链表
基础知识(青铜挑战)
单链表基础及构造方法
链表的内部结构
链表,是用来存储数据的一种数据结构,其由若干个节点依次连接而成。
一个节点就是一个数据元素,一个节点由两部分构成:数据域和指针域。
数据域存放数据元素的值,指针域存放指针,而该指针用来指向下一个节点。
链表的构造
-
链表的构造过程很简单:
-
创建头节点,创建head指针指向头节点
-
依次创建每个节点,初始化其数据域,并令前驱节点的指针域指向该节点
-
链表创建完成,返回该链表的head指针
-
下面给出具体的代码实现
static class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
Node(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"val=" + val +
", next=" + next +
'}';
}
}
// 使用数组构建单链表
private static Node initLinkedList(int[] array) {
// 1.定义head指针, cur指针
Node head = null, cur = null
// 2.遍历数组, 构建单链表
for (int i = 0
// 2.1.新建节点, 依次获取数组元素, 并赋值给该节点的数据域
Node newNode = new Node(array[i])
// 2.2.链表为空, 插入头节点
if (i == 0) {
// 2.2.1.初始化head指针
head = newNode
// 2.2.2.更新cur指针, 指向新节点
cur = newNode
// 2.3.链表不为空, 插入后继节点
} else {
// 2.3.1.更新每个结点的指针域, 指向后继节点
cur.next = newNode
// 2.3.2.更新cur指针, 指向新节点
cur = newNode
}
}
// 3.单链表构建完成, 返回头指针
return head
}
// 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Node head = initLinkedList(a)
System.out.println(head)
}
遍历链表
-
打印链表:头指针依次向后移动,打印每个节点的数据域
-
获取链表长度:头指针依次向后移动,累加节点个数,打印链表长度
-
代码实现如下:
/**
* 打印链表
*
* @param head 头节点
*/
public static String toString(Node head) {
Node current = head
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder()
while (current != null) {
sb.append(current.data).append("\t")
current = current.next
}
return sb.toString()
}
/**
* 获取链表长度
*
* @param head 链表头节点
* @return 链表长度
*/
public static int getLength(Node head) {
int length = 0
Node node = head
while (node != null) {
length++
node = node.next
}
return length
}
链表插入
-
向链表中插入节点分以下三种情况:
-
表头插入:创建新节点,新节点指针域指向原头节点;head指针指向新节点
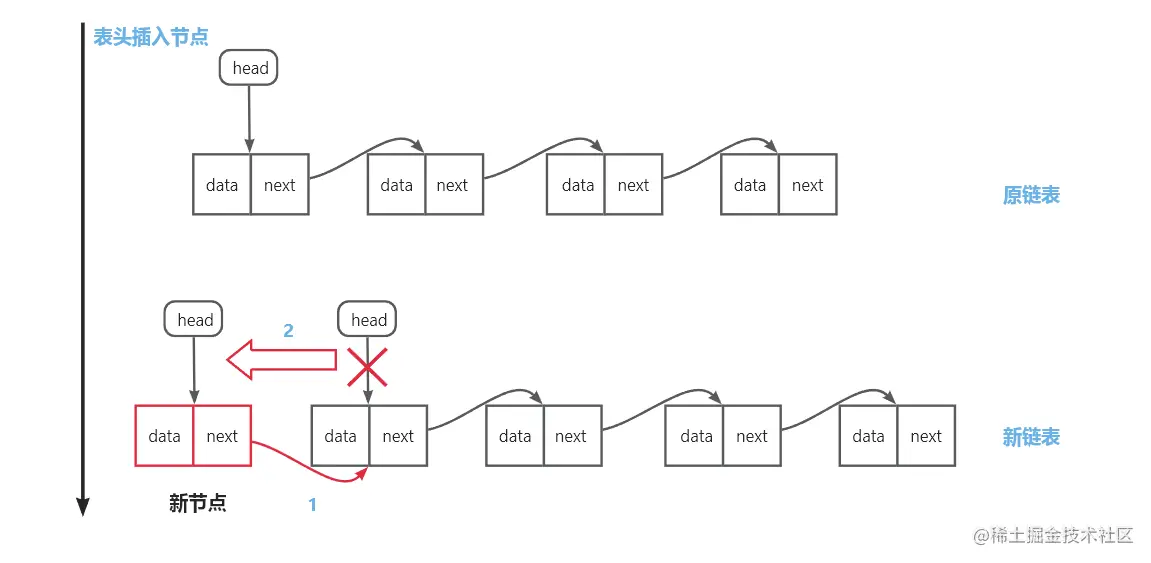
-
在表中插入:遍历到插入位置的前驱节点,依次为新节点分配后继节点和前驱节点
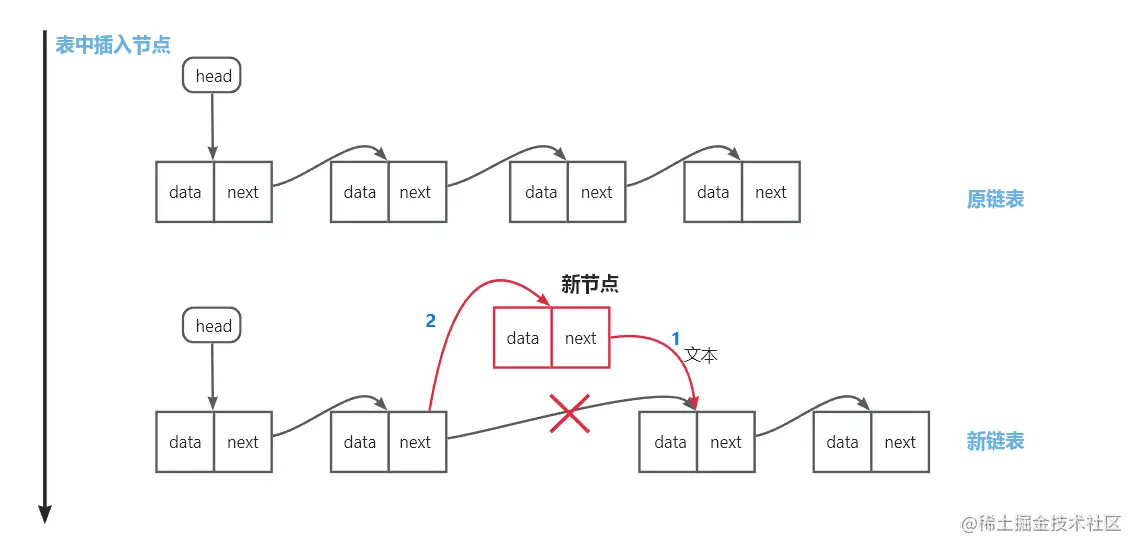
-
表尾插入:可视为 2 的特殊情况,新节点的后继节点为 NULL
-
代码设计如下:
/**
* 链表插入
*
* @param head 链表头节点
* @param nodeInsert 待插入节点
* @param position 待插入位置,取值从2开始
* @return 插入后得到的链表头节点
*/
public static Node insertNode(Node head, Node nodeInsert, int position) {
// 1.头节点判空
if (head == null) {
return nodeInsert
}
// 2.越界判断
int size = getLength(head)
if (position > size + 1 || position < 1) {
System.out.println("位置参数越界")
return head
}
// 3.表头插入
if (position == 1) {
nodeInsert.next = head
head = nodeInsert
return head
}
// 4.表中/表尾插入
Node pNode = head
int count = 1
while (count < position - 1) {
pNode = pNode.next
count++
}
nodeInsert.next = pNode.next
pNode.next = nodeInsert
// 5.插入完成, 返回头节点
return head
}
链表删除
-
删除链表节点同样分三种情况:
-
删除表头元素:head指针指向要删除节点的后继节点
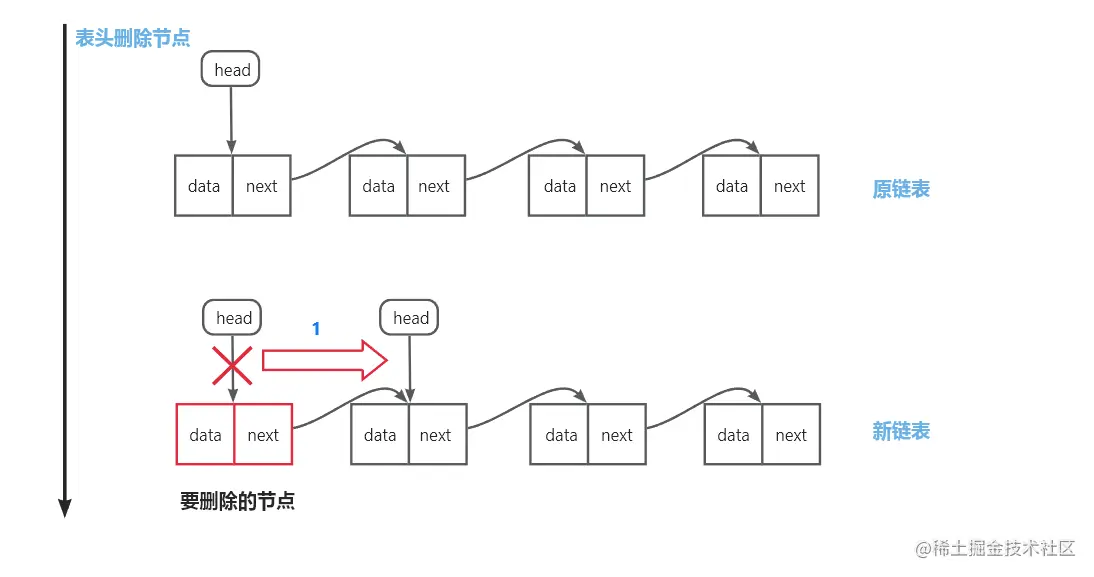
-
删除表中元素:拿到要删除节点的前驱节点的指针域,指向要删除节点的后继节点
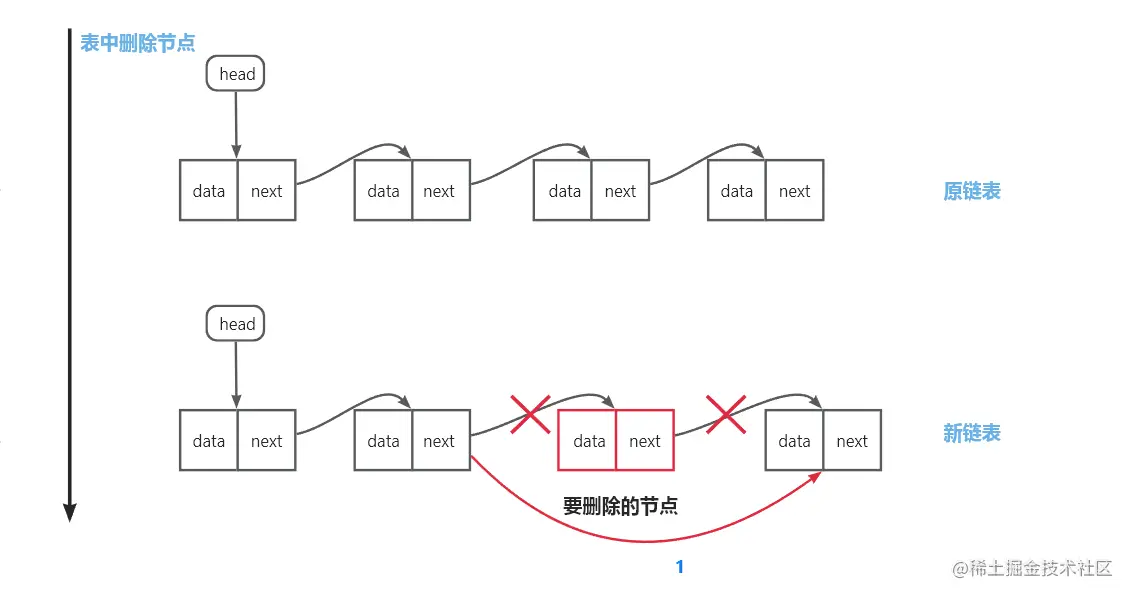
-
删除表尾元素:可视为 2 的特殊情况,要删除节点的后继节点为 NULL
-
代码设计如下:
/**
* 删除节点
*
* @param head 链表头节点
* @param position 删除节点位置,取值从1开始
* @return 删除后的链表头节点
*/
public static Node deleteNode(Node head, int position) {
// 1.头节点判空
if (head == null) {
return null
}
// 2.越界判断
int size = getLength(head)
if (position > size || position <= 0) {
System.out.println("输入的参数有误")
return head
}
// 3.表头删除
if (position == 1) {
// head.next就是链表的新head
return head.next
}
// 4.表中/表尾删除
Node preNode = head
int count = 1
while (count < position - 1) {
preNode = preNode.next
count++
}
Node curNode = preNode.next
preNode.next = curNode.next
// 5.删除成功, 返回头节点
return head
}
双向链表设计
双向链表的内部结构
双向链表与单链表的最大区别,就是每个节点增加了一个前驱指针域,指向前驱节点
链表的构造
遍历链表
-
head指针依次向后移动,遍历每个节点,输出数据域的值:
链表插入
-
向链表中插入节点分以下三种情况:
-
表头插入:新建新节点,原头节点作新节点的后继节点,新节点作为原头结点的前驱节点,head指针指向新节点
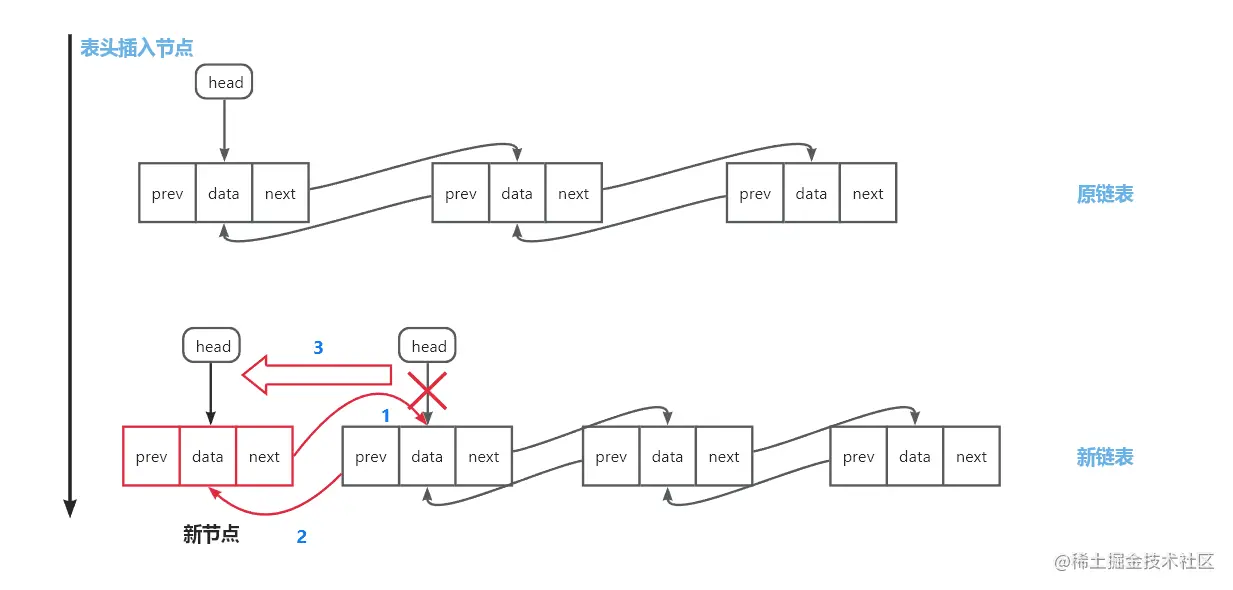
-
表尾插入:新建新节点,原尾节点作新节点的前驱节点,新节点作为头结点的后继节点,tail指针指向新节点
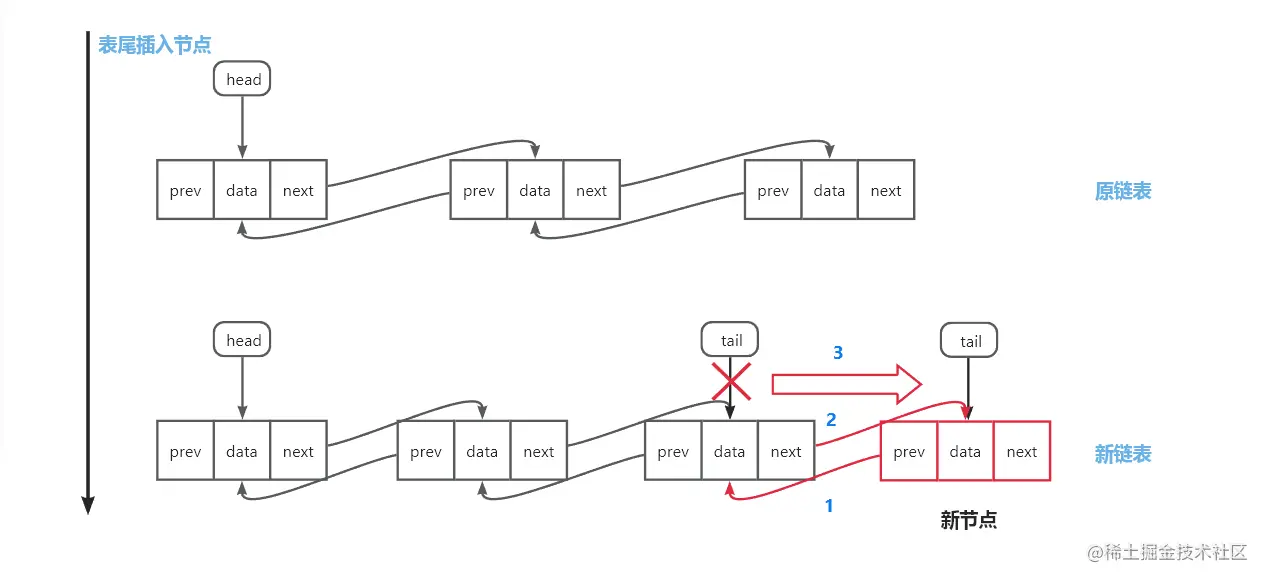
链表删除
-
删除双向链表中的节点分以下三种情况:
-
表头删除:head指针指向原头节点的后继节点,并将该后继节点的前驱指针置空
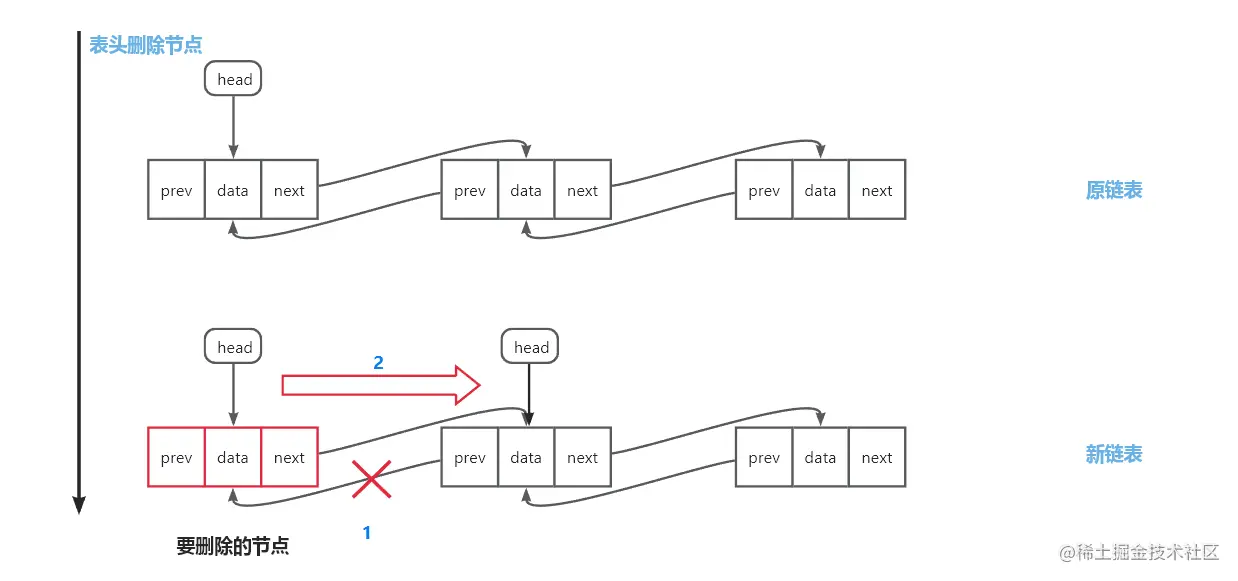
-
表尾删除:tail指针指向原尾节点的前驱节点,并将该前驱节点的后继指针置空
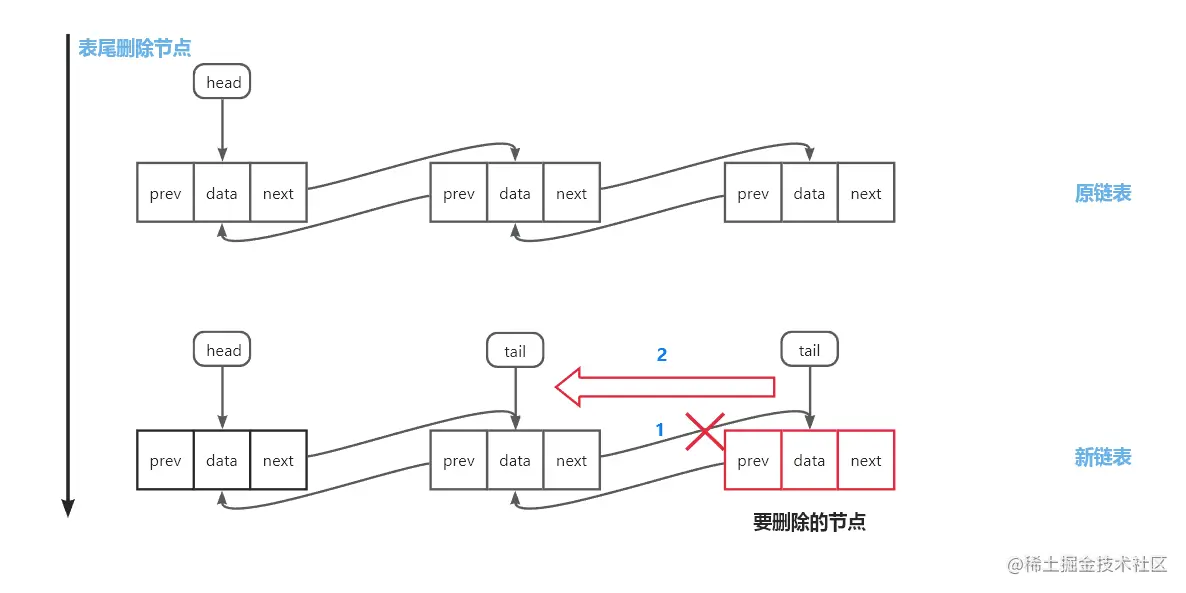
实战训练(白银挑战)
两个链表第一个公共子节点
-
前情提要:什么情况下,两条链表存在公共子节点呢?如下图所示:
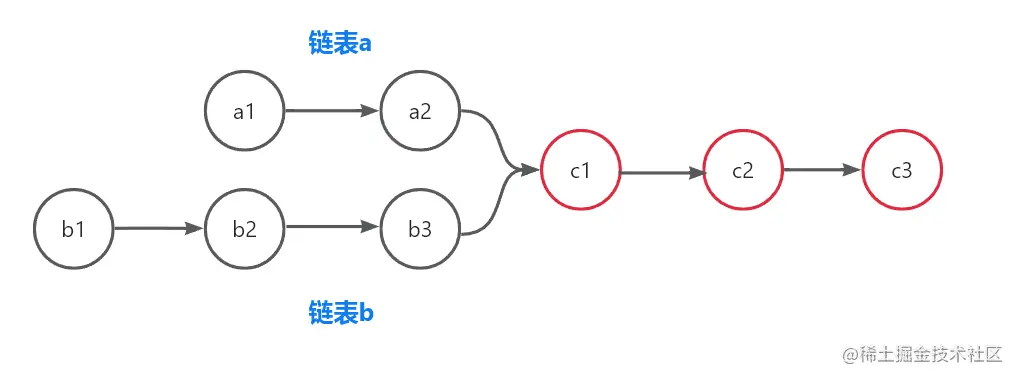
-
显而易见,c1、c2、c3均为两链表的公共子节点,且c1是两链表的第一个公共子节点
-
我们先废话少说,给出四种解题思路:
public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeByMap(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if (pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode current1 = pHead1;
ListNode current2 = pHead2;
HashMap<ListNode, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<ListNode, Integer>();
while (current1 != null) {
hashMap.put(current1, null);
current1 = current1.next;
}
while (current2 != null) {
if (hashMap.containsKey(current2))
return current2;
current2 = current2.next;
}
return null;
}
public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeBySet(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (headA != null) {
set.add(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
while (headB != null) {
if (set.contains(headB))
return headB;
headB = headB.next;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 方法3:通过栈
*/
public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeByStack(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 1.将两条链表从头节点开始, 分别压入栈中
Stack<ListNode> stackA = new Stack<>()
Stack<ListNode> stackB = new Stack<>()
while (headA != null) {
stackA.push(headA)
headA = headA.next
}
while (headB != null) {
stackB.push(headB)
headB = headB.next
}
// 2.两栈依次出栈, 当栈顶元素相同时, 保存该元素
ListNode preNode = null
while (stackB.size() > 0 && stackA.size() > 0) {
if (stackA.peek() == stackB.peek()) {
preNode = stackA.pop()
stackB.pop()
} else {
break
}
}
// 3.返回第一个公共节点
return preNode
}
public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeByCombine(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if (pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode p1 = pHead1;
ListNode p2 = pHead2;
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
if (p1 != p2) {
if (p1 == null) {
p1 = pHead2;
}
if (p2 == null) {
p2 = pHead1;
}
}
}
return p1;
}
if (p1 == null) {
...............
}
-
考虑这个问题:当前链表遍历结束后,什么情况下允许切换遍历另一条链表呢?
-
答案包括两种情况:未找到公共节点/第一次切换遍历链表结束
-
未找到公共节点很好理解,只有切换遍历另一条链表,才能判断是否有公共节点
-
/第一次切换遍历链表结束,此时p1、p2指针均为null,说明两链表就没有公共节点,我们就结束链表的遍历
-
所以结束两链表的遍历(p1 == p2)有两种情况:第一个公共节点已找到/不存在公共节点
-
差和双指针
/**
* 方法5:通过差值来实现
*
* @param pHead1 链表a
* @param pHead2 链表b
* @return
*/
public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeBySub(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
// 1.判断链表是否为空
if (pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) {
return null
}
ListNode current1 = pHead1
ListNode current2 = pHead2
int l1 = 0, l2 = 0
// 2.分别拿到两链表的长度
while (current1 != null) {
current1 = current1.next
l1++
}
while (current2 != null) {
current2 = current2.next
l2++
}
current1 = pHead1
current2 = pHead2
// 3.计算两链表长度之差
int sub = l1 > l2 ? l1 - l2 : l2 - l1
// 4.长度较大的链表先遍历, 遍历次数即为长度之差
if (l1 > l2) {
int a = 0
while (a < sub) {
current1 = current1.next
a++
}
}
if (l1 < l2) {
int a = 0
while (a < sub) {
current2 = current2.next
a++
}
}
// 5.同时遍历两链表
while (current2 != current1) {
current2 = current2.next
current1 = current1.next
}
// 6.返回第一个公共节点
return current1
}
-
上面代码里的注释,已经把解题思路解释的很清晰了
-
基于我个人的理解,下面讲解一下这些方法的共同点,也就是解题思路的形成过程:
我们的目标是:查出两条链表的第一个公共节点
公共节点是什么我们已经搞清楚了,那如何拿到第一个公共节点呢?
不论是分别正序/倒序遍历两条链表,我们的执行思路始终是:
从两链表的头节点/尾节点开始,分别依次向后遍历链表的每个节点,再比较两节点,判断它们是否相同,即是否为两链表的公共节点
我们能够判断出两链表的公共节点,那么第一个公共节点就好找了:
如果遍历顺序为正序,则选出第一组公共节点;如果遍历顺序为倒序,则选出最后一组公共节点
只需要根据正序/倒序遍历链表,选出第一组公共节点/最后一组公共节点,就找到了两链表的第一个公共节点
这里问题来了,我们要明确一点,即两链表的长度不一定相同
这就带来了问题:
我们上面查找两链表公共节点的思路,其实只有在两链表长度相同时,才行得通
那我们的目标就是,如何构造出两链表长度相同的环境:
哈希和集合:直接消除了链表长度带来的影响,通过开辟了新的空间,判断节点是否相等,进而查找出两链表的公共节点
栈、两链表拼接、差和双指针:本质上都是构造出两链表长度相同的环境,进而查找出两链表的公共节点
-
这就是查找两链表的第一个公共节点的解题思路了,希望对你有帮助
回文链表的判断
-
给出一个链表,判断其是否为回文链表,那什么是回文链表?
-
以下即为一条回文链表:
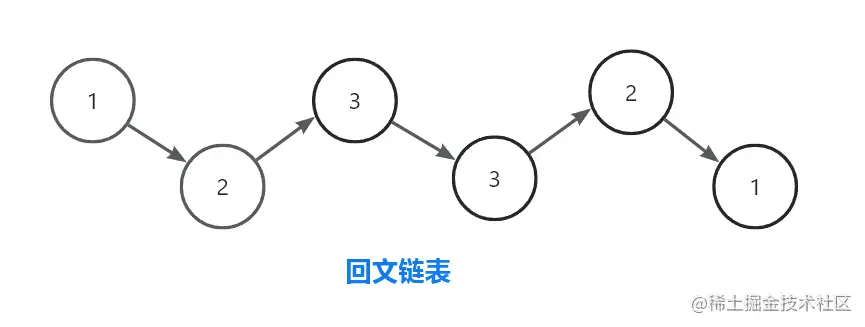
-
即对回文链表正序遍历和倒序遍历,得到的结果是一样的
-
这种题解法很多,我们列举常见的、简单的且容易理解的解法:
public static boolean isPalindromeByAllStack(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp = head;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp.val);
temp = temp.next;
}
while (head != null) {
if (head.val != stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 方法2:全部压栈遍历 一半出栈遍历
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindromeByHalfStack(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return true
ListNode temp = head
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>()
//链表的长度
int len = 0
//把链表节点的值存放到栈中
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
len++
}
//len长度除以2
len >>= 1
//然后再出栈
while (len-- >= 0) {
if (head.val != stack.pop())
return false
head = head.next
}
return true
}
-
倒序链表法,代码如下:
-
根据原链表构造一条倒序链表,遍历这两条链表,
/**
* 构造倒序链表
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static boolean isPalindromeByReverseList(ListNode head) {
// 1.构造反转链表
ListNode newHead = head, temp = head
while (temp != null) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(temp.val)
node.next = newHead
newHead = node
temp = temp.next
}
// 2.同时遍历两链表
while (newHead != null && head != null) {
if (head.val != newHead.val)
return false
head = head.next
newHead = newHead.next
}
return true
}
-
此外还有双指针法(之后双指针专题练习结束后回来补充)、递归法(不推荐掌握,容易绕晕)
合并两条有序链表
-
常见的解法就是构造第三条链表,然后依次遍历两条有序链表,比较各节点大小,依次连接到新链表中,整个过程如下图所示:
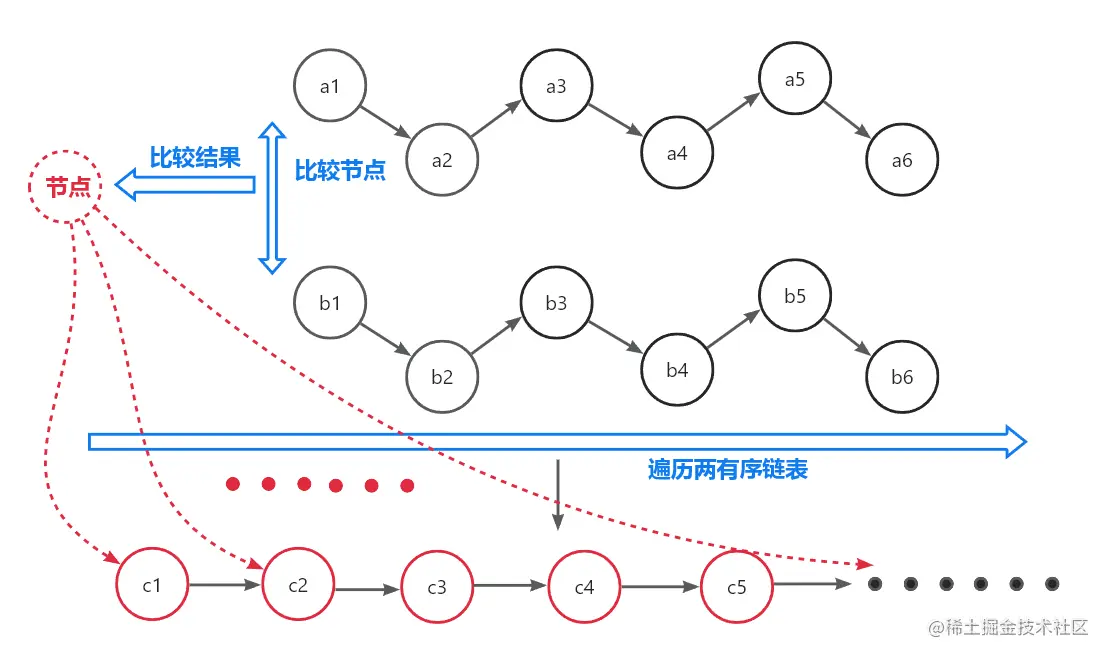
-
由于两条链表长度不一定相同,可能出现一条链表遍历完,另一条链表还没有的情况,这其实是一个优化点
-
具体代码如下:
/**
* 方法1:面试时就能写出来的方法
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// write code here
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1)
ListNode res = newHead
while (list1 != null || list2 != null) {
if (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
newHead.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
} else if (list1.val > list2.val) {
newHead.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
} else { //相等的情况,分别接两个链
newHead.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
newHead = newHead.next
newHead.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
}
newHead = newHead.next
} else if (list1 != null && list2 == null) {
newHead.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
newHead = newHead.next
} else if (list1 == null && list2 != null) {
newHead.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
newHead = newHead.next
}
}
return res.next
}
-
上面的解法当中,我们把两条链表是否都为空/只有一条为空放在了一个循环下,这次我们把它拆开来:
/**
* 思路更清晰的写法
*
* @param list1
* @param list2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists2(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// write code here
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1)
ListNode res = newHead
// 1.两链表均不为空
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
newHead.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
} else if (list1.val > list2.val) {
newHead.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
} else { //相等的情况,分别接两个链
newHead.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
newHead = newHead.next
newHead.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
}
newHead = newHead.next
}
// 2.链表a为空
while (list1 != null) {
newHead.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
newHead = newHead.next
}
// 3.链表b为空
while (list2 != null) {
newHead.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
newHead = newHead.next
}
return res.next
}
/**
* 方法2:比方法1更加精简的实现方法
*
* @param l1
* @param l2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeTwoListsMoreSimple(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1)
ListNode prev = prehead
// 节点之间的比较,简化为两种情况
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
} else {
prev.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
}
prev = prev.next
}
// 一条链表合并完成,直接拼接剩余链表的节点即可
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1
return prehead.next
}
合并K个链表
/**
* 合并K个链表
*
* @param lists
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode res = null
for (ListNode list : lists) {
res = mergeTwoListsMoreSimple(res, list)
}
return res
}
简单的合并链表
-
随便给你两条链表,你会怎么连接这两条链表?(比如:将链表b连接到链表a后面)
-
正确的思路只有一个,那就是拿到链表a的尾节点,拿到链表b的头节点,作:a.next = b,连接完成
-
举个例子:将链表a的[a,b]区间删掉,把链表b连接进去,代码如下:
/**
* 简单的合并链表
*
* @param listA
* @param a
* @param b
* @param listB
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode listA, int a, int b, ListNode listB) {
ListNode preA = listA
ListNode postA = listA
ListNode postB = listB
int i = 0, j = 0
while (postA != null && preA != null && j < b) {
// 1.拿到listA的前半段preA的尾节点
if (i < a - 1) {
preA = preA.next
i++
}
// 2.拿到listA的后半段postA的头节点
if (j != b) {
postA = postA.next
j++
}
}
// 3.分别连接preA与listB, postA与listB
while (postB.next != null) {
postB = postB.next
}
preA.next = listB
postB.next = postA
return preA
}
双指针
寻找中间节点
-
快慢指针均指向头节点
-
快指针一次跳俩步,慢指针一次跳一步,两指针同时移动
-
当快指针指向节点为空(偶数个节点)或快指针指向节点的后继节点为空(奇数个节点)时,两指针停止移动
-
此时,慢指针指向链表中间节点
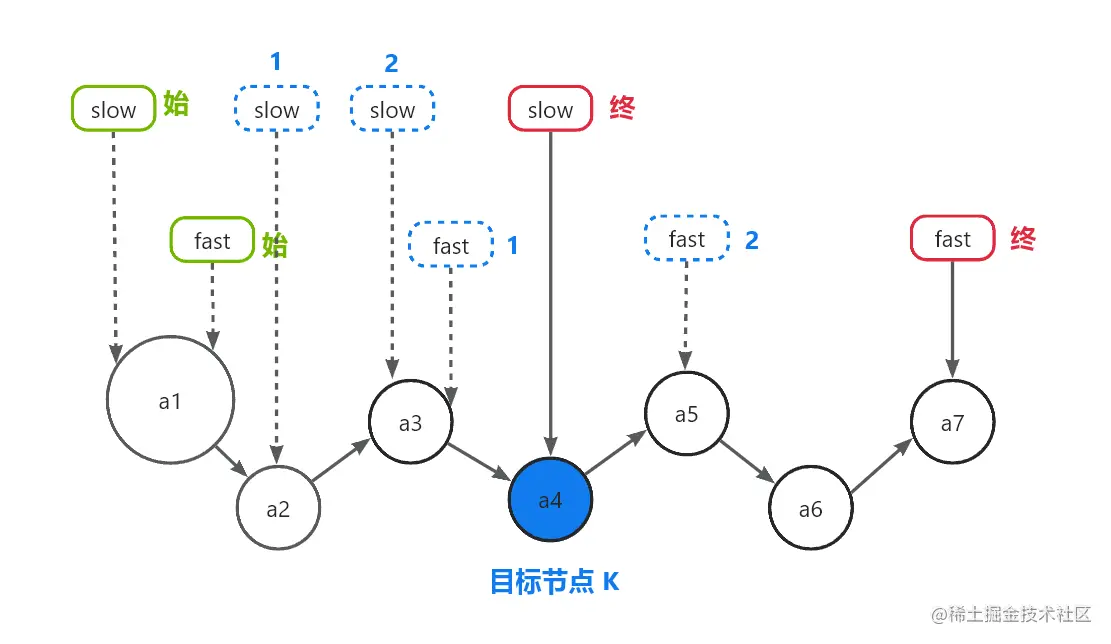
public static ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
寻找倒数第K个节点
-
快慢指针均指向头节点
-
快指针跳到第K+1个节点,此时慢指针与快指针相距K个节点
-
快慢指针同时移动,当快指针指向链表末端(即空节点)时,两指针停止移动
-
此时,慢指针指向链表的倒数第K个节点
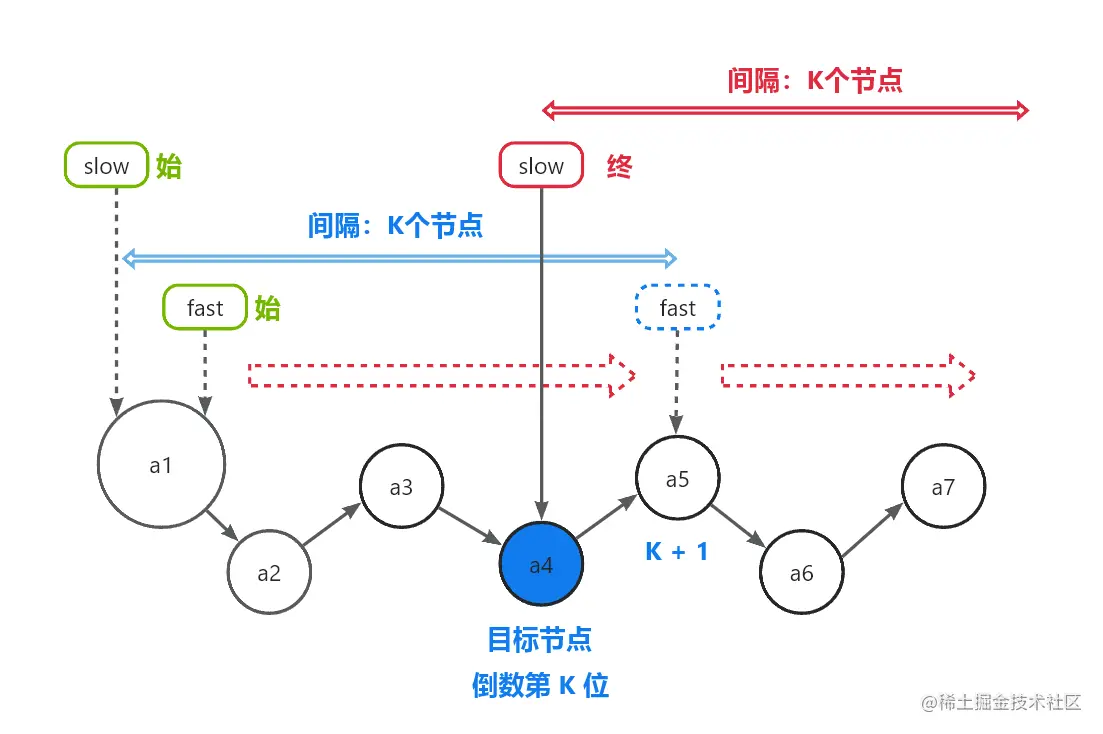
public static ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && k > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
k--;
}
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
-
寻找倒数第 K 个节点还有两种方法:遍历链表法和压栈法
-
遍历链表:先遍历一遍链表,得到链表长度 L,再遍历一遍链表,取第 L-K+1个节点
-
压栈:将链表压入栈,再出栈,取第 K 个出栈的节点
-
这两种方法很好理解,具体代码择日实现(2023/07/24晚)
旋转链表
-
常见的情景题:把链表的每个节点,都向右移动K个位置
-
这个是有两种思路的:反转链表、转化为寻找倒数第 K-1 个节点
-
反转链表暂且不表,这里可以看看第二种方法:转化为寻找倒数第 K-1 个节点
-
把链表的每个节点,都向右移动K个位置 => 把链表的后 K 个节点,都旋转成前 K 个节点
-
那就把问题转换成了:转化为寻找倒数第 K-1 个节点:
-
此时慢指针指向了倒数第 K-1 个节点,快指针指向了链表的尾节点
-
倒数第 K 个节点为头节点(断掉慢指针指向节点的后继,快指针指向原头节点)
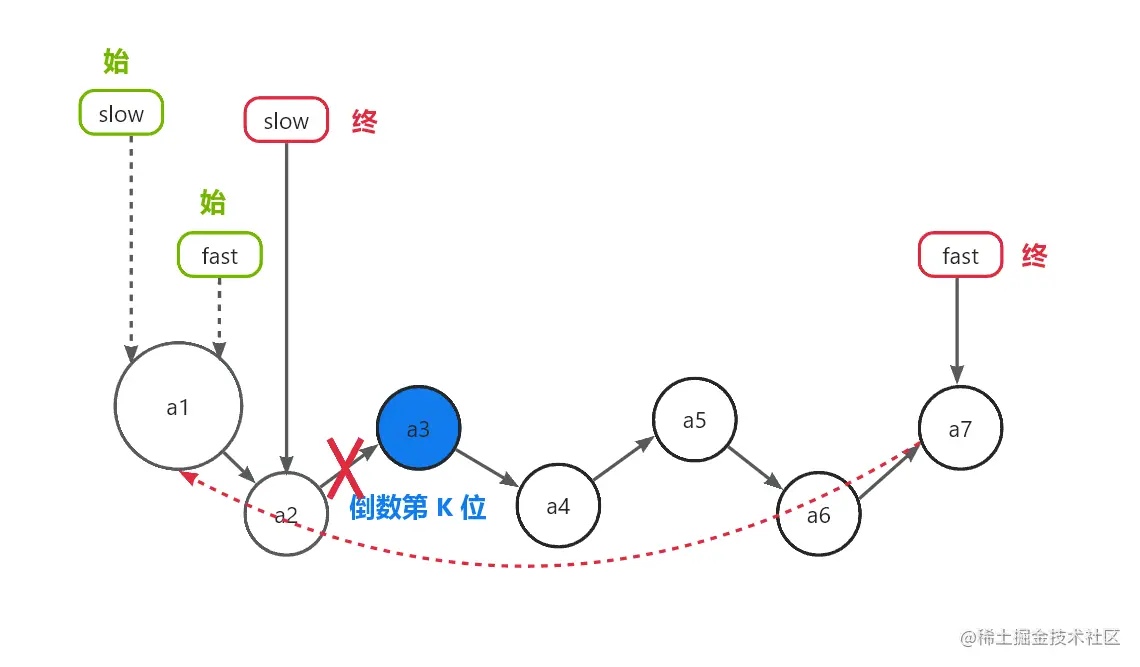
/**
* 旋转链表
*
* @param head
* @param k
* @return
*/
public static ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || k == 0) {
return head
}
// 1.快慢节点
ListNode temp = head
ListNode fast = head
ListNode slow = head
// 2.获取链表长度
int len = 0
while (head != null) {
head = head.next
len++
}
// 3.以首尾旋转
if (k % len == 0) {
return temp
}
// 4.快指针先走K步
while ((k % len) > 0) {
k--
fast = fast.next
}
// 5.快慢指针同时走
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
}
// 6.获得截断处
ListNode res = slow.next
slow.next = null
// 7.重置头节点
fast.next = temp
return res
}
删除特定节点
-
这类型题目本身不难,因为我们之前学过删除节点,但删除节点有两种情况:删除头节点和删除尾节点
-
这两种情况的处理方式是不一样的,所以我们提供一个全新的思路:创建虚拟头节点,消除被删节点可能为头节点的情况
/**
* 删除特定值的结点
*
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
public static ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 虚拟头节点
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0)
dummyHead.next = head
// 向后遍历,删除指定节点
ListNode temp = dummyHead
while (temp.next != null) {
if (temp.next.val == val) {
temp.next = temp.next.next
} else {
temp = temp.next
}
}
// 返回头节点
return dummyHead.next
}
删除倒数第K个节点
-
我们之前学过如何查找倒数第K个节点,它们本质上是一样的,我们还是提供三种思路:
-
具体代码如下:
/**
* 方法1:遍历链表法
*
* @param head
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static ListNode removeNthFromEndByLength(ListNode head, int n) {
// 虚拟头节点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
// 获取链表长度
int length = getLength(head)
ListNode cur = dummy
// 删除第L-n+1个节点
for (int i = 1
cur = cur.next
}
cur.next = cur.next.next
// 返回头节点
return dummy.next
}
/**
* 方法2:压栈法
*
* @param head
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static ListNode removeNthFromEndByStack(ListNode head, int n) {
// 虚拟头节点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
// 栈
Deque<ListNode> stack = new LinkedList<ListNode>()
// 全部压入栈
ListNode cur = dummy
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.next
}
// 依次出栈,删除第n个节点
for (int i = 0
stack.pop()
}
ListNode prev = stack.peek()
assert prev != null
prev.next = prev.next.next
// 返回头节点
return dummy.next
}
/**
* 方法3:双指针法
*
* @param head
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static ListNode removeNthFromEndByTwoPoints(ListNode head, int n) {
// 虚拟头节点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
// 快慢指针
ListNode first = head
ListNode second = dummy
// 快指针先走n步
for (int i = 0
first = first.next
}
// 快慢指针同时走
while (first != null) {
first = first.next
second = second.next
}
// 删除节点
assert second.next != null
second.next = second.next.next
return dummy.next
}
删除重复节点
-
删除重复节点当然有两种情况了:仅留一个或者删除全部,废话少说,直接上代码:
/**
* 重复元素保留一个
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static ListNode deleteDuplicate(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head
}
// 删除重复元素
ListNode cur = head
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next
} else {
cur = cur.next
}
}
// 返回头节点
return head
}
/**
* 重复元素都不要
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head
}
//虚拟节点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
ListNode cur = dummy
// 找到重复元素
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
// 删除所有重复元素
if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {
int x = cur.next.val
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == x) {
cur.next = cur.next.next
}
} else {
cur = cur.next
}
}
// 返回头节点
return dummy.next
}
通关(过关挑战)
-
题目内容:
-
算法训练营开课了,小伙伴们踊跃报名,请用链表来帮忙统计学员信息:
-
学院方向不同:Java、Python、C++,仅有一条链表,其前中后三部分,分别是:Java、Python、C++的同学
-
每种语言都会不断有学生进来,每次都要将对应的同学插入到对应的段的末尾
-
具体代码如下:(2023/07/27早)
/**
* @author 邓哈哈
* 2023/7/27 9:17
* Function:
* Version 1.0
*/
public class InsertStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode("Node 1", "Java")
ListNode node2 = new ListNode("Node 2", "Python")
ListNode node3 = new ListNode("Node 3", "C++")
// 创建节点数组并存储节点
ListNode[] nodes = new ListNode[3]
nodes[0] = node1
nodes[1] = node2
nodes[2] = node3
// 初始化链表
ListNode head = initLinkList(nodes)
ListNode node4 = new ListNode("Node 4", "Java")
ListNode node5 = new ListNode("Node 5", "C++")
ListNode node6 = new ListNode("Node 6", "Python")
ListNode node8 = new ListNode("Node 8", "C++")
ListNode node9 = new ListNode("Node 9", "Python")
ListNode node7 = new ListNode("Node 7", "Java")
// 插入学生节点
insertStudentByLanguage(node4, head)
insertStudentByLanguage(node5, head)
insertStudentByLanguage(node6, head)
insertStudentByLanguage(node7, head)
insertStudentByLanguage(node8, head)
insertStudentByLanguage(node9, head)
printLinkList(head)
}
// 插入学生节点
public static void insertStudentByLanguage(ListNode node, ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head
String language = node.language
switch (language) {
case "Java":
while (!cur.next.language.equals("Python")) {
cur = cur.next
}
node.next = cur.next
cur.next = node
break
case "Python":
while (!cur.next.language.equals("C++")) {
cur = cur.next
}
node.next = cur.next
cur.next = node
break
case "C++":
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next
}
cur.next = node
break
default:
break
}
}
// 打印链表
public static void printLinkList(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp = head
while (temp != null) {
System.out.println(temp + "--> ")
temp = temp.next
}
}
// 初始化链表
public static ListNode initLinkList(ListNode[] array) {
int i = 0
ListNode head = null, cur = null
while (i < array.length) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(array[i].name, array[i].language)
if (head == null) {
head = newNode
cur = head
} else {
cur.next = newNode
cur = newNode
}
i++
}
return head
}
// 节点结构
static class ListNode {
public String name
public String language
public ListNode next
public ListNode(String name, String language) {
this.name = name
this.language = language
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ListNode{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", language='" + language + ''' +
'}'
}
}
}