学习Three.js--基于GeoJSON绘制2D矢量地图
前置核心说明
开发目标
基于Three.js实现纯矢量2D地图,核心能力包括:
- 将GeoJSON地理数据(经纬度)转换为Three.js可渲染的平面图形;
- 支持墨卡托投影(经纬度→平面坐标)、地图居中缩放适配视口;
- 实现鼠标点击省份高亮(填充+边框变色);
- 纯2D交互(仅平移/缩放,禁用旋转),模拟传统地图体验。
- 开发效果如下
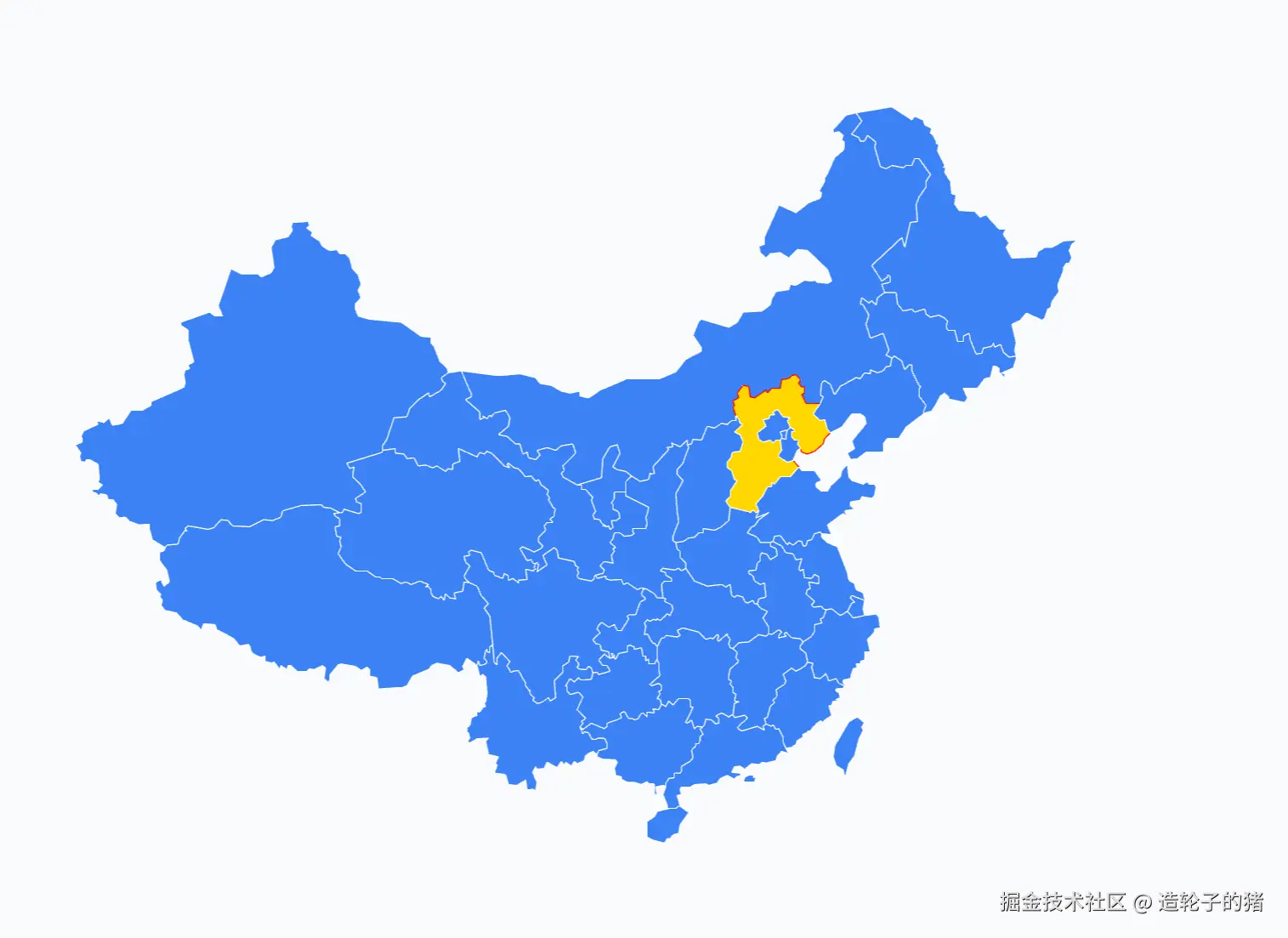
核心技术栈
| 技术点 | 作用 |
|---|
OrthographicCamera(正交相机) | 实现无透视的2D效果(无近大远小),是2D地图的核心相机类型 |
| 墨卡托投影函数 | 将地理经纬度(lon/lat)转换为平面笛卡尔坐标(x/y) |
Shape/ShapeGeometry | 将GeoJSON的多边形坐标转换为Three.js可渲染的几何形状 |
Raycaster(射线检测) | 实现鼠标点击与省份图形的交互(命中检测) |
OrbitControls(轨道控制器) | 自定义交互规则(禁用旋转,仅保留平移/缩放) |
| GeoJSON | 行业标准地理数据格式,存储省份的多边形坐标信息 |
分步开发详解
步骤1:基础环境搭建(场景/相机/渲染器/控制器)
1.1 核心代码
const provinceMeshes = [];
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.background = new THREE.Color(0xf8fafc);
const aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
const frustumSize = 800;
const camera = new THREE.OrthographicCamera(
-frustumSize * aspect / 2,
frustumSize * aspect / 2,
frustumSize / 2,
-frustumSize / 2,
1,
1000
);
camera.position.set(0, 0, 10);
camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true });
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
controls.enableRotate = false;
controls.enablePan = true;
controls.enableZoom = true;
controls.zoomSpeed = 1.5;
1.2 关键参数解析
- 正交相机参数:区别于透视相机(PerspectiveCamera),正交相机的视口是矩形,所有物体无论距离远近大小一致,完美适配2D地图;
- frustumSize:控制相机视口高度,值越大地图初始显示范围越大;
- 控制器配置:禁用旋转是2D地图的核心要求,避免视角倾斜。
步骤2:墨卡托投影函数(经纬度→平面坐标)
2.1 核心代码
function mercator(lon, lat) {
const R = 6378137;
const x = (lon * Math.PI / 180) * R;
const y = Math.log(Math.tan((90 + lat) * Math.PI / 360)) * R;
return { x, y };
}
2.2 原理说明
- 墨卡托投影是地图领域的标准投影方式,将球形地球的经纬度转换为平面矩形坐标;
- 经度(lon)范围:-180°
180°,纬度(lat)范围:-90°90°;
- 核心公式:
- 经度转换:直接将角度转为弧度后乘以地球半径;
- 纬度转换:通过正切+对数函数,解决纬度越靠近极点拉伸越大的问题。
步骤3:GeoJSON加载与全局边界计算
3.1 核心代码
let bounds = { minX: Infinity, maxX: -Infinity, minY: Infinity, maxY: -Infinity };
async function loadAndDrawMap() {
const response = await fetch('./china.json');
const geojson = await response.json();
const SPECIAL_REGION_OFFSETS = {
'香港特别行政区': { dx: 80000, dy: -60000 },
'澳门特别行政区': { dx: 100000, dy: -80000 }
};
geojson.features.forEach(feature => {
traverseCoordinates(feature.geometry.coordinates, (lon, lat) => {
const { x, y } = mercator(lon, lat);
bounds.minX = Math.min(bounds.minX, x);
bounds.maxX = Math.max(bounds.maxX, x);
bounds.minY = Math.min(bounds.minY, y);
bounds.maxY = Math.max(bounds.maxY, y);
});
});
const centerX = (bounds.minX + bounds.maxX) / 2;
const centerY = (bounds.minY + bounds.maxY) / 2;
const width = bounds.maxX - bounds.minX;
const height = bounds.maxY - bounds.minY;
const scale = 700 / Math.max(width, height);
}
function traverseCoordinates(coords, callback) {
if (typeof coords[0] === 'number') {
callback(coords[0], coords[1]);
} else {
coords.forEach(c => traverseCoordinates(c, callback));
}
}
3.2 关键逻辑解析
- 边界计算:遍历所有省份的所有坐标,得到地图的最小/最大x/y,用于后续居中;
- 港澳偏移:解决GeoJSON中港澳坐标投影后位置偏差的问题;
- 缩放比例:
700 / Math.max(width, height) 保证地图的最大维度适配视口(700为经验值,可调整);
- 递归遍历坐标:GeoJSON的
Polygon是单层数组,MultiPolygon是双层数组,需递归处理所有嵌套坐标。
步骤4:创建Shape与省份Mesh
4.1 核心代码
geojson.features.forEach(feature => {
const shapes = [];
const provinceName = feature.properties.name;
const offset = SPECIAL_REGION_OFFSETS[provinceName] || { dx: 0, dy: 0 };
if (feature.geometry.type === 'Polygon') {
const shape = createShape(feature.geometry.coordinates[0], centerX, centerY, scale, offset);
if (shape) shapes.push(shape);
}
else if (feature.geometry.type === 'MultiPolygon') {
feature.geometry.coordinates.forEach(polygon => {
const shape = createShape(polygon[0], centerX, centerY, scale, offset);
if (shape) shapes.push(shape);
});
}
shapes.forEach(shape => {
const geometry = new THREE.ShapeGeometry(shape);
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x3b82f6,
side: THREE.DoubleSide
});
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh.userData = {
provinceName: feature.properties.name,
originalColor: 0x3b82f6,
isHighlighted: false
};
scene.add(mesh);
provinceMeshes.push(mesh);
const borderGeo = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(shape.getPoints());
const borderMat = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffffff, linewidth: 2 });
const border = new THREE.Line(borderGeo, borderMat);
mesh.border = border;
scene.add(border);
});
});
function createShape(ring, centerX, centerY, scale, offset = { dx: 0, dy: 0 }) {
if (ring.length < 3) return null;
const shape = new THREE.Shape();
const points = ring.map(([lon, lat]) => {
const { x, y } = mercator(lon, lat);
const shiftedX = x + offset.dx;
const shiftedY = y + offset.dy;
return {
x: (shiftedX - centerX) * scale,
y: (shiftedY - centerY) * scale
};
});
shape.moveTo(points[0].x, points[0].y);
for (let i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
shape.lineTo(points[i].x, points[i].y);
}
return shape;
}
4.2 关键逻辑解析
- Shape创建:
THREE.Shape是Three.js的2D形状对象,通过moveTo+lineTo绘制多边形;
- MultiPolygon处理:包含多个多边形的省份(如海南=海南岛+南海诸岛),需为每个多边形创建独立Shape;
- userData绑定:Three.js的Object3D对象可通过
userData存储自定义数据,这里绑定省份名称/原始颜色,是交互的核心;
- 边框创建:通过
shape.getPoints()获取Shape的顶点,创建Line实现边框效果。
步骤5:Raycaster射线检测(鼠标点击高亮)
5.1 核心代码
let highlightedProvince = null;
window.addEventListener('click', onDocumentMouseDown, false);
function onDocumentMouseDown(event) {
const mouse = new THREE.Vector2();
mouse.x = (event.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1;
mouse.y = -(event.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1;
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster();
raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera);
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(provinceMeshes);
if (intersects.length > 0) {
const clickedMesh = intersects[0].object;
if (highlightedProvince) {
highlightedProvince.material.color.set(highlightedProvince.userData.originalColor);
if (highlightedProvince.border) {
highlightedProvince.border.material.color.set(0xffffff);
}
highlightedProvince.userData.isHighlighted = false;
}
clickedMesh.material.color.set(0xffd700);
if (clickedMesh.border) {
clickedMesh.border.material.color.set(0xff0000);
}
clickedMesh.userData.isHighlighted = true;
highlightedProvince = clickedMesh;
console.log('点击了:', clickedMesh.userData.provinceName);
} else {
if (highlightedProvince) {
highlightedProvince.material.color.set(highlightedProvince.userData.originalColor);
if (highlightedProvince.border) {
highlightedProvince.border.material.color.set(0xffffff);
}
highlightedProvince.userData.isHighlighted = false;
highlightedProvince = null;
}
}
}
5.2 射线检测核心原理
- NDC坐标转换:屏幕坐标(clientX/clientY)转换为归一化设备坐标(-1~1),是Raycaster的标准输入;
- 射线创建:
raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera) 生成从相机位置指向鼠标位置的射线;
- 相交检测:
raycaster.intersectObjects(provinceMeshes) 返回射线与Mesh的相交结果,优先返回最近的Mesh;
- 高亮逻辑:通过修改材质颜色实现高亮,利用
userData存储原始颜色,保证切换回退。
步骤6:窗口适配与渲染循环
6.1 核心代码
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
const aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
const frustumSize = 800;
camera.left = -frustumSize * aspect / 2;
camera.right = frustumSize * aspect / 2;
camera.top = frustumSize / 2;
camera.bottom = -frustumSize / 2;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
});
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
animate();
loadAndDrawMap().catch(err => console.error('加载失败:', err));
6.2 关键注意点
- 投影矩阵更新:正交相机参数修改后,必须调用
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()使修改生效;
- 渲染循环:Three.js需要持续调用
renderer.render()才能显示画面,requestAnimationFrame保证帧率稳定。
核心方法/参数速查表
1. 核心类/函数参数
| 类/函数 | 关键参数 | 说明 |
|---|
OrthographicCamera | left/right/top/bottom/near/far | 正交相机边界,near/far控制可见距离 |
mercator(lon, lat) | lon(经度)、lat(纬度) | 返回{x,y}平面坐标,R=6378137(地球半径) |
traverseCoordinates(coords, callback) | coords(GeoJSON坐标)、callback(遍历回调) | 递归处理嵌套坐标,回调参数为lon/lat |
createShape(ring, centerX, centerY, scale, offset) | ring(多边形坐标环)、centerX/Y(地图中心)、scale(缩放)、offset(偏移) | 返回THREE.Shape,实现坐标居中+缩放 |
Raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera) | mouse(NDC坐标)、camera(相机) | 创建从相机到鼠标的射线 |
2. 交互核心参数
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|
mesh.userData | 存储省份名称/原始颜色/高亮状态,交互时读取 |
intersects[0].object | 射线检测命中的第一个Mesh(最近的省份) |
controls.enableRotate | 禁用旋转(false),保证2D地图体验 |
完整优化代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Three.js 中国地图 - 2D矢量版</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
background: #f8fafc;
}
.loading {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
font-size: 18px;
color: #666;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="loading">加载地图中...</div>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from 'https://esm.sh/three@0.174.0';
import { OrbitControls } from 'https://esm.sh/three@0.174.0/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js';
const provinceMeshes = [];
let highlightedProvince = null;
let bounds = { minX: Infinity, maxX: -Infinity, minY: Infinity, maxY: -Infinity };
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.background = new THREE.Color(0xf8fafc);
const aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
const frustumSize = 800;
const camera = new THREE.OrthographicCamera(
-frustumSize * aspect / 2,
frustumSize * aspect / 2,
frustumSize / 2,
-frustumSize / 2,
1, 1000
);
camera.position.set(0, 0, 10);
camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true });
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
controls.enableRotate = false;
controls.enablePan = true;
controls.enableZoom = true;
controls.zoomSpeed = 1.5;
function mercator(lon, lat) {
const R = 6378137;
const x = (lon * Math.PI / 180) * R;
const y = Math.log(Math.tan((90 + lat) * Math.PI / 360)) * R;
return { x, y };
}
function traverseCoordinates(coords, callback) {
if (typeof coords[0] === 'number') {
callback(coords[0], coords[1]);
} else {
coords.forEach(c => traverseCoordinates(c, callback));
}
}
function createShape(ring, centerX, centerY, scale, offset = { dx: 0, dy: 0 }) {
if (ring.length < 3) return null;
const shape = new THREE.Shape();
const points = ring.map(([lon, lat]) => {
const { x, y } = mercator(lon, lat);
const shiftedX = x + offset.dx;
const shiftedY = y + offset.dy;
return {
x: (shiftedX - centerX) * scale,
y: (shiftedY - centerY) * scale
};
});
shape.moveTo(points[0].x, points[0].y);
for (let i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
shape.lineTo(points[i].x, points[i].y);
}
return shape;
}
async function loadAndDrawMap() {
try {
const response = await fetch('./china.json');
const geojson = await response.json();
const SPECIAL_REGION_OFFSETS = {
'香港特别行政区': { dx: 80000, dy: -60000 },
'澳门特别行政区': { dx: 100000, dy: -80000 }
};
geojson.features.forEach(feature => {
traverseCoordinates(feature.geometry.coordinates, (lon, lat) => {
const { x, y } = mercator(lon, lat);
bounds.minX = Math.min(bounds.minX, x);
bounds.maxX = Math.max(bounds.maxX, x);
bounds.minY = Math.min(bounds.minY, y);
bounds.maxY = Math.max(bounds.maxY, y);
});
});
const centerX = (bounds.minX + bounds.maxX) / 2;
const centerY = (bounds.minY + bounds.maxY) / 2;
const width = bounds.maxX - bounds.minX;
const height = bounds.maxY - bounds.minY;
const scale = 700 / Math.max(width, height);
geojson.features.forEach(feature => {
const shapes = [];
const provinceName = feature.properties.name;
const offset = SPECIAL_REGION_OFFSETS[provinceName] || { dx: 0, dy: 0 };
if (feature.geometry.type === 'Polygon') {
const shape = createShape(feature.geometry.coordinates[0], centerX, centerY, scale, offset);
if (shape) shapes.push(shape);
}
else if (feature.geometry.type === 'MultiPolygon') {
feature.geometry.coordinates.forEach(polygon => {
const shape = createShape(polygon[0], centerX, centerY, scale, offset);
if (shape) shapes.push(shape);
});
}
shapes.forEach(shape => {
const geometry = new THREE.ShapeGeometry(shape);
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x3b82f6,
side: THREE.DoubleSide
});
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh.userData = {
provinceName: provinceName,
originalColor: 0x3b82f6,
isHighlighted: false
};
scene.add(mesh);
provinceMeshes.push(mesh);
const borderGeo = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(shape.getPoints());
const borderMat = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffffff, linewidth: 2 });
const border = new THREE.Line(borderGeo, borderMat);
mesh.border = border;
scene.add(border);
});
});
document.querySelector('.loading').style.display = 'none';
} catch (err) {
console.error('地图加载失败:', err);
document.querySelector('.loading').textContent = '加载失败,请检查GeoJSON文件';
}
}
function onDocumentMouseDown(event) {
const mouse = new THREE.Vector2();
mouse.x = (event.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1;
mouse.y = -(event.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1;
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster();
raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera);
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(provinceMeshes);
if (intersects.length > 0) {
const clickedMesh = intersects[0].object;
if (highlightedProvince) {
highlightedProvince.material.color.set(highlightedProvince.userData.originalColor);
highlightedProvince.border.material.color.set(0xffffff);
highlightedProvince.userData.isHighlighted = false;
}
clickedMesh.material.color.set(0xffd700);
clickedMesh.border.material.color.set(0xff0000);
clickedMesh.userData.isHighlighted = true;
highlightedProvince = clickedMesh;
console.log('点击省份:', clickedMesh.userData.provinceName);
} else {
if (highlightedProvince) {
highlightedProvince.material.color.set(highlightedProvince.userData.originalColor);
highlightedProvince.border.material.color.set(0xffffff);
highlightedProvince.userData.isHighlighted = false;
highlightedProvince = null;
}
}
}
window.addEventListener('click', onDocumentMouseDown, false);
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
const aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
camera.left = -frustumSize * aspect / 2;
camera.right = frustumSize * aspect / 2;
camera.top = frustumSize / 2;
camera.bottom = -frustumSize / 2;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
});
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
animate();
loadAndDrawMap();
</script>
</body>
</html>
总结与扩展建议
核心总结
- 2D地图核心:正交相机(
OrthographicCamera)是实现无透视2D效果的关键,区别于透视相机;
- 坐标转换:墨卡托投影是地理数据可视化的基础,需掌握经纬度→平面坐标的转换逻辑;
- GeoJSON处理:递归遍历嵌套坐标、计算全局边界是地图居中缩放的核心;
- 交互实现:
Raycaster射线检测是Three.js实现鼠标点击交互的标准方式,userData是存储自定义数据的最佳实践;
- 性能优化:复用几何体/材质、减少不必要的顶点数,可提升大地图的渲染性能。
扩展建议
- 添加省份标签:基于省份中心坐标创建
CSS2DLabel,显示省份名称;
- hover高亮:监听
mousemove事件,实现鼠标悬浮高亮;
- 数据可视化:根据省份数据(如GDP、人口)动态修改填充颜色;
- 层级优化:为南海诸岛等小区域单独缩放,提升显示效果;
- 性能优化:使用
BufferGeometry替代ShapeGeometry,减少内存占用;
- 地图交互增强:添加缩放限制(最小/最大缩放)、地图复位按钮。