字节跳动青训营的掘金官号在第五届青训营开营前发布了一些练习题。在本届练习题发布前,可以先用作练练手。
编程题
编程题 1: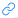 code.juejin.cn
code.juejin.cn
思路:
参考:zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/353841876
是LC415 大数相加的拓展
code
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {
int carry = 0;
int i = num1.size() - 1, j = num2.size() - 1;
string res;
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry) {
int x = i >= 0 ? num1[i] - '0' : 0;
int y = j >= 0 ? num2[j] - '0' : 0;
int temp = x + y + carry;
res += '0' + temp % 10;
carry = temp / 10;
i--, j--;
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
char getChar(int n) {
if (n < 10)
return n + '0';
else
return n - 10 + 'a';
}
int getInt(char ch) {
if(isdigit(ch))
return ch - '0';
else
return ch - 'a' + 10;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
string num1;
string num2;
cin >> num1 >> num2;
int carry = 0;
string res;
int i = num1.size() - 1;
int j = num2.size() - 1;
while(i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry) {
int x = i >= 0 ? getInt(num1[i]) : 0;
int y = j >= 0 ? getInt(num2[j]) : 0;
int tmp = x + y + carry;
res += getChar(tmp % 36);
carry = tmp / 36;
i--; j--;
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
编程题 2: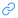 code.juejin.cn\
code.juejin.cn\
思路
图遍历模板题,用BFS或者DFS都可以。
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = {1,0, 0,1, -1,0, 0,-1};
int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& vec, const vector<int>& cur) {
int n = vec.size();
int m = vec[0].size();
vec[cur[0]][cur[1]] = 1;
int cnt = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int nextx = cur[0] + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cur[1] + dir[i][1];
if(nextx < 0 || nextx >= n ||
nexty < 0 || nexty >= m ||
vec[nextx][nexty] != 0)
{
continue;
}
cnt += dfs(vec, vector<int>{nextx, nexty});
}
return cnt;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
vector<vector<int>> vec{{1,0,0,1,0,0,0}, {1,0,0,0,0,1,1}, {0,0,0,1,0,0,0}, {1,1,0,1,1,0,0}};
int n = vec.size();
int m = vec[0].size();
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if(vec[i][j] == 0)
res = max(dfs(vec, vector<int>{i,j}), res);
}
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
编程题 3: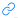 code.juejin.cn
code.juejin.cn
思路
经典的回溯算法问题,leetcode原题: LC93.复原IP地址
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<string> res;
string path;
bool isValid(const string& seg) {
if(stoi(seg) > 255)
return false;
if(seg.size() > 1 && seg[0] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
void backTracing(string& src, int n, int start) {
if(n == 4) {
if(isValid((src.substr(start, src.size()-start)))) {
path += src.substr(start, src.size()-start);
cout << path << endl
path.erase(path.begin()+start+3, path.end());
}
return ;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i) {
string tmp = src.substr(start, i);
if(!isValid(tmp) || src.size()-(start+i)>3*(4-n)) continue;
path += tmp + '.';
backTracing(src, n+1, start+i);
path.erase(path.end()-i-1, path.end());
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
string src;
cin >> src;
backTracing(src, 1, 0);
return 0;
}
语言与计算机基础
选择题 1:
Client 在使用 Https 协议访问网站进行通信的过程中,以下说法正确的是?
A. 只用到了对称加密技术
B. 只用到了非对称加密技术
C. 没有用到任何加密技术
D. 同时用到了对称加密和非对称加密技术
答:选D
选择题 2:
以下哪些是操作系统中堆和栈的区别?
A. 增长方向
B. 空间大小
C. 分配方式
D. 管理方式
答:选ABCD。
增长方向不同:对于堆来讲,生长方向是向上的,也就是向着内存地址增加的方向;对于栈来讲,它的生长方式是向下的,是向着内存地址减小的方向增长。
空间大小不同。堆的大小远远大于栈的大小
分配方式不同:堆都是动态分配的;栈有静态和动态两种分配方式。静态分配由编译器完成,比如局部变量的分配。动态分配由alloca函数进行、但栈的动态分配和堆是不同的,它的动态分配由编译器进行释放,无需我们手工实现。
管理方式不同:栈由操作系统自动分配释放,无需我们手动控制;堆的申请和释放工作由程序员控制,容易产生内存泄漏