps === 'object')
? wrapMapToPropsConstant(dispatch => bindActionCreators(mapDispatchToProps, dispatch))
: undefined
}
export default [
whenMapDispatchToPropsIsFunction,
whenMapDispatchToPropsIsMissing,
whenMapDispatchToPropsIsObject
]
// connect/wrapMapToProps
export function wrapMapToPropsConstant(getConstant) {
return function initConstantSelector(dispatch, options) {
const constant = getConstant(dispatch, options)
function constantSelector() { return constant }
constantSelector.dependsOnOwnProps = false
return constantSelector
}
}
export function wrapMapToPropsFunc(mapToProps, methodName) {
return function initProxySelector(dispatch, { displayName }) {
const proxy = function mapToPropsProxy(stateOrDispatch, ownProps) {
return proxy.dependsOnOwnProps
? proxy.mapToProps(stateOrDispatch, ownProps)
: proxy.mapToProps(stateOrDispatch)
}
proxy.dependsOnOwnProps = true
proxy.mapToProps = function detectFactoryAndVerify(stateOrDispatch, ownProps) {
proxy.mapToProps = mapToProps
// getDependsOnOwnProps 判断 mapToProps 是否依赖于父组件传入的 props
// 通过 mapToProps.dependsOnOwnProps 属性进行判断
proxy.dependsOnOwnProps = getDependsOnOwnProps(mapToProps)
let props = proxy(stateOrDispatch, ownProps)
if (typeof props === 'function') {
proxy.mapToProps = props
proxy.dependsOnOwnProps = getDependsOnOwnProps(props)
props = proxy(stateOrDispatch, ownProps)
}
return props
}
return proxy
}
}上述代码中,wrapMapToPropsFunc 函数的写法相当有趣。如果想使用 ownProps 的某个方法决定当前组件需要 store 中的哪些状态值,首先需设定 mapStateToProps.dependsOnOwnProps 为真值,其次用户配置的 mapDispatchToProps 函数须以 ownProps 的那个方法作为返回值,该返回值将构成新的 mapDispatchToProps 函数,用于计算 dispatchProps。在源码编写上,react-redux 采用在函数执行过程中改变函数指向,两次调用自身的方式实现。以 proxy 字样命名函数也值得借鉴,因为 mapToPropsProxy 函数与 mapToProps 功能相同。
2.2. mergeProps
mergeProps 处理流程可以参见上文,其意义是针对复杂的应用场景,能设置更灵活的 props 获取方式。下方代码展示的是 mergeProps 执行机制,mergePropsProxy 实现参看源码,与 mapToPropsFactory 相似。
// connect/selectorFactory
function impureFinalPropsSelectorFactory(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps,
mergeProps,
dispatch
) {
return function impureFinalPropsSelector(state, ownProps) {
return mergeProps(
mapStateToProps(state, ownProps),
mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, ownProps),
ownProps
)
}
}
function pureFinalPropsSelectorFactory(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps,
mergeProps,
dispatch,
{ areStatesEqual, areOwnPropsEqual, areStatePropsEqual }
) {
let hasRunAtLeastOnce = false
let state
let ownProps
let stateProps
let dispatchProps
let mergedProps
function handleFirstCall(firstState, firstOwnProps) {
state = firstState
ownProps = firstOwnProps
stateProps = mapStateToProps(state, ownProps)
dispatchProps = mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, ownProps)
mergedProps = mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps)
hasRunAtLeastOnce = true
return mergedProps
}
function handleNewPropsAndNewState() {
stateProps = mapStateToProps(state, ownProps)
if (mapDispatchToProps.dependsOnOwnProps)
dispatchProps = mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, ownProps)
mergedProps = mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps)
return mergedProps
}
function handleNewProps() {
if (mapStateToProps.dependsOnOwnProps)
stateProps = mapStateToProps(state, ownProps)
if (mapDispatchToProps.dependsOnOwnProps)
dispatchProps = mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, ownProps)
mergedProps = mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps)
return mergedProps
}
function handleNewState() {
const nextStateProps = mapStateToProps(state, ownProps)
const statePropsChanged = !areStatePropsEqual(nextStateProps, stateProps)
stateProps = nextStateProps
if (statePropsChanged)
mergedProps = mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps)
return mergedProps
}
function handleSubsequentCalls(nextState, nextOwnProps) {
const propsChanged = !areOwnPropsEqual(nextOwnProps, ownProps)
const stateChanged = !areStatesEqual(nextState, state)
state = nextState
ownProps = nextOwnProps
if (propsChanged && stateChanged) return handleNewPropsAndNewState()
if (propsChanged) return handleNewProps()
if (stateChanged) return handleNewState()
return mergedProps
}
return function pureFinalPropsSelector(nextState, nextOwnProps) {
return hasRunAtLeastOnce
? handleSubsequentCalls(nextState, nextOwnProps)
: handleFirstCall(nextState, nextOwnProps)
}
}
// initMapStateToProps, initMapDispatchToProps 为 _图 6_ 中的 initSelector
// 源码中实际表现为 wrapMapToProps 模块的 initProxySelector
// 通过传参 dispatch, options,获取实际可用的 mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps
function finalPropsSelectorFactory(dispatch, {
initMapStateToProps,
initMapDispatchToProps,
initMergeProps,
...options
}) {
const mapStateToProps = initMapStateToProps(dispatch, options)
const mapDispatchToProps = initMapDispatchToProps(dispatch, options)
const mergeProps = initMergeProps(dispatch, options)
const selectorFactory = options.pure
? pureFinalPropsSelectorFactory
: impureFinalPropsSelectorFactory
return selectorFactory(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps,
mergeProps,
dispatch,
options
)
}3 connect
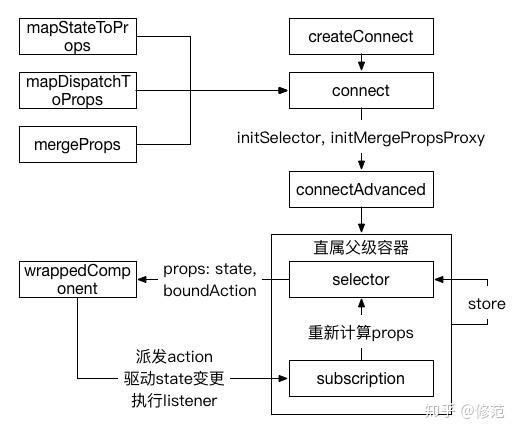
如前文所指出的,dispatch 只能通过直属父级容器获得,state 又在 listener(直属父级容器的方法)执行过程中获取,因此对于用户配置项 mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps, mergeProps,react-redux 通过 connect 函数构建直属父级容器的时候将其转变为 initSelector, mergeProps,并注入直属父级容器中。当直属父级容器获得 store.dispatch 时,initSelector, mergeProps 又会通过 selectorFactory 转变为最终的 sourceSelector = (state, ownProps) => props,用于获取注入自定义组件的 props(包含状态值以及驱动状态转变的方法)。
在上述过程中,react-redux 为了实现逻辑的灵活性,connect 通过 createConnect 函数生成,执行逻辑中所使用的 mapStateToPropsFactory, mapDispatchToPropsFactory, mergePropsFactory, selectorFactory 均为 createConnect 的入参。而 sourceSelector 又用于构建直属父级容器的 this.selector,其 run 方法用于重新计算 props,shouldComponentUpdate 属性用于判断 props 是否便能,props 属性即是注入自定义组件的 props。
当 state 状态变更时,直属父级容器的 onStateChange 方法将以 listener 回调形式被执行。在 onStateChange 方法体中,首先调用 selector.run 重新计算 props,若变更,调用直属父级容器的 setState 方法重绘自定义组件。同时,无论 props 变更与否,直属父级容器都会驱动其子孙组件父容器的 onStateChange 执行。
// connect/connect.js
// 上文 selector 内容输出的模块
import defaultMapDispatchToPropsFactories from './mapDispatchToProps'
import defaultMapStateToPropsFactories from './mapStateToProps'
import defaultMergePropsFactories from './mergeProps'
import defaultSelectorFactory from './selectorFactory'
import connectAdvanced from '../components/connectAdvanced'
import shallowEqual from '../utils/shallowEqual'
function createConnect({
connectHOC = connectAdvanced,
mapStateToPropsFactories = defaultMapStateToPropsFactories,
mapDispatchToPropsFactories = defaultMapDispatchToPropsFactories,
mergePropsFactories = defaultMergePropsFactories,
selectorFactory = defaultSelectorFactory
} = {}) {
return function connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps,
mergeProps,
{
pure = true,
areStatesEqual = strictEqual,
areOwnPropsEqual = shallowEqual,
areStatePropsEqual = shallowEqual,
areMergedPropsEqual = shallowEqual,
...extraOptions
} = {}
) {
// match 用于使用 factory 链式处理 mapToProps,以获得 initSelector = (dispatch, options) => selector
const initMapStateToProps = match(mapStateToProps, mapStateToPropsFactories, 'mapStateToProps')
const initMapDispatchToProps = match(mapDispatchToProps, mapDispatchToPropsFactories, 'mapDispatchToProps')
const initMergeProps = match(mergeProps, mergePropsFactories, 'mergeProps')
return connectHOC(selectorFactory, {
initMapStateToProps,
initMapDispatchToProps,
initMergeProps,
pure,
areStatesEqual,
areOwnPropsEqual,
areStatePropsEqual,
areMergedPropsEqual,
...extraOptions
})
}
}
// components/connectAdvanced.js
import hoistStatics from 'hoist-non-react-statics'
const dummyState = {}
function noop() {}
function makeSelectorStateful(sourceSelector, store) {
const selector = {
run: function runComponentSelector(props) {
try {
const nextProps = sourceSelector(store.getState(), props)
if (nextProps !== selector.props || selector.error) {
selector.shouldComponentUpdate = true
selector.props = nextProps
selector.error = null
}
} catch (error) {
selector.shouldComponentUpdate = true
selector.error = error
}
}
}
return selector
}
function connectAdvanced(
selectorFactory,
{
storeKey = 'store'
} = {}
) {
const subscriptionKey = storeKey + 'Subscription'
const contextTypes = {
[storeKey]: storeShape,
// 子孙容器的 onStateChange 挂载到当前父容器创建的 listener 中,用于减少 listener 的数量
[subscriptionKey]: subscriptionShape,
}
const childContextTypes = {
[subscriptionKey]: subscriptionShape,
}
return function wrapWithConnect(WrappedComponent) {
class Connect extends Component {
constructor(props, context) {
super(props, context)
this.state = {}
this.store = context[storeKey]
this.initSelector()
this.initSubscription()
}
getChildContext() {
const subscription = this.subscription
return { [subscriptionKey]: this.subscription || this.context[subscriptionKey] }
}
componentDidMount() {
this.subscription.trySubscribe()
this.selector.run(this.props)
if (this.selector.shouldComponentUpdate) this.forceUpdate()
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
this.selector.run(nextProps)
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this.subscription) this.subscription.tryUnsubscribe()
this.subscription = null
this.notifyNestedSubs = noop
this.store = null
this.selector.run = noop
this.selector.shouldComponentUpdate = false
}
initSelector() {
const sourceSelector = selectorFactory(this.store.dispatch, selectorFactoryOptions)
this.selector = makeSelectorStateful(sourceSelector, this.store)
this.selector.run(this.props)
}
initSubscription() {
const parentSub = this.context[subscriptionKey]
this.subscription = new Subscription(this.store, parentSub, this.onStateChange.bind(this))
this.notifyNestedSubs = this.subscription.notifyNestedSubs.bind(this.subscription)
}
onStateChange() {
this.selector.run(this.props)
if (!this.selector.shouldComponentUpdate) {
this.notifyNestedSubs()
} else {
this.componentDidUpdate = this.notifyNestedSubsOnComponentDidUpdate
this.setState(dummyState)
}
}
notifyNestedSubsOnComponentDidUpdate() {
this.componentDidUpdate = undefined
this.notifyNestedSubs()
}
render() {
const selector = this.selector
selector.shouldComponentUpdate = false
if (selector.error) {
throw selector.error
} else {
return createElement(WrappedComponent, selector.props)
}
}
}
Connect.childContextTypes = childContextTypes
Connect.contextTypes = contextTypes
Connect.propTypes = contextTypes
return hoistStatics(Connect, WrappedComponent)
}
}上述代码展示了直属父级容器的构建过程,其实例化过程中首先创建 selector 筛选器和 subscription 订阅器。随后,在 componentDidMount 生命周期执行过程中,将容器的 onStateChange 方法挂载为 store 的 listener 回调;调用 selector.run 方法重新计算 props,若 props 值变更,调用 forceUpdate 方法重绘组件。在 componentWillReceiveProps 生命周期中,再次调用 selector.run 方法重新计算 props,因为 ownProps 的变更可能影响注入自定义组件的 state, boundAction 数据(react-redux 为直属父级容器的 componentWillReceiveProps 和 componentDidUpdate 方法分派了不同的职能,前者驱动 ownProps, stateProps, dispatchProps 变更时自定义组件的重绘,后者驱动 stateProps, dispatchProps 变更时子孙容器的重绘。因此在 stateProps, dispatchProps 无变更的情形下,componentDidUpdate 方法将置为 undefined)。在 componentWillUnmount 生命周期里,将重置 selector 筛选器和 subscription 订阅器。
在状态值变更的情形下,容器的 onStateChange 方法将以 listener 回调形式得到执行,其将调用 selector.run 方法重新计算 props。若 props 已变更,调用 setState 方法驱动直属父级容器重绘;在自定义组件重绘完成后,通过 componentDidUpdate 生命周期方法通知子孙容器状态已更新,尝试执行其 onStateChange 方法。若 props 未作变更,直接通知子孙容器状态已更新,尝试执行其 onStateChange 方法。
3.1. subscription
subscription 用于将直属父级容器的 onStateChange 方法挂载为 store 中的 listener 回调,而子孙容器的 onStateChange 方法将存储在 subscription.listeners 数组中。当 action 被派发引起 state 变更时,直属父级容器的 onStateChange 方法自然会执行,而子孙容器的 onStateChange 方法则需要在当前直属父级容器中通过调用 subscription.notifyNestedSubs 执行(其执行时机参见上方代码,即在当前直属父级容器的 onStateChange 方法调用过程中唤起执行)。其源码如下:
const CLEARED = null
const nullListeners = { notify() {} }
function createListenerCollection() {
let current = []
let next = []
return {
clear() {
next = CLEARED
current = CLEARED
},
notify() {
const listeners = current = next
for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
listeners[i]()
}
},
get() {
return next
},
subscribe(listener) {
let isSubscribed = true
if (next === current) next = current.slice()
next.push(listener)
return function unsubscribe() {
if (!isSubscribed || current === CLEARED) return
isSubscribed = false
if (next === current) next = current.slice()
next.splice(next.indexOf(listener), 1)
}
}
}
}
export default class Subscription {
constructor(store, parentSub, onStateChange) {
this.store = store
this.parentSub = parentSub
this.onStateChange = onStateChange
this.unsubscribe = null
this.listeners = nullListeners
}
addNestedSub(listener) {
this.trySubscribe()
return this.listeners.subscribe(listener)
}
notifyNestedSubs() {
this.listeners.notify()
}
isSubscribed() {
return Boolean(this.unsubscribe)
}
trySubscribe() {
if (!this.unsubscribe) {
this.unsubscribe = this.parentSub
? this.parentSub.addNestedSub(this.onStateChange)
: this.store.subscribe(this.onStateChange)
this.listeners = createListenerCollection()
}
}
tryUnsubscribe() {
if (this.unsubscribe) {
this.unsubscribe()
this.unsubscribe = null
this.listeners.clear()
this.listeners = nullListeners
}
}
}4. 后记
俗语,”麻雀虽小,五脏俱全“,”苔米花虽小,也学牡丹开“。使用 react-redux 无非 '<Provider store={store}/>' 和 'connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Component)' 两段代码,而在 react-redux 的设计和实现上,我们又可以看见丰富的矿藏,真是”人不可貌相,海不可斗量,代码不可管窥“。