前言
本文介绍了金字塔稀疏 Transformer(PST)与 YOLOv11 的结合。主流基于注意力的特征融合方法计算复杂度高、实现难度大,作者提出 PST 模块,融合粗到细令牌选择与共享注意力参数机制,在保留空间细节的同时降低计算量。该模块通过层级化注意力机制、动态令牌选择与参数共享,实现高效多尺度特征融合
文章目录: YOLOv11改进大全:卷积层、轻量化、注意力机制、损失函数、Backbone、SPPF、Neck、检测头全方位优化汇总
专栏链接: YOLOv11改进专栏
介绍

摘要
特征融合对于高性能视觉模型至关重要,但往往会带来难以承受的复杂度。然而,主流的基于注意力的融合方法通常存在显著的计算复杂度和实现难度,这限制了它们在资源受限环境中的效率。为解决这些问题,我们提出了金字塔稀疏 Transformer(PST)—— 一种轻量级、即插即用的模块,其融合了粗到细令牌选择与共享注意力参数机制,在保留空间细节的同时降低计算量。PST 仅需通过粗注意力进行训练,且可在推理阶段无缝激活细注意力以进一步提升精度,无需重新训练。将其集成到 YOLOv11-N/S/M 等最先进的实时检测模型中时,PST 在 MS COCO 数据集上实现了 0.9%、0.5% 和 0.4% 的 mAP 提升,且对延迟的影响极小。同样地,将 PST 嵌入 ResNet-18/50/101 作为骨干网络时,分别将 ImageNet 数据集的 top-1 准确率提升了 6.5%、1.7% 和 1.0%。这些结果证明,PST 作为一种简单、硬件友好的增强模块,在检测和分类任务中均具有显著效果。相关代码已开源(链接见此处)。
文章链接
论文地址:论文地址
代码地址:代码地址
基本原理
Pyramid Sparse Transformer(PST)的核心原理是通过层级化注意力机制、动态令牌选择与参数共享,在极低计算开销下实现高效多尺度特征融合,同时保留空间细节与训练-推理灵活性。
1. 粗到细(Coarse-to-Fine)层级注意力机制
这是PST降低复杂度、保留细节的核心,分两阶段协同工作:
- 粗注意力阶段(Cross-layer Coarse Attention):用高维特征图(如1/2分辨率的U)作为Key(K)和Value(V),低维特征图(如原始分辨率的X)作为Query(Q)。通过跨层注意力计算,将令牌交互复杂度从传统自注意力的(O(N^2))降至(\frac{1}{4}O(N^2))(因高维特征图令牌数为低维的1/4)。
- 细注意力阶段(Sparse Fine Attention):基于粗注意力的Q-K相似度得分,筛选top-k个最具信息量的令牌(默认k=8)。每个选中的粗令牌对应原始低维特征图的2×2补丁,最终仅处理4k个细令牌,复杂度为(O(4Nk)),精准聚焦关键区域。
2. 跨阶段参数共享与训练-推理解耦
- 粗注意力和细注意力共享QKV卷积、MLP等核心参数,无需为细分支额外训练。
- 训练时仅激活粗注意力分支,简化训练流程、降低显存占用;推理时可灵活开启细注意力,无需重训即可获得精度提升,实现“训练简便性”与“推理高精度”的灵活切换。
3. 轻量架构与硬件友好设计
-
用1×1卷积+BatchNorm替代传统Transformer的Linear+LayerNorm层,减少参数冗余,整体参数规模等价于一个4×4卷积。
-
引入卷积位置编码(CPE):通过7×7深度卷积替代正弦/可学习位置编码,增强特征空间对齐,同时兼容GPU高效计算库(如FlashAttention、SageAttention)。
-
特征融合方式:结合CSPNet、ELAN等架构的特征聚合思路,通过元素相加+1×1卷积融合粗/细注意力输出与CPE结果,兼顾表达力与效率。
核心代码
class PST(nn.Module):
"""
Pyramid Sparse Transformer (PST) module for enhanced feature fusion with attention mechanisms.
This module integrates Pyramid Sparse Attention (PSA) blocks to fuse features from different scales,
leveraging cross-attention and dynamic token selection for efficient computation. It is designed to
enhance feature representations in tasks such as object detection and image classification.
Attributes:
cv1 (Conv): Initial 1x1 convolution layer that reduces input channels to hidden channels.
cvup (Conv): Initial 1x1 convolution layer that reduces input channels from upper-level feature to hidden channels.
cv2 (Conv): Final 1x1 convolution layer that processes concatenated features.
attnlayer_{i} (PSAttnBlock): Stacked Pyramid Sparse Attention blocks for feature fusion.
Examples:
>>> m = PST(512, 512, 256, n=1, mlp_ratio=2.0, e=0.5, k=0)
>>> x = (torch.randn(1, 512, 32, 32), torch.randn(1, 512, 16, 16))
>>> output = m(x)
>>> print(output.shape)
torch.Size([1, 256, 32, 32])
"""
def __init__(self, c1, c_up, c2, n=1, mlp_ratio=2.0, e=0.5, k=0):
"""
Initialize the Pyramid Sparse Transformer module.
Args:
c1 (int): Number of input channels.
c_up (int): Number of input channels from upper-level feature.
c2 (int): Number of output channels.
n (int): Number of PSAttnBlock modules to stack.
mlp_ratio (float): Expansion ratio for MLP hidden dimension in PSAttnBlock.
e (float): Channel expansion ratio for hidden channels.
k (int): Number of top-k tokens in fine attention, set to 0 in training phase.
"""
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # Calculate hidden channels
assert c_ % 32 == 0, "Hidden channels must be a multiple of 32."
# Initial convolutions to reduce input and upper feature channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1) # Convolution for input feature
self.cvup = Conv(c_up, c_, 1, 1) # Convolution for upper-level feature
self.cv2 = Conv((1 + n) * c_, c2, 1) # Final convolution to output channels
self.num_layers = n
for i in range(n):
# Stack PSAttnBlock modules for feature fusion
layer = PSAttnBlock(c_, c_ // 32, mlp_ratio, topk=k)
self.add_module(f"attnlayer_{i}", layer)
def forward(self, x):
"""
Forward pass through the PST module.
Processes the input feature and upper-level feature through initial convolutions,
applies stacked PSAttnBlock modules for feature fusion, and concatenates the outputs
before a final convolution to produce the output tensor.
Args:
x (tuple): Tuple containing two tensors:
- x[0] (torch.Tensor): Input feature map; shape [B, c1, H, W].
- x[1] (torch.Tensor): Upper-level feature map; shape [B, c_up, H/2, W/2].
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Output feature map after processing; shape [B, c2, H, W].
"""
# Extract input and upper-level features from tuple
upper_feat = x[1]
x = self.cv1(x[0])
# Apply initial convolution to upper-level feature
upper_feat = self.cvup(upper_feat)
# Initialize list to collect outputs from attention blocks
y = [x]
for i in range(self.num_layers):
# Retrieve and apply the i-th attention block
layer = getattr(self, f"attnlayer_{i}")
attened = layer(y[-1], upper_feat)
y.append(attened)
# Concatenate all outputs and apply final convolution
y = self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
return y
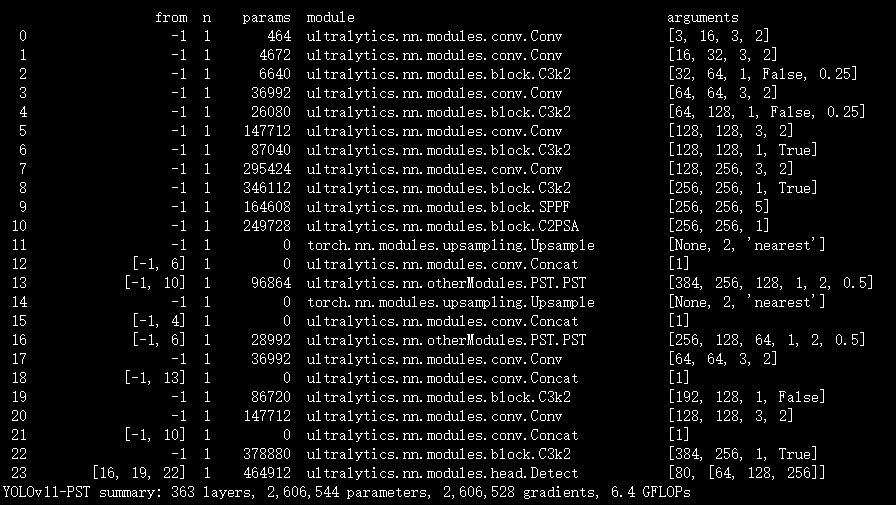
实验
脚本
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from ultralytics import YOLO
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 修改为自己的配置文件地址
model = YOLO('/root/ultralytics-main/ultralytics/cfg/models/11/yolov11-PST.yaml')
# 修改为自己的数据集地址
model.train(data='/root/ultralytics-main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco8.yaml',
cache=False,
imgsz=640,
epochs=10,
single_cls=False, # 是否是单类别检测
batch=8,
close_mosaic=10,
workers=0,
optimizer='SGD',
amp=True,
project='runs/train',
name='PST',
)
结果