介绍
- 解决回调地狱的一种方式,可以理解为 promise 的升级版本,基于 promise
特点
- async 是一个位于 function 之前的前缀,只有 async 函数中,才能使用 await
- 在 async 函数中,await 规定了只能一个个排队执行。从而达到用同步方式,执行异步操作的效果
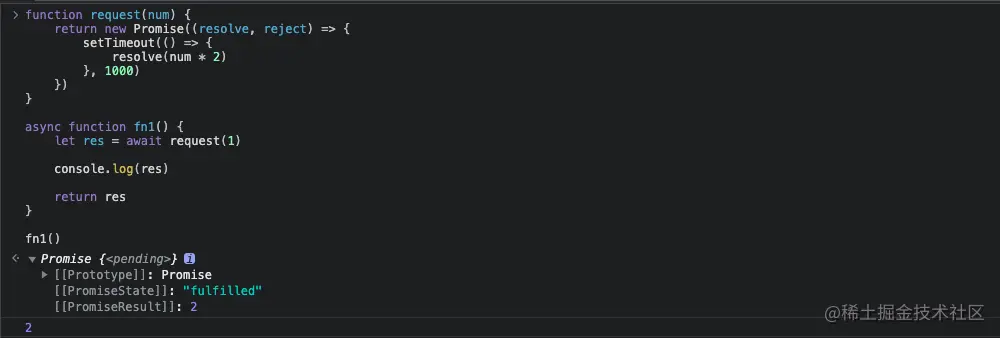
- async 函数返回的是一个 fulfilled 状态的 promise 对象,promise 对象的 PromiseResult 为 async函数的返回值
function request(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
async function fn1() {
let res = await request(1)
console.log(res)
}
fn1()
注意
- 如果 await 后面接收的不是 promise 对象,是不能够达到同步的效果的
- 所以,通常情况下,await 后面接收的都是 promise 对象。await 下面的内容,相当于 promise.then,那么我们的 promise 异常的时候,如何捕获呢?这里的异常我们建议使用 try catch 来捕获,使代码更健壮
function request(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
async function fn1() {
try {
let res = await request(1)
} catch (error) {
}
}
fn1()
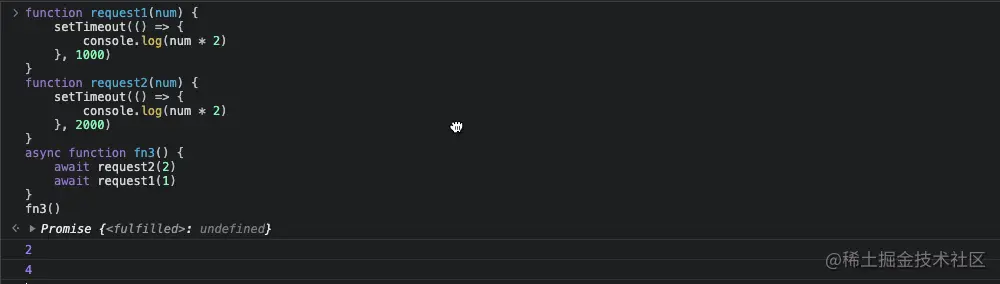
串行和并行
function sleep() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, 3000)
})
}
async function serial() {
await sleep()
await sleep()
}
serial().then(() => {
console.log("6 seconds over")
})
async function parallel() {
var a = sleep()
var b = sleep()
await a
await b
}
parallel().then(() => {
console.log("3 seconds over")
})
async / await 原理
- async / await 底层的实现原理借助了迭代函数 generator,我们先来简单介绍一下 generator 函数
generator 介绍
- generator 函数和普通函数在写法上的区别就是多了一个 * 号
- 只有在 generator 函数内才可以使用 yield 关键字
- yield 相当于 generator 函数的中途暂停点
- 使用 next 方法可以向下执行暂停点
- next 方法返回一个对象,对象中有 value 和 done 两个属性
- value:yield 后面接的值
- done:generator 函数是否已经走完,走完为 true,没走完为 false
基础示例
function* gen() {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
- 可以看到最后一个 next 方法返回的是 undefined,这个取决于 generator 函数有无返回值。下面我们将 generator 函数,添加个返回值
function* gen() {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
return 4
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
yield 后接函数
function fn(num) {
return num
}
function* gen() {
yield fn(1)
yield fn(2)
yield fn(3)
return 4
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
yield 接 promise
function fn(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num)
}, 1000)
})
}
function* gen() {
yield fn(1)
yield fn(2)
yield fn(3)
return 4
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
console.log(g.next())
- 如果想获取到 promise 的值,可以使用 promise 的 then 方法
function fn(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num)
}, 1000)
})
}
function* gen() {
yield fn(1)
yield fn(2)
yield fn(3)
return 4
}
const g = gen()
const next1 = g.next()
next1.value.then(res1 => {
console.log(next1)
console.log(res1)
const next2 = g.next()
next2.value.then(res2 => {
console.log(next2)
console.log(res2)
const next3 = g.next()
next3.value.then(res3 => {
console.log(next3)
console.log(res3)
const next4 = g.next()
console.log(next4)
})
})
})
next 函数传参
- genenator 函数可以用 next 方法来传参,可以通过 yield 来接收这个参数。并且第一次传参不生效,第二次传参的时候才会生效
function* gen() {
const num1 = yield 1
console.log(num1)
const num2 = yield 2
console.log(num2)
return 3
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next(111))
console.log(g.next(222))
console.log(g.next(333))
yield 接 promise & next 函数传参
function fn(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
function* gen() {
const num1 = yield fn(1)
const num2 = yield fn(num1)
const num3 = yield fn(num2)
return num3
}
const g = gen()
const next1 = g.next()
next1.value.then(res1 => {
console.log(next1)
console.log(res1)
const next2 = g.next(res1)
next2.value.then(res2 => {
console.log(next2)
console.log(res2)
const next3 = g.next(res2)
next3.value.then(res3 => {
console.log(next3)
console.log(res3)
const next4 = g.next(res3)
console.log(next4)
})
})
})
基于 generator 实现一个类似于 async / await 的函数
- 封装一个高阶函数,来实现同步实现异步操作的功能。什么是高阶函数,参数和返回值都是函数的函数,就是高阶函数
function genenatorToAsync(genenatorFn) {
return function () {
}
}
- 根据我们上面所说的,async 函数的返回值是一个 promise
function genenatorToAsync(genenatorFn) {
return function () {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
})
}
}
function* gen() {
}
function genenatorToAsync(genenatorFn) {
return function () {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
})
}
}
const asyncFn = genenatorToAsync(gen)
console.log(asyncFn)
- 将我们之前 yield 接 promise & next 函数传参 的例子,结合到我们上述的代码中
function fn(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
function* gen() {
const num1 = yield fn(1)
const num2 = yield fn(num1)
const num3 = yield fn(num2)
return num3
}
function genenatorToAsync(genenatorFn) {
return function () {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const g = genenatorFn()
const next1 = g.next()
next1.value.then(res1 => {
const next2 = g.next(res1)
next2.value.then(res2 => {
const next3 = g.next(res2)
next3.value.then(res3 => {
const next4 = g.next(res3)
resolve(next4.value)
})
})
})
})
}
}
const asyncFn = genenatorToAsync(gen)
asyncFn().then(res => console.log(res))
- 到这里,对照下方代码,我们发现已经实现了 async / await 的初始功能了
function fn(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
async function asyncFn() {
const num1 = await fn(1)
const num2 = await fn(num1)
const num3 = await fn(num2)
return num3
}
asyncFn().then(res => console.log(res))
- 那么问题来了,如果我们存在多个 await 该如何处理我们的 generatorToAsync 函数呢?
function fn(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
function* gen() {
const num1 = yield fn(1)
const num2 = yield fn(num1)
const num3 = yield fn(num2)
const num4 = yield fn(num3)
const num5 = yield fn(num4)
const num6 = yield fn(num5)
return num6
}
function genenatorToAsync(genenatorFn) {
return function () {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const g = genenatorFn()
function go(key, arg) {
let res = null
try {
res = g[key](arg)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
return
}
const { value, done } = res
if (done) {
resolve(value)
} else {
return Promise.resolve(value).then(val => go('next', val), err => go('throw', err))
}
}
go('next')
})
}
}
const asyncFn = genenatorToAsync(gen)
asyncFn().then(res => console.log(res))
function fn(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
async function gen() {
const num1 = await fn(1)
const num2 = await fn(num1)
const num3 = await fn(num2)
const num4 = await fn(num3)
const num5 = await fn(num4)
const num6 = await fn(num5)
return num6
}
gen().then(res => console.log(res))
- 这样我们就实现了一个类似于 async / await 功能的函数