一、链表的访问问题
1. 环形链表
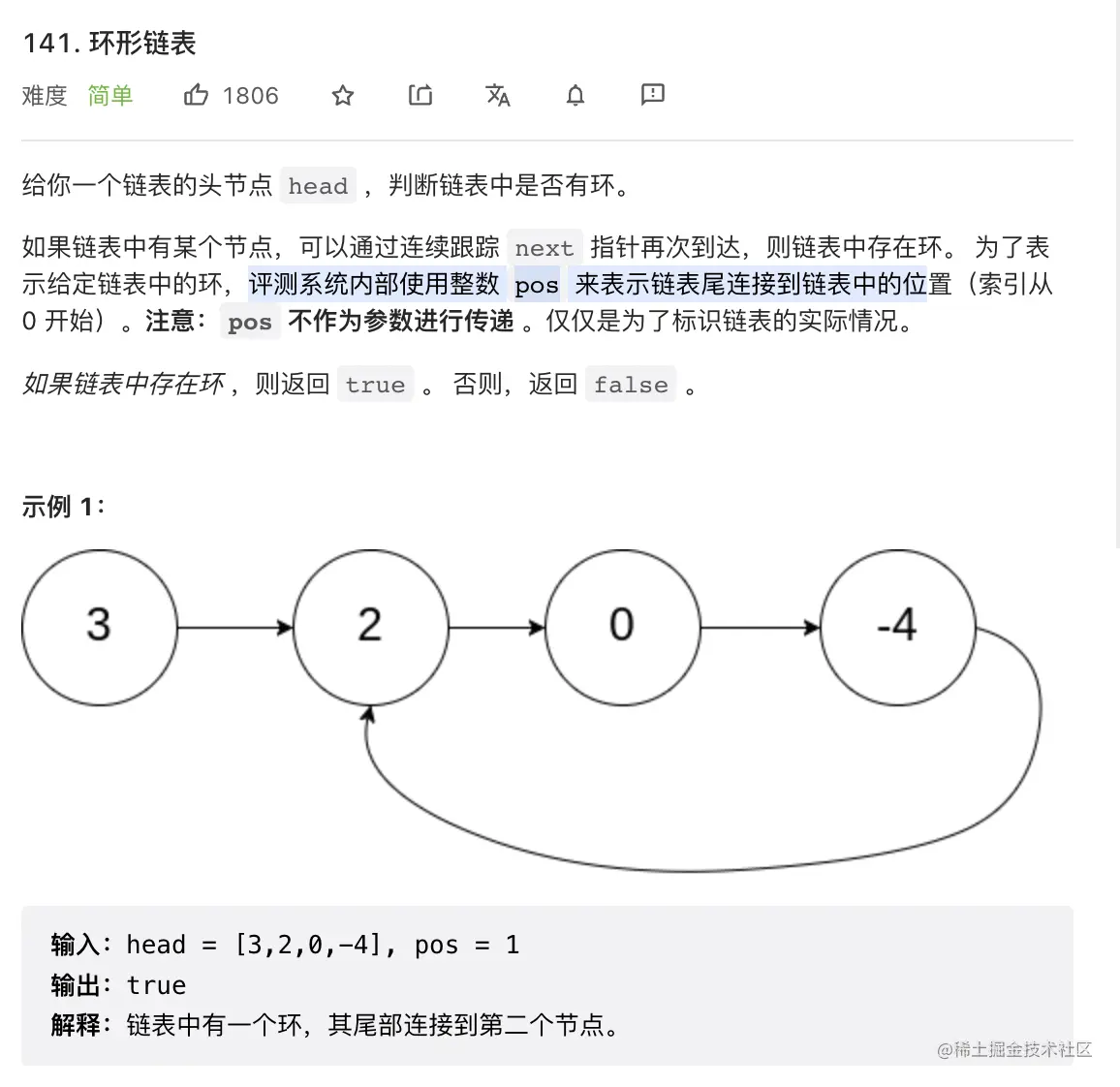
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode quick = head;
while (quick != null && quick.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next.next;
if (slow == quick) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
2. 环形链表II
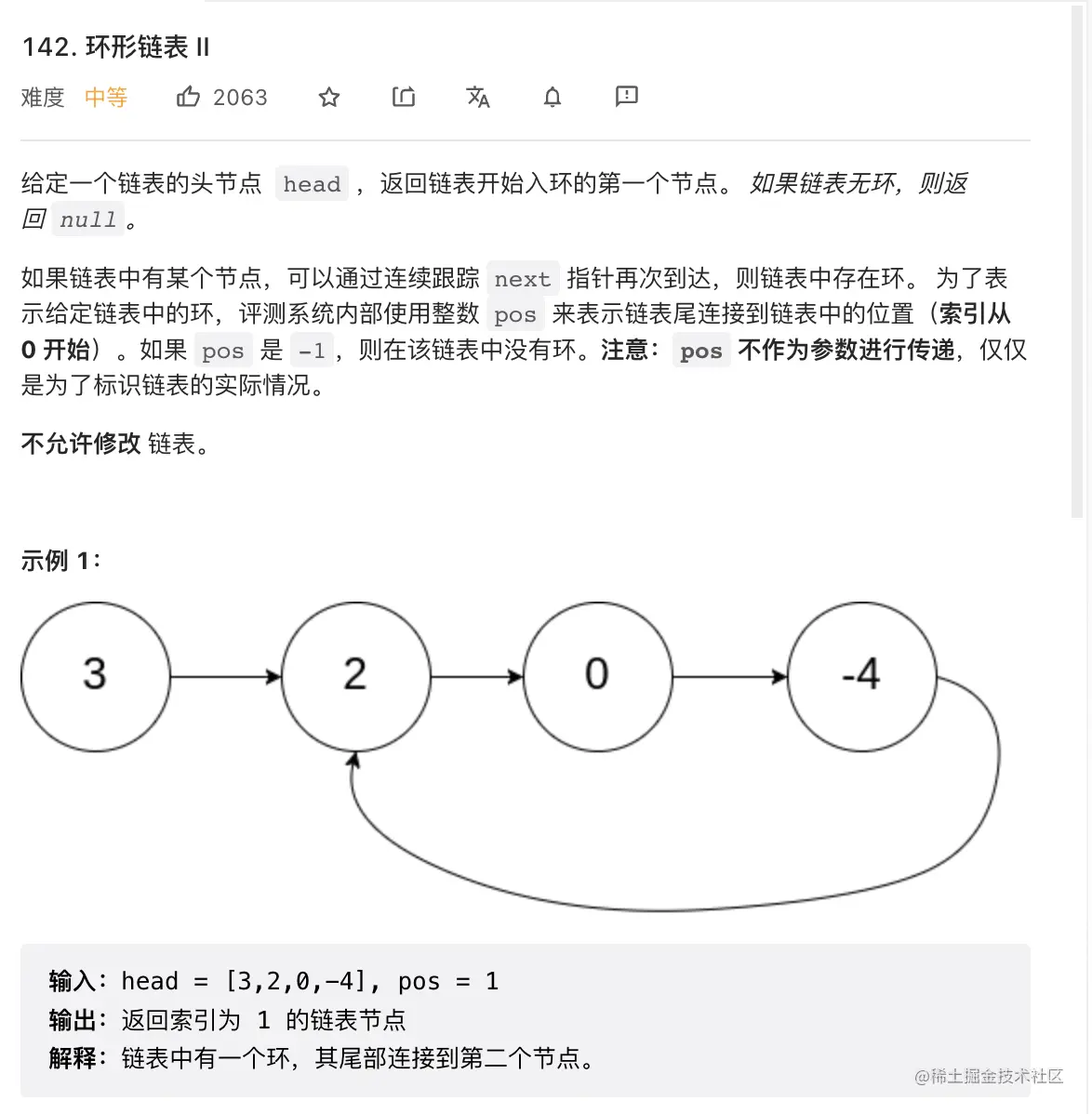
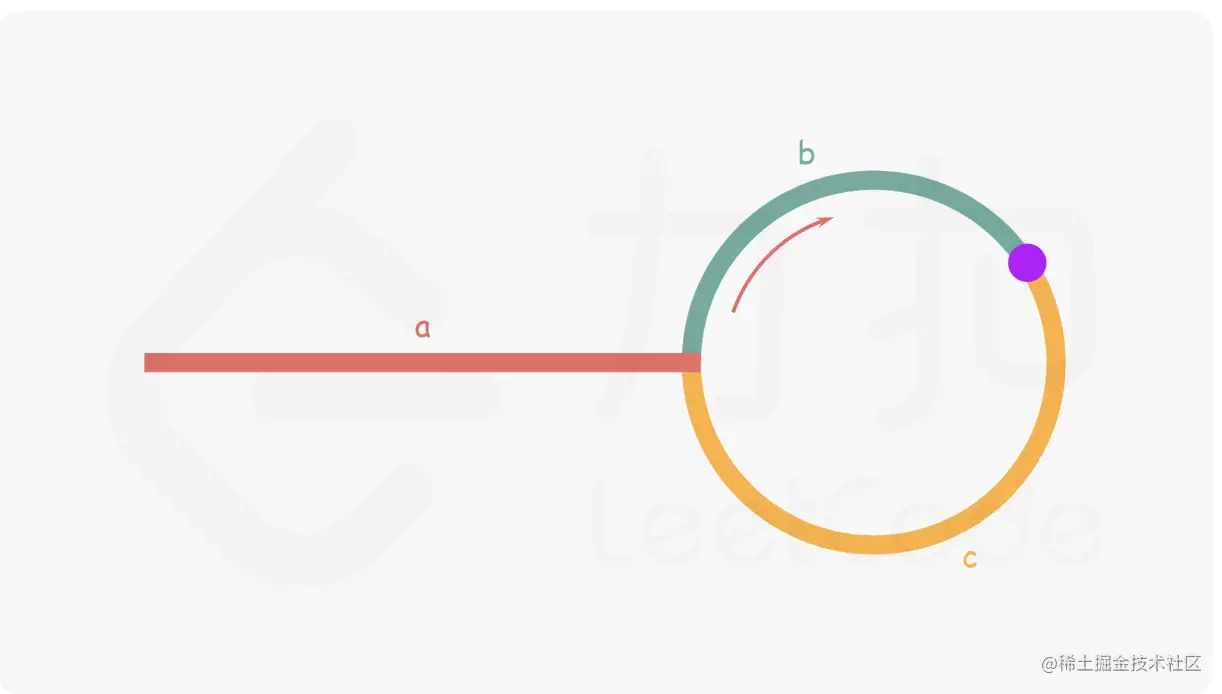
定理: 任意时间快指针的路程都是慢指针路程的2倍
分析: 快慢指针相遇时的路程关系
2 * (a + b) = a + b + n*(b+c)
a = c + (n-1) *(b+c)
所以: 从相遇点和head位置出发的两个节点,将来会在入环处相遇
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode quick = head;
while (quick != null && quick.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next.next;
if (slow == quick) {
while (slow != head) {
slow = slow.next;
head = head.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
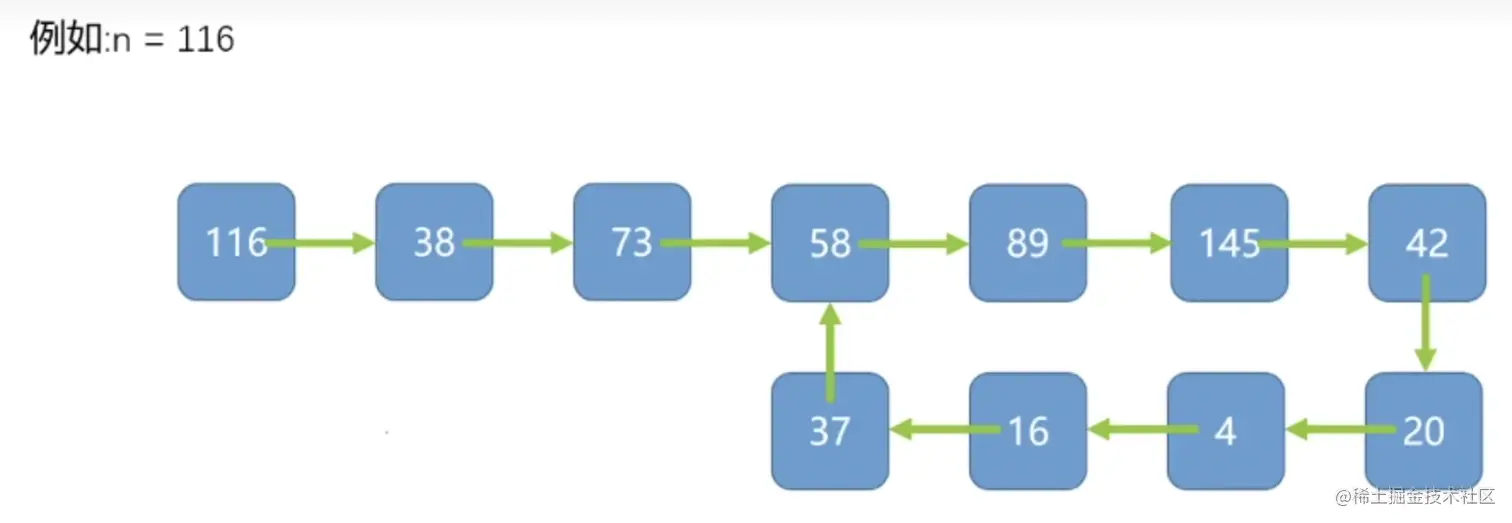
3. 快乐数
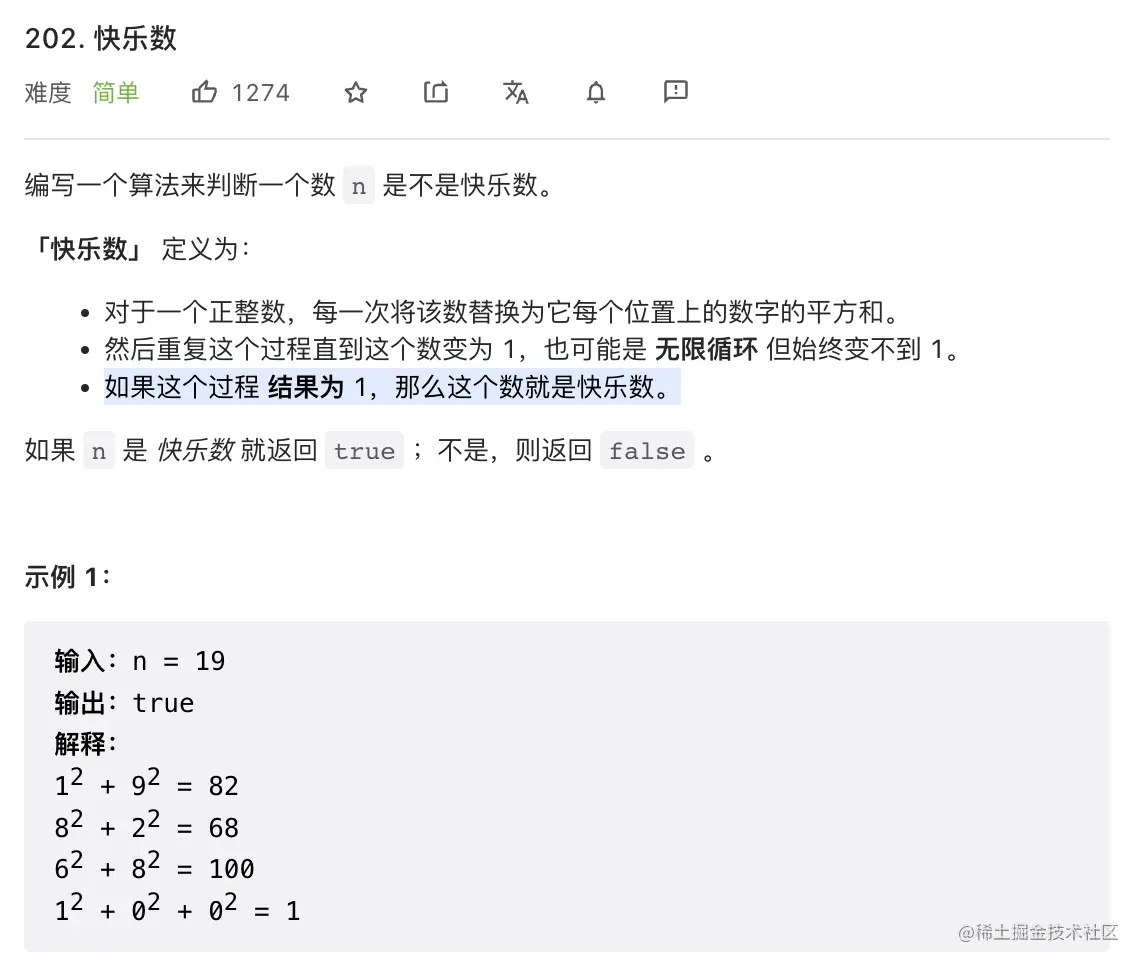
什么情况下能够判断他不是一个快乐数呢,总不能一直循环吧。
其实很简单,一张图就可以说明,就是说这个遍历成环了
解题重点: 将快乐数问题映射成链表是否有环问题
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
int slow = n;
int fast = n;
while( fast != 1 && getNext(fast) != 1){
slow = getNext(slow);
fast = getNext(getNext(fast));
if(slow == fast){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public int getNext(int n){
int sum = 0;
while(n!=0){
int mod = n%10;
sum += mod*mod;
n = n/10;
}
return sum;
}
}
二、链表的节点删除问题
4. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
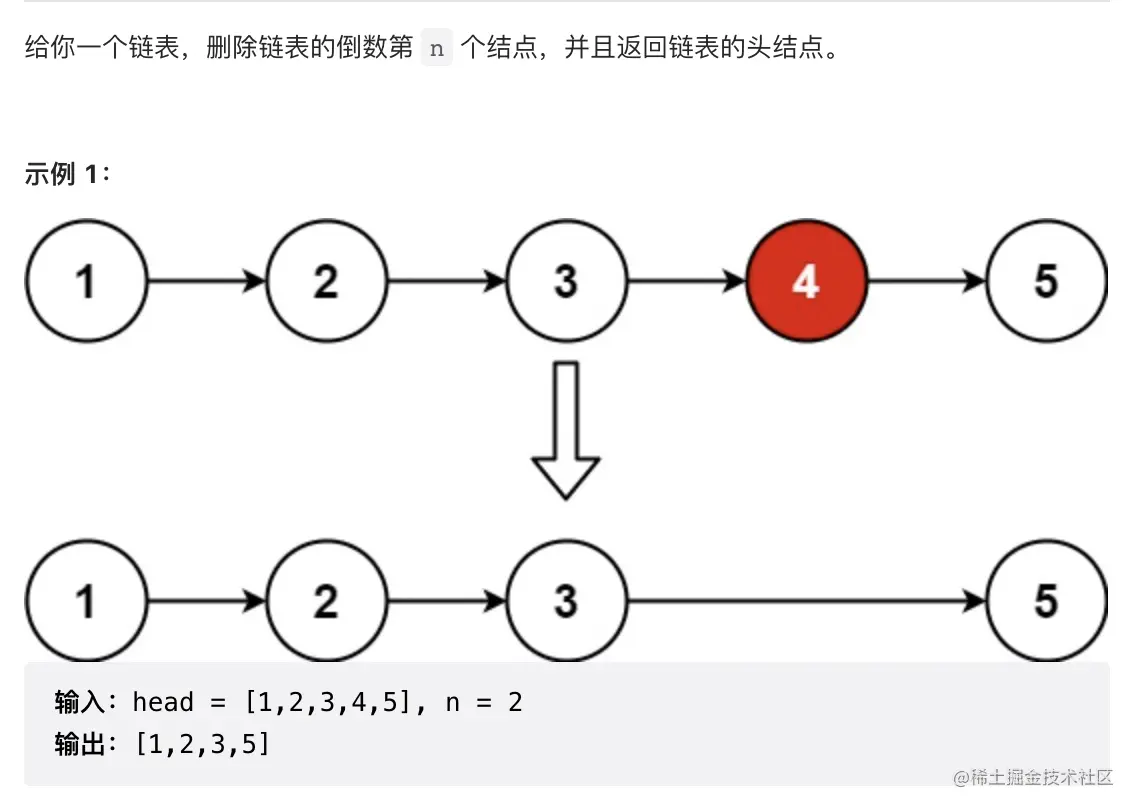
删除链表的倒数第N个结点 = 删除链表的倒数第N-1个结点的下一个结点
问题: 如果只有一个头结点呢?删除后如何返回null.
方案: 通常都会增加一个虚拟头结点来实现
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode virHead = new ListNode();
virHead.next = head;
ListNode p = virHead;
ListNode q = head;
while (n != 0 && q != null) {
n--;
q = q.next;
}
while (q != null) {
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
}
p.next = p.next.next;
return virHead.next;
}
}
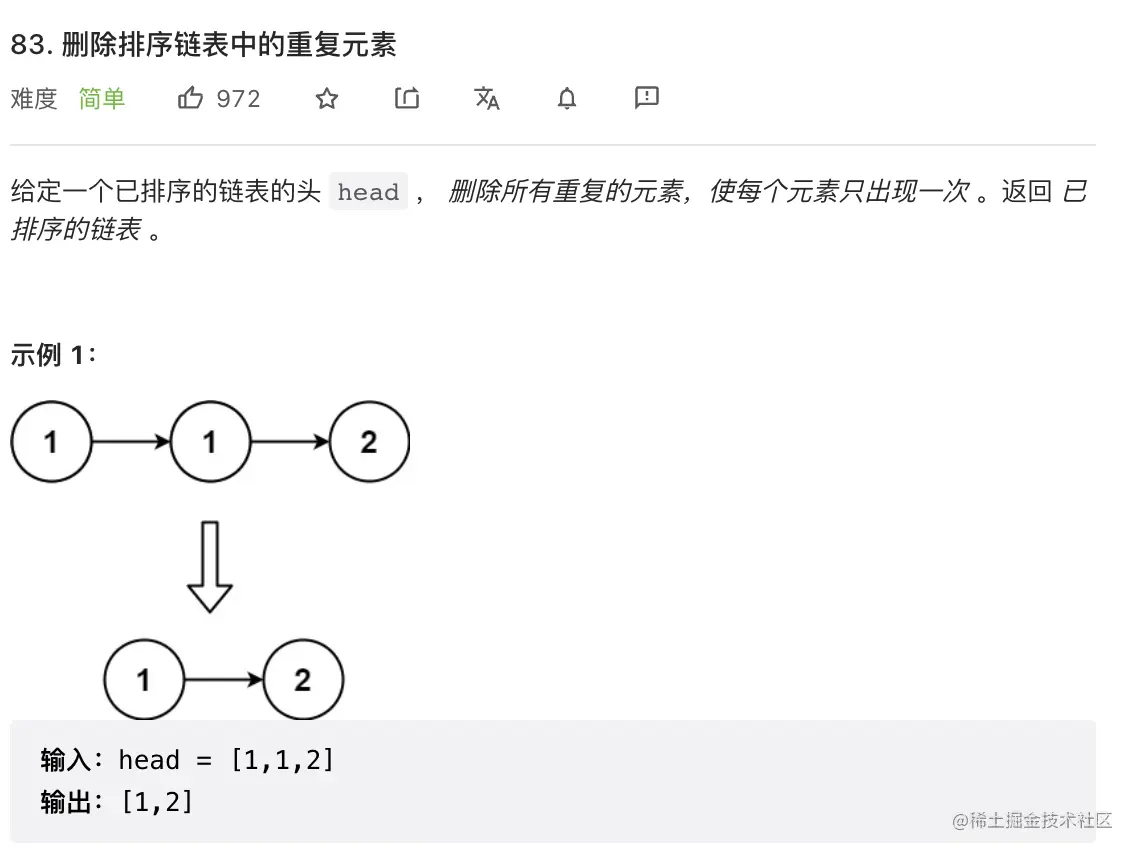
5. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode p = head;
ListNode q = head;
while(q!=null){
while(q != null && p.val == q.val){
q = q.next;
}
p.next = q;
p=q;
}
return head;
}
}
6. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
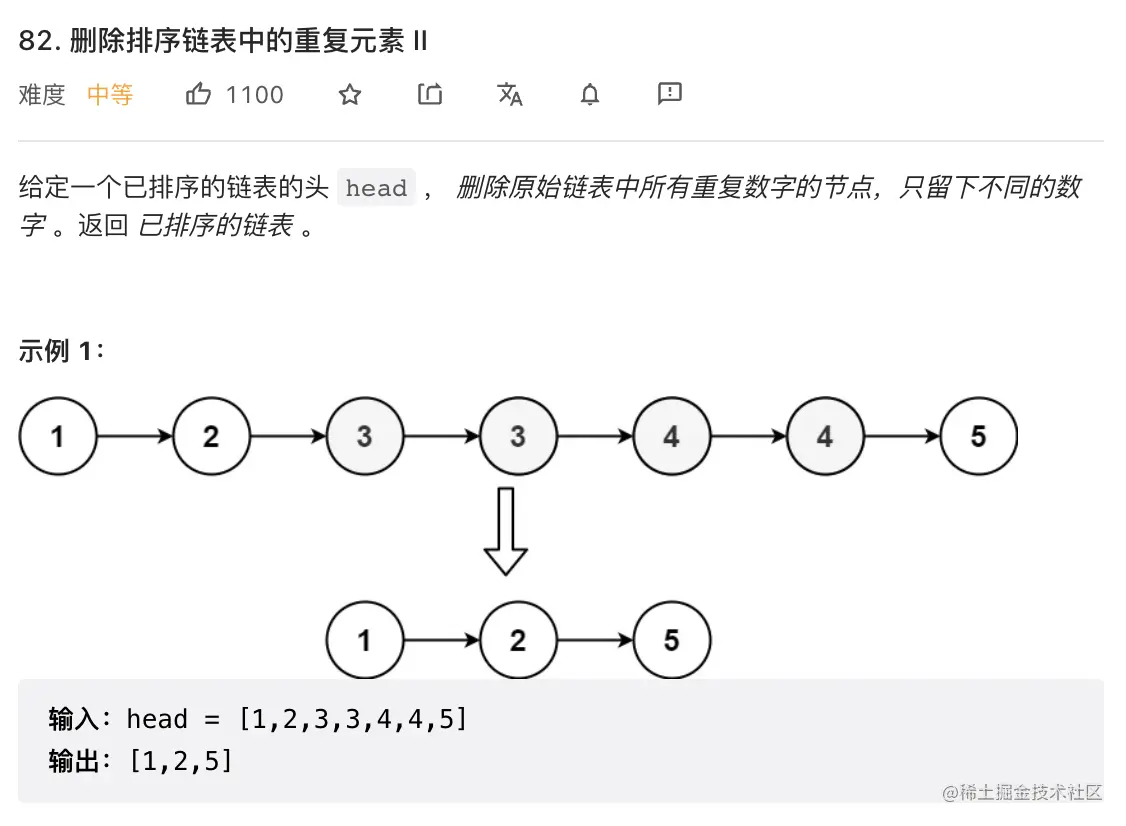
解题重点:删除重复的元素,可能头结点也会被删除,需要引入虚拟结点
引入临时变量: 记录重复值然后依次删除
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode virHead = new ListNode(-1);
virHead.next = head;
ListNode cur = virHead;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {
int val = cur.next.val;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return virHead.next;
}
}
三、链表的反转问题
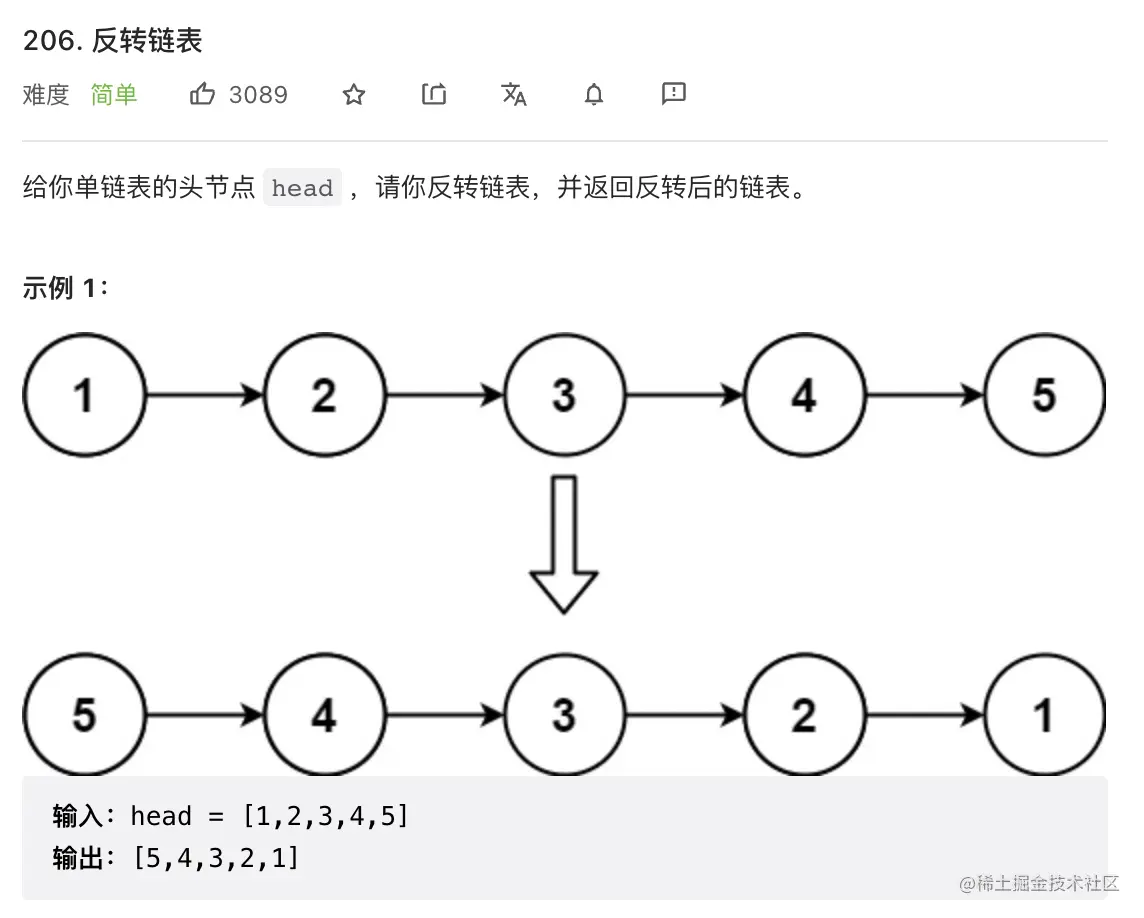
7. 反转链表
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode virHead = new ListNode();
virHead.next = null;
while(head != null){
ListNode p = head.next;
ListNode temp = virHead.next;
virHead.next = head;
head.next = temp;
head = p;
}
return virHead.next;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode p = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (p != null) {
ListNode temp = p.next;
p.next = head;
head = p;
p = temp;
}
return head;
}
}
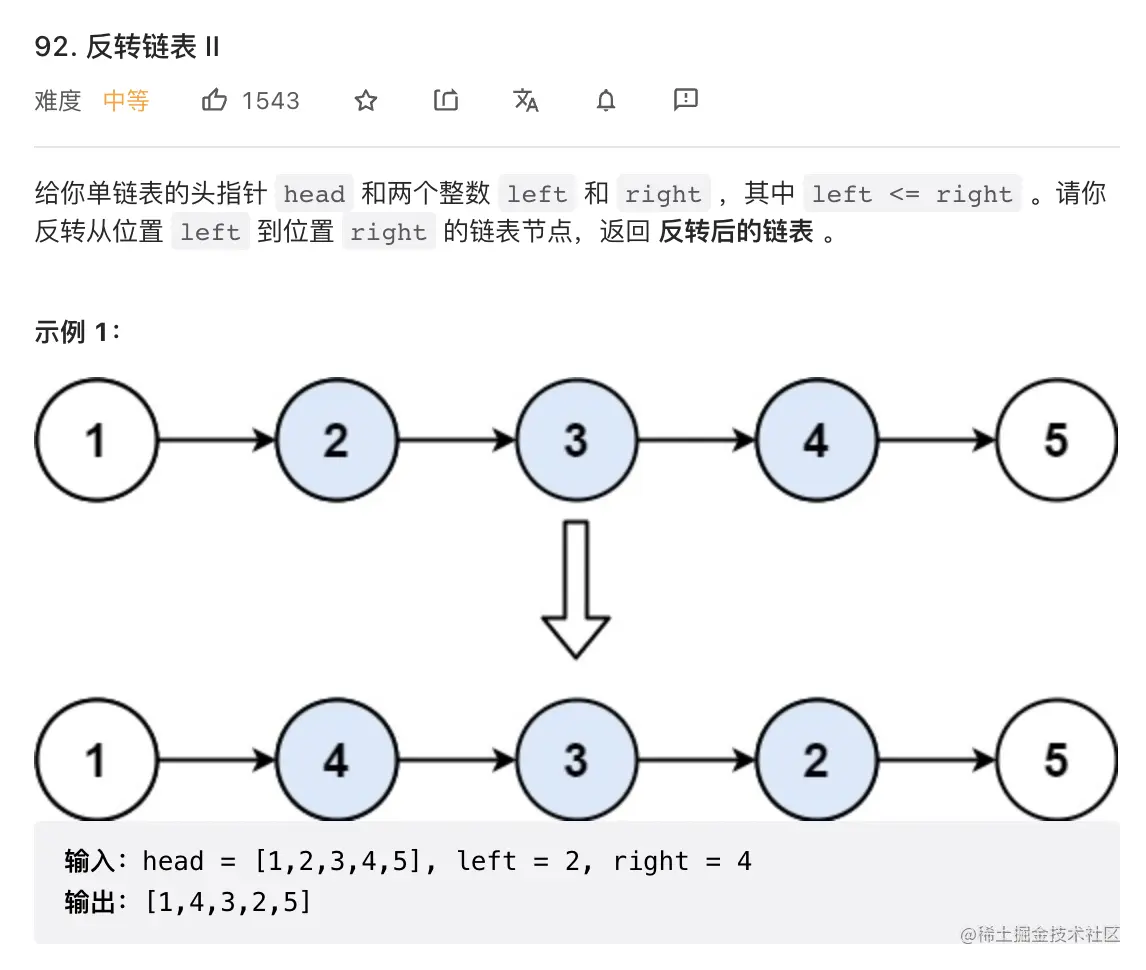
8. 反转链表II
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode virHead = new ListNode();
virHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = virHead;
int num = 0;
while (num < left - 1) {
num++;
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode cur = pre.next;
ListNode tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {
tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp.next;
tmp.next = pre.next;
pre.next = tmp;
}
return virHead.next;
}
}
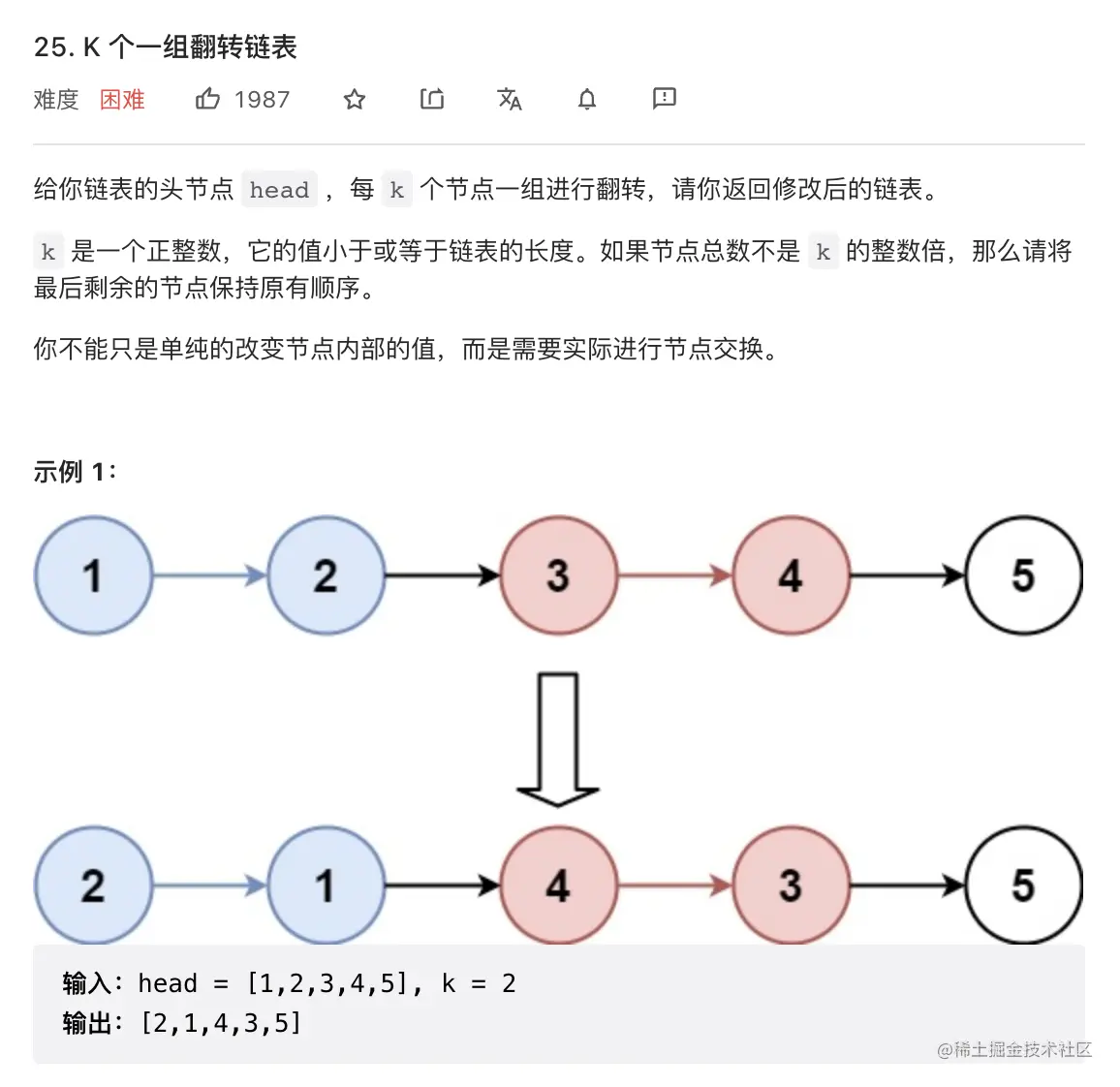
9. K个一组翻转链表
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode virHead = new ListNode();
virHead.next = head;
ListNode right = virHead;
while (right != null) {
ListNode pre = right;
ListNode left = right.next;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (right != null) {
right = right.next;
}
}
ListNode temp = new ListNode(0);
temp.next = left;
if (right != null) {
pre.next = right.next;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ListNode leftNext = left.next;
left.next = pre.next;
pre.next = left;
left = leftNext;
}
right = temp.next;
}
}
return virHead.next;
}
}
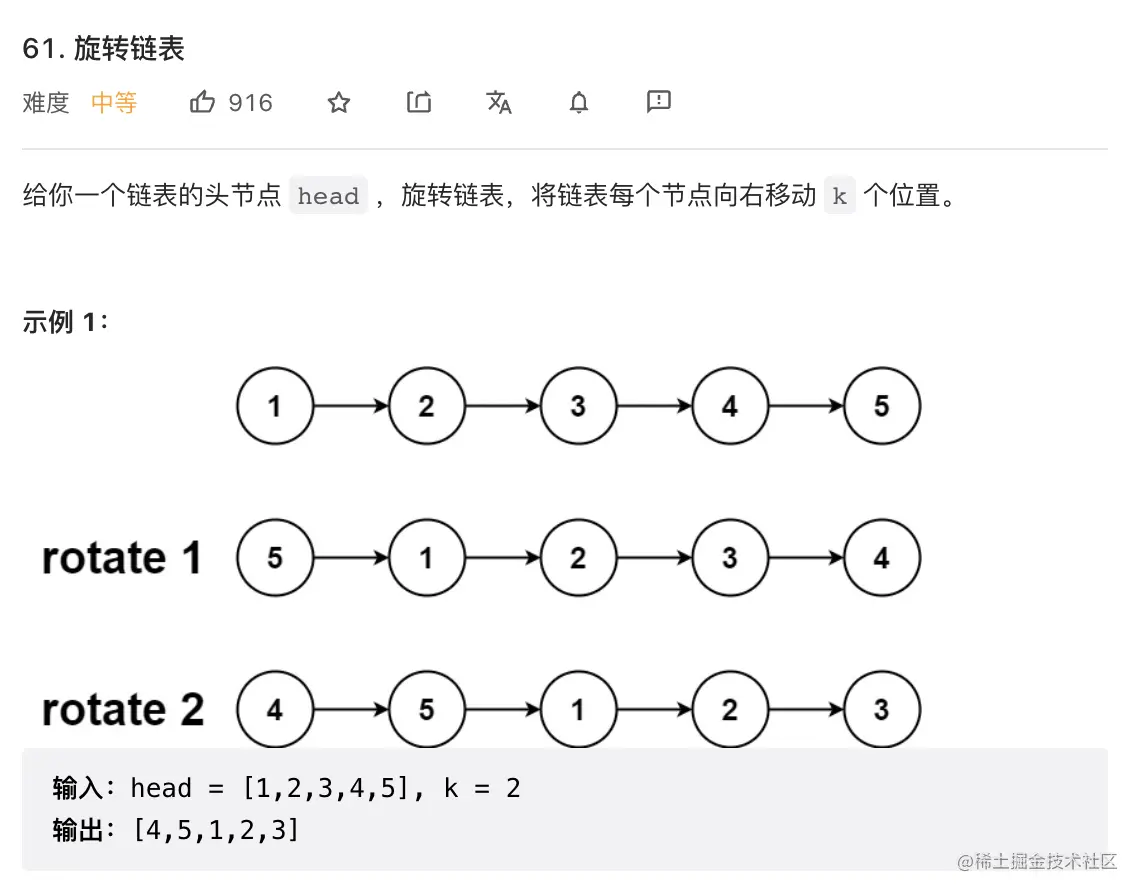
10. 旋转链表
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head;
int len = 1;
while (cur.next != null) {
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = head;
ListNode pre = cur;
cur = head;
int div = len - k % len;
for (int i = 0; i < div; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next = null;
return cur;
}
}
11. 两两交换链表中的节点
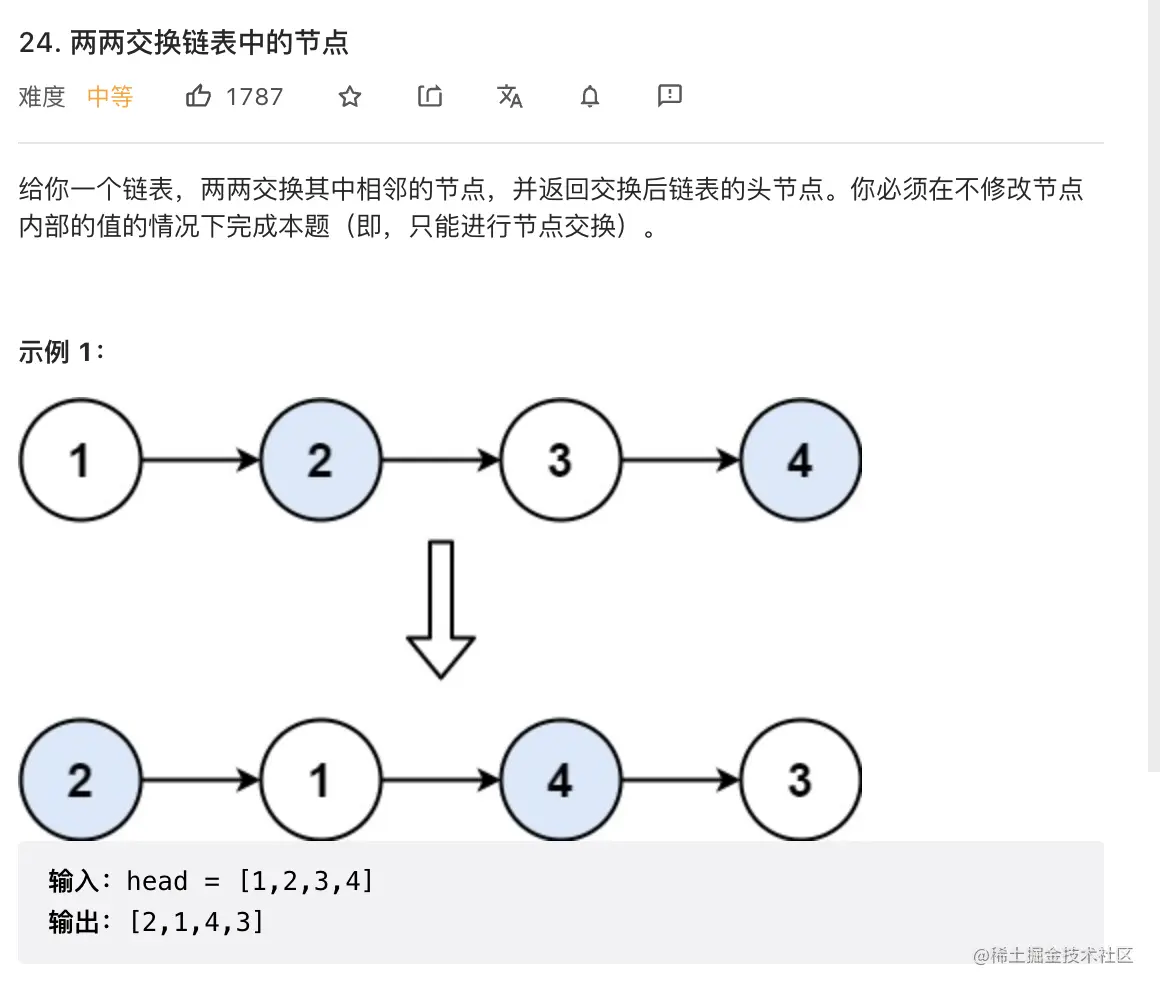
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode virHead = new ListNode();
virHead.next = head;
ListNode p = virHead.next;
ListNode q = p.next;
ListNode pre = virHead;
while (p != null && q != null) {
ListNode next = q.next;
pre.next = q;
q.next = p;
p.next = next;
if (p.next != null && p.next.next != null) {
pre = p;
p = pre.next;
q = p.next;
} else {
return virHead.next;
}
}
return virHead.next;
}
}
四、链表习题
12. 分隔链表

class Solution {
public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode head, int k) {
int sum = 0;
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
sum++;
temp = temp.next;
}
int n = sum / k, div = sum % k;
ListNode[] res = new ListNode[k];
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k && cur != null; i++) {
ListNode subHead = cur;
int size = n + (i < div ? 1 : 0);
for (int j = 1; j < size; j++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = next;
res[i] = subHead;
}
return res;
}
}
13. 复制带随机指针的链表

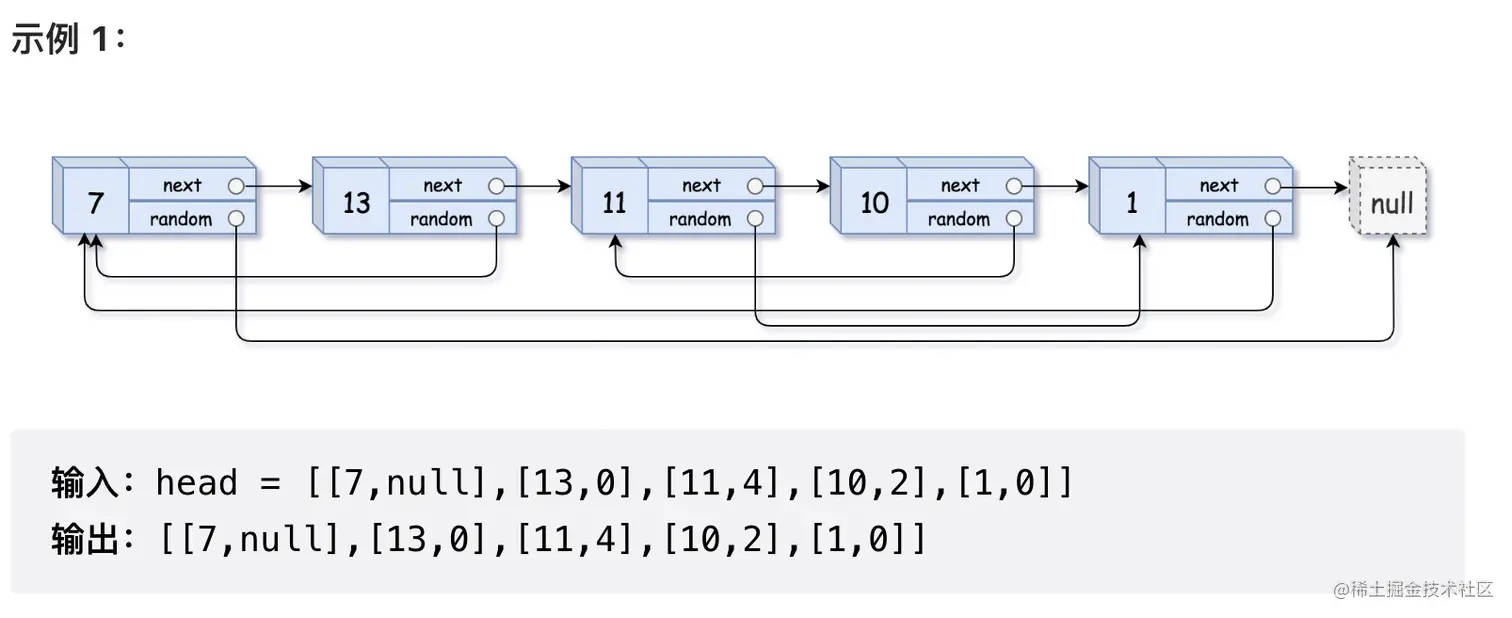
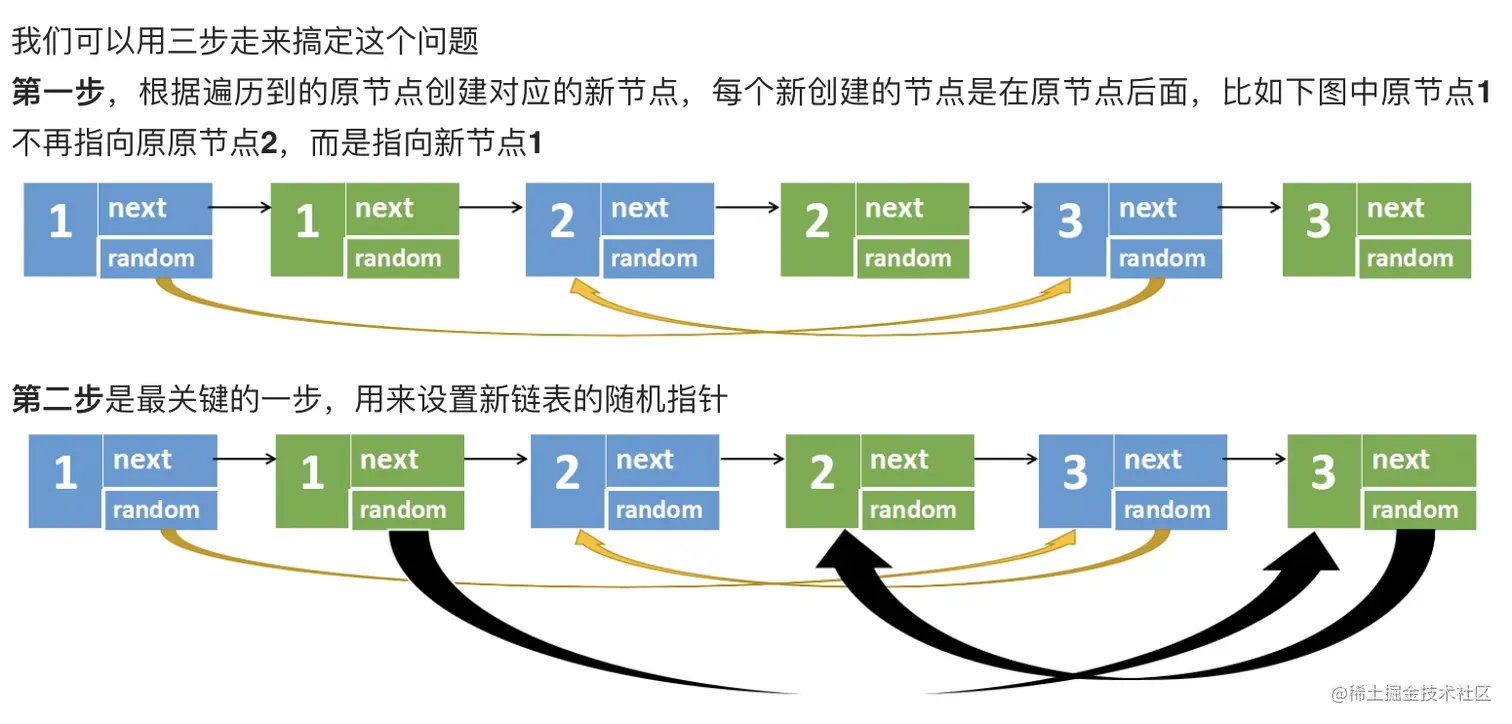
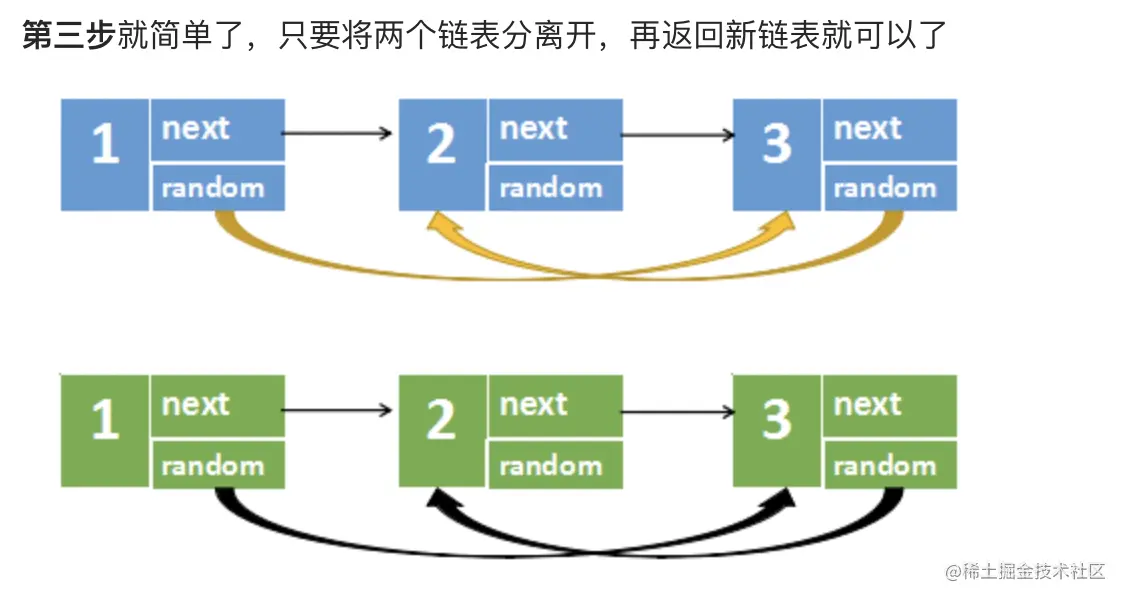
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next) {
Node newNode = new Node(node.val);
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
}
for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next) {
Node newNode = node.next;
if (node.random != null) {
newNode.random = node.random.next;
}
}
Node headNew = head.next;
for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next) {
Node nodeNew = node.next;
node.next = nodeNew.next;
nodeNew.next = (nodeNew.next != null) ? nodeNew.next.next : null;
}
return headNew;
}
}
14. 链表中的下一个更大节点
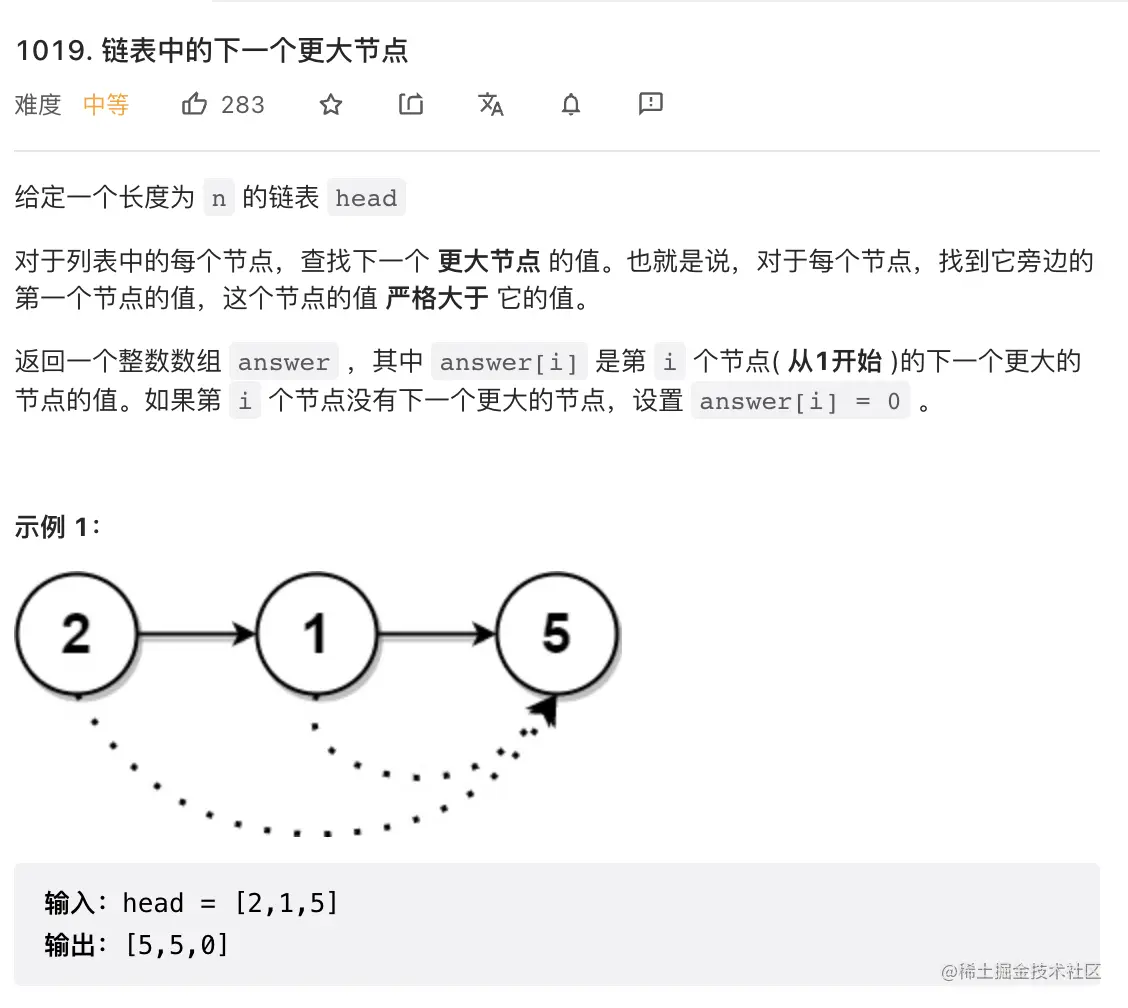
class Solution {
public int[] nextLargerNodes(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode slow = head;
while (slow != null) {
ListNode quick = slow.next;
while (quick != null) {
if (quick.val > slow.val) {
list.add(quick.val);
break;
}else {
quick=quick.next;
}
}
if (quick == null) {
list.add(0);
}
slow = slow.next;
}
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
res[i] = list.get(i);
}
return res;
}
}