1. 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
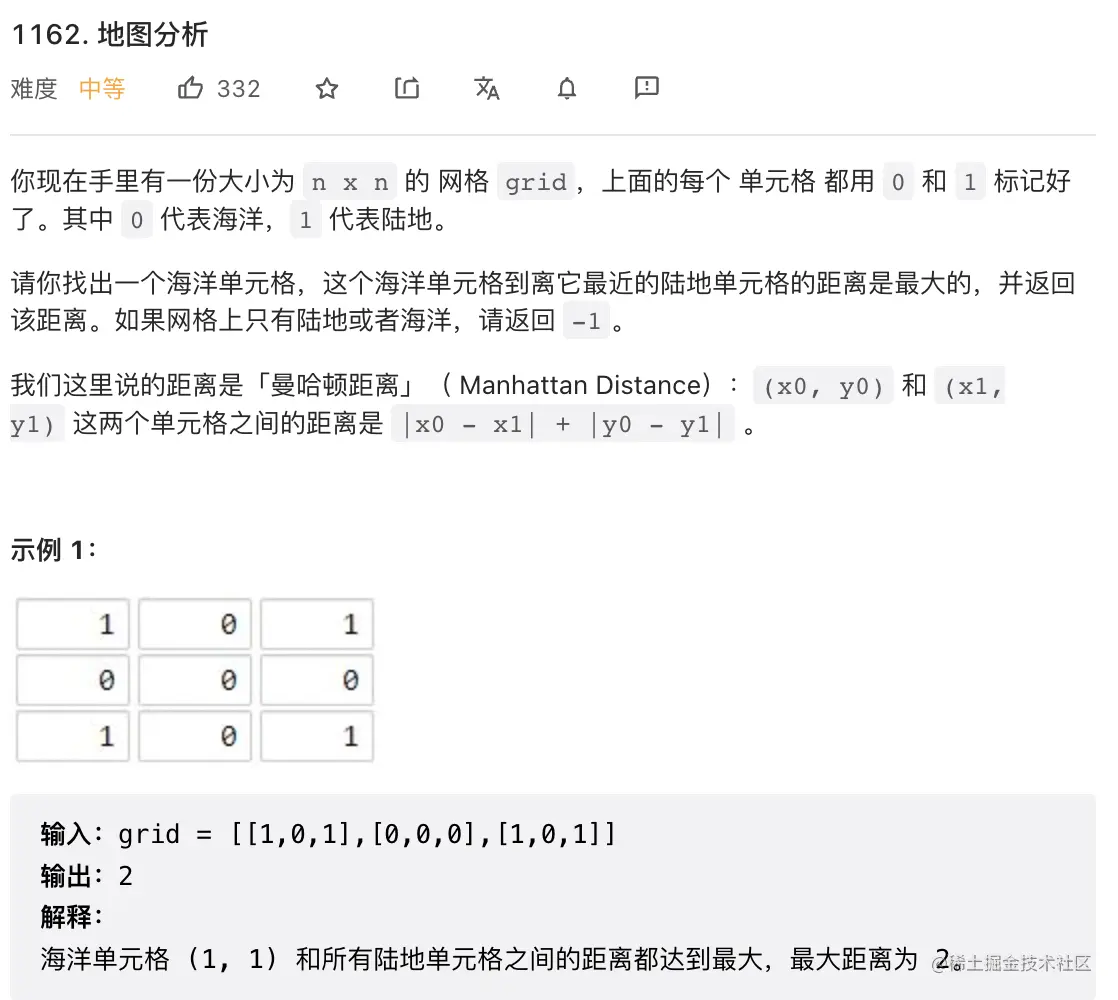
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出: 2
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 1;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (queue != null) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left == null & cur.right == null) {
return depth;
}
if (cur.left != null) queue.add(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.add(cur.right);
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
2. 二叉树的层序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 `root` ,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
list.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) queue.add(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.add(cur.right);
}
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
}
3. 单词接龙

class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(wordList);
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(beginWord);
int step = 1;
int n = beginWord.length();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.equals(endWord)) {
return step;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (char letter = 'a'; letter <= 'z'; letter++) {
StringBuffer next = new StringBuffer(cur);
next.setCharAt(j, letter);
String nextWord = next.toString();
if (set.contains(nextWord)) {
if (nextWord.equals(endWord)) {
return step + 1;
}
set.remove(nextWord);
queue.add(nextWord);
}
}
}
}
step++;
}
return 0;
}
}
4. 迷宫

输入 1: 迷宫由以下二维数组表示
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
输入 2: 起始位置坐标 (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
输入 3: 目的地坐标 (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4)
输出: true
解析: 一个可能的路径是 : 左 -> 下 -> 左 -> 下 -> 右 -> 下 -> 右。
public boolean hasPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
int row = maze.length;
int col = maze[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = new int[]{0, 1, 0, -1};
int[][] visited = new int[row][col];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(start);
visited[start[0]][start[1]] = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
if (Arrays.equals(cur, destination)) {
return true;
}
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int x = cur[0];
int y = cur[1];
while (x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 && y < col && maze[x][y] == 0) {
x += dx[d];
y += dy[d];
}
x -= dx[d];
y -= dy[d];
if (visited[x][y] == 0) {
queue.add(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = 1;
}
}
}
return false;
}
5. 迷宫II

public int shortestDistance(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
int row = maze.length;
int col = maze[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = new int[]{0, 1, 0, -1};
int[][] visited = new int[row][col];
PriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[0] - o2[0];
}
});
queue.add(new int[]{0, start[0], start[1]});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
if (visited[cur[1]][cur[2]] == 1) {
continue;
}
visited[cur[1]][cur[2]] = 1;
if (Arrays.equals(new int[]{cur[1], cur[2]}, destination)) {
return cur[0];
}
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int x = cur[1];
int y = cur[2];
int dist = cur[0];
while (x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 && y < col && maze[x][y] == 0) {
x += dx[d];
y += dy[d];
dist++;
}
x -= dx[d];
y -= dy[d];
dist--;
if (visited[x][y] == 0) {
queue.add(new int[]{dist, x, y});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
6. 迷宫III
由空地和墙组成的迷宫中有一个球。球可以向上(u)下(d)左(l)右(r)四个方向滚动,但在遇到墙壁前不会停止滚动。
当球停下时,可以选择下一个方向。迷宫中还有一个洞,当球运动经过洞时,就会掉进洞里。
给定球的起始位置,目的地和迷宫,找出让球以最短距离掉进洞里的路径。
距离的定义是球从起始位置(不包括)到目的地(包括)经过的空地个数。
通过’u’, ‘d’, ‘l’ 和 ‘r’输出球的移动方向。
由于可能有多条最短路径, 请输出字典序最小的路径。如果球无法进入洞,输出”impossible”。
迷宫由一个0和1的二维数组表示。1表示墙壁,0表示空地。
你可以假定迷宫的边缘都是墙壁。起始位置和目的地的坐标通过行号和列号给出。
public class MazeIII {
@Test
public void test(){
int[][] maze = {
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0}
};
String b = findShortestWay(maze, new int[]{4, 3}, new int[]{0, 0});
System.out.println(b);
}
public String findShortestWay(int[][] maze, int[] ball, int[] hole) {
int row = maze.length;
int col = maze[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = new int[]{0, 1, 0, -1};
char[] chars = new char[]{'u', 'r', 'd', 'l'};
int min_size = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
String res = "impossible";
int[][] visited = new int[row][col];
PriorityQueue<Position> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Position>() {
@Override
public int compare(Position o1, Position o2) {
return o1.dist - o2.dist;
}
});
queue.add(new Position(ball[0], ball[1], 0, ""));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Position cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.dist > min_size) {
continue;
}
if (Arrays.equals(new int[]{cur.x, cur.y}, hole)) {
if (cur.dist < min_size) {
min_size = cur.dist;
res = cur.path;
} else if (cur.dist == min_size && cur.path.compareTo(res) < 0) {
res = cur.path;
}
}
visited[cur.x][cur.y] = 1;
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int x = cur.x;
int y = cur.y;
int dist = cur.dist;
String path = cur.path;
path += chars[d];
while (x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 && y < col && maze[x][y] == 0) {
if (Arrays.equals(new int[]{x, y}, hole)) {
x += dx[d];
y += dy[d];
dist++;
break;
}
x += dx[d];
y += dy[d];
dist++;
}
x -= dx[d];
y -= dy[d];
dist--;
if (visited[x][y] == 0) {
queue.add(new Position(x, y, dist, path));
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Position {
int x;
int y;
int dist;
String path;
public Position(int x, int y, int dist, String path) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.dist = dist;
this.path = path;
}
}
7. 地图分析
class Solution {
public int maxDistance(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] dx = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int[] dy = {1, 0, -1, 0};
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
int[] point = null;
boolean hasOcean = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
point = queue.poll();
int x = point[0];
int y = point[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = point[0] + dx[i];
int newY = point[1] + dy[i];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || grid[newX][newY] != 0) {
continue;
}
hasOcean = true;
grid[newX][newY] = grid[x][y] + 1;
queue.offer(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
if (hasOcean == false || point == null) {
return -1;
}
return grid[point[0]][point[1]] - 1;
}
}
8. 跳跃游戏III

class Solution {
public boolean canReach(int[] arr, int start) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visit = new boolean[arr.length];
queue.add(start);
visit[start] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer index = queue.poll();
if (arr[index] == 0) {
return true;
}
int idx1 = index + arr[index];
if (idx1 >=0 && idx1 < arr.length && !visit[idx1]){
queue.offer(idx1);
visit[idx1] = true;
}
int idx2 = index - arr[index];
if (idx2 >=0 && idx2 < arr.length && !visit[idx2]){
queue.offer(idx2);
visit[idx2] = true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
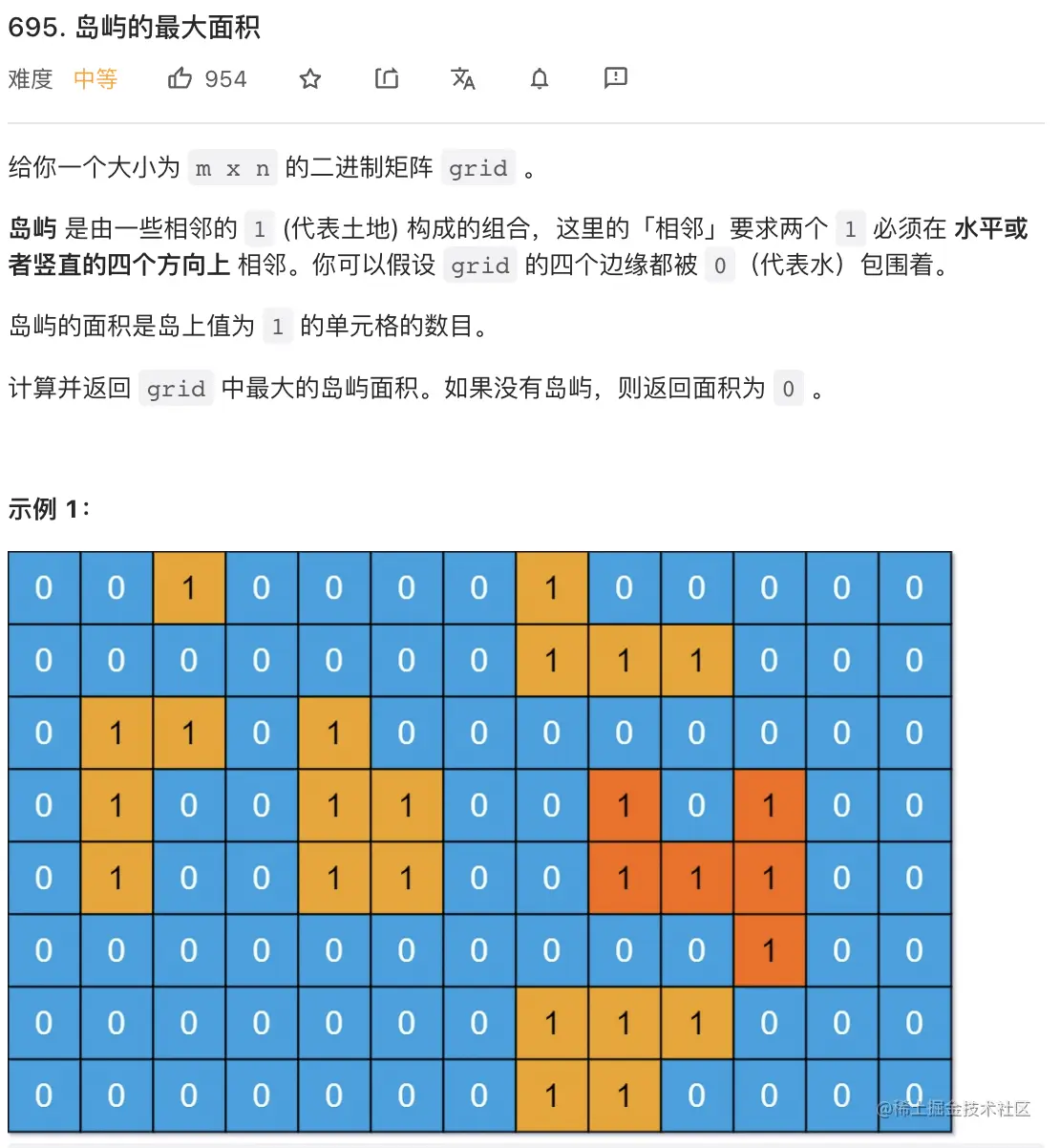
9. 岛屿的最大面积
class Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
int area = 1;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
grid[poll[0]][poll[1]] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int newX = poll[0] + dx[k];
int newY = poll[1] + dy[k];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || grid[newX][newY] != 1) {
continue;
}
area += 1;
grid[newX][newY] = 0;
queue.offer(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
res = Math.max(res, area);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
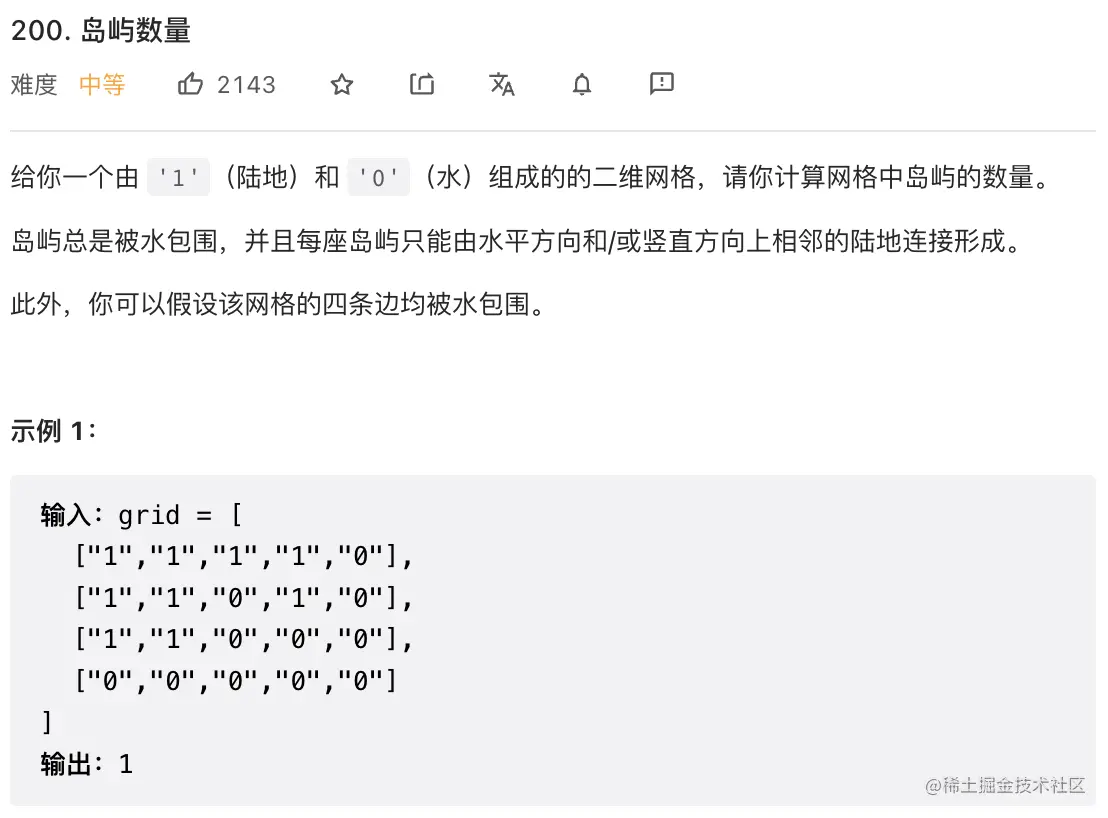
10. 岛屿数量
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
grid[i][j] = '0';
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
res += 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int newX = poll[0] + dx[k];
int newY = poll[1] + dy[k];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || grid[newX][newY] != '1') {
continue;
}
grid[newX][newY] = '0';
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
11. 被围绕的区域

class Solution {
public void solve(char[][] board) {
int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int n = board.length;
if (n == 0) {
return;
}
int m = board[0].length;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (board[i][0] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, 0});
board[i][0] = 'A';
}
if (board[i][m - 1] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, m - 1});
board[i][m - 1] = 'A';
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; i++) {
if (board[0][i] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{0, i});
board[0][i] = 'A';
}
if (board[n - 1][i] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{n - 1, i});
board[n - 1][i] = 'A';
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = queue.poll();
int x = cell[0], y = cell[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int mx = x + dx[i], my = y + dy[i];
if (mx < 0 || my < 0 || mx >= n || my >= m || board[mx][my] != 'O') {
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{mx, my});
board[mx][my] = 'A';
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'A') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
} else if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
}
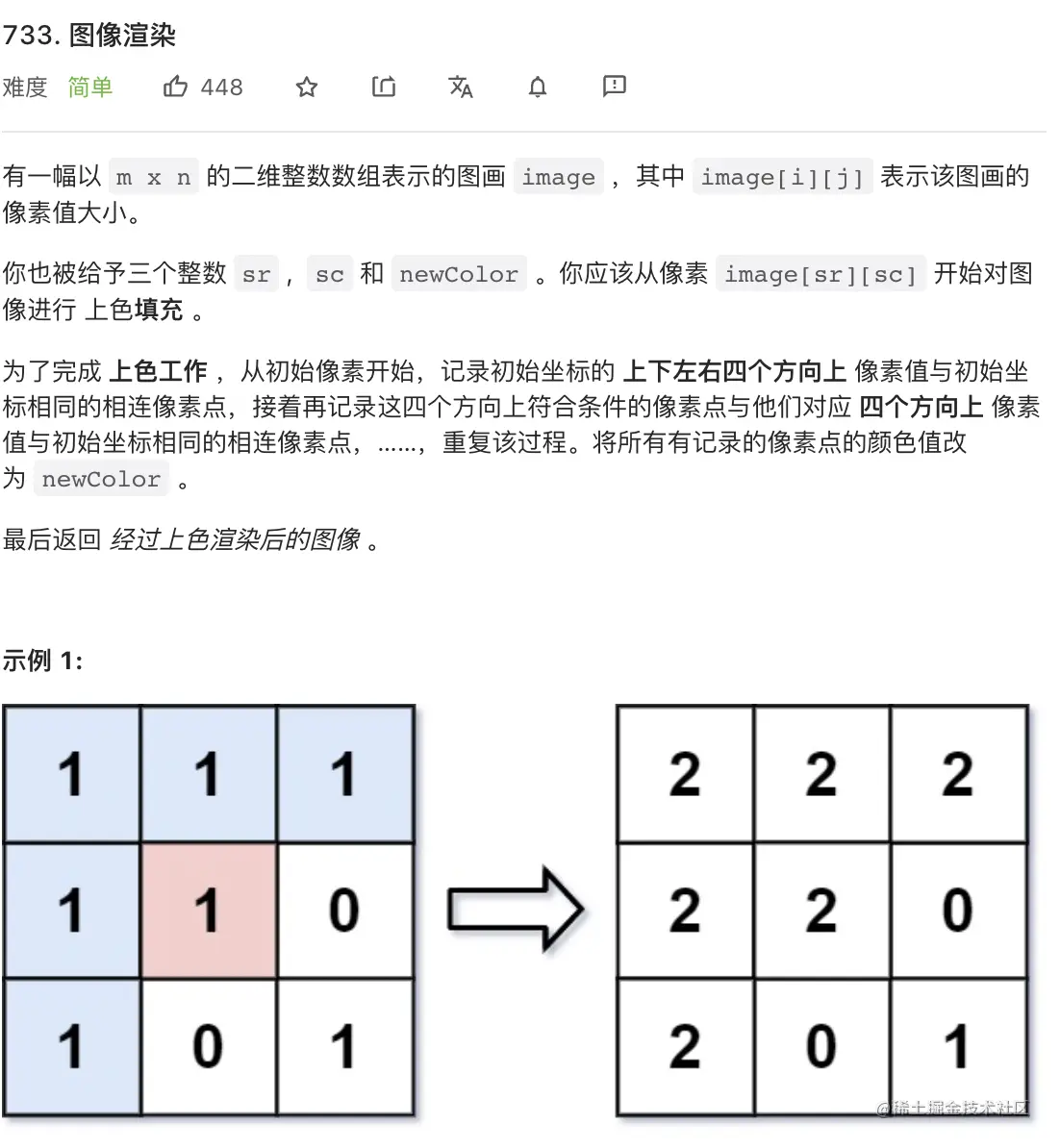
12. 图像渲染
class Solution {
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int color) {
int m = image.length;
int n = image[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
int value = image[sr][sc];
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[]{sr, sc});
visit[sr][sc] = true;
image[sr][sc] = color;
image[sr][sc] = color;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
int x = poll[0];
int y = poll[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = x + dx[i];
int newY = y + dy[i];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || visit[newX][newY] == true || value != image[newX][newY]) {
continue;
}
visit[newX][newY] = true;
image[newX][newY] = color;
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
return image;
}
}
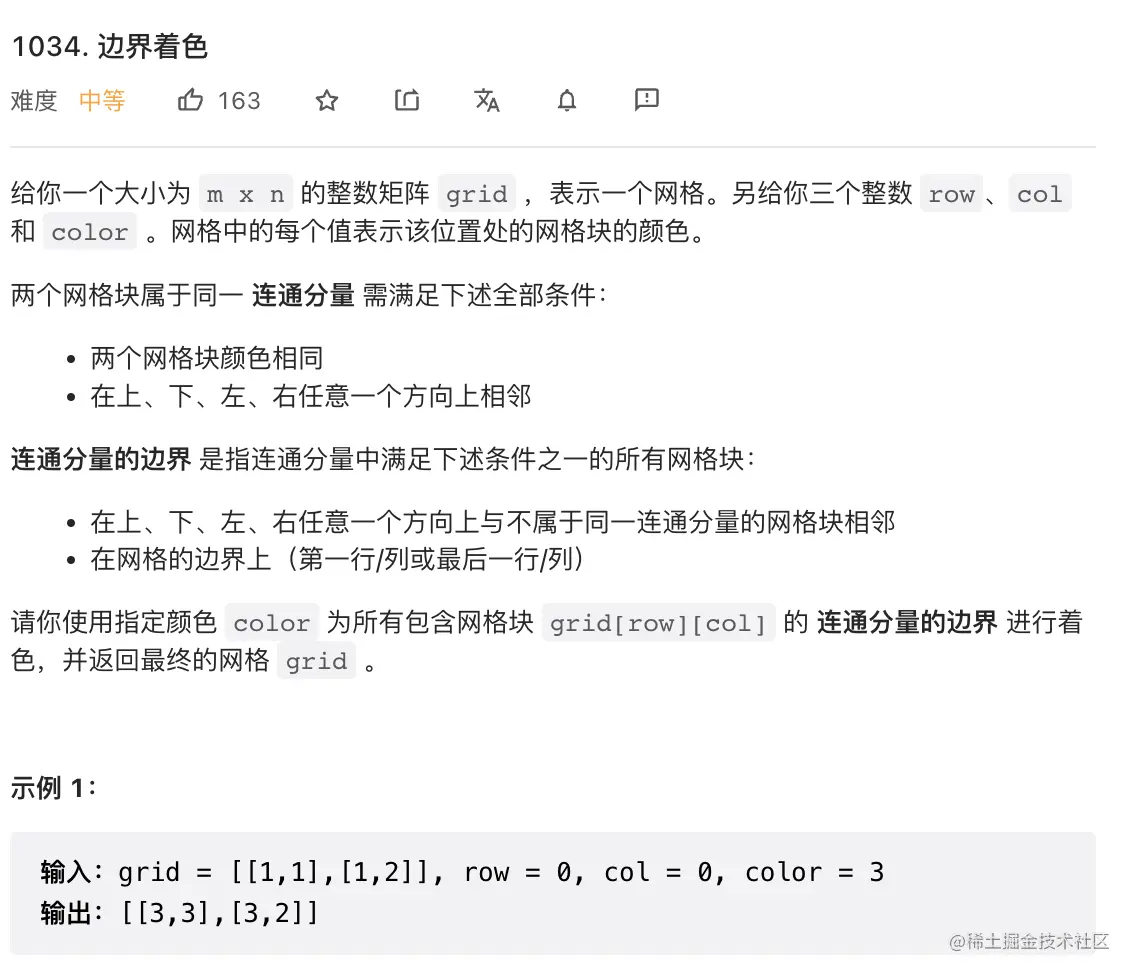
13. 边界着色
class Solution {
public int[][] colorBorder(int[][] grid, int row, int col, int color) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
int value = grid[row][col];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<int[]> updateQueue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[]{row, col});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
int x = poll[0];
int y = poll[1];
visit[x][y] = true;
boolean flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = x + dx[i];
int newY = y + dy[i];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n ) {
flag = false;
continue;
}
if (grid[newX][newY] != value){
flag = false;
continue;
}
if (visit[newX][newY] == false){
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
if (flag == false) {
updateQueue.add(new int[]{x, y});
}
}
while (!updateQueue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = updateQueue.poll();
grid[poll[0]][poll[1]] = color;
}
return grid;
}
}
14. 员工的重要性

class Solution {
public int getImportance(List<Employee> employees, int id) {
int res = 0;
Map<Integer , Employee> map = new HashMap();
for (Employee employee : employees) {
map.put(employee.id , employee);
}
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(id);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Integer idx = queue.poll();
Employee employee = map.get(idx);
res += employee.importance;
List<Integer> subordinates = employee.subordinates;
for (Integer subordinate : subordinates) {
queue.add(subordinate);
}
}
return res;
}
}
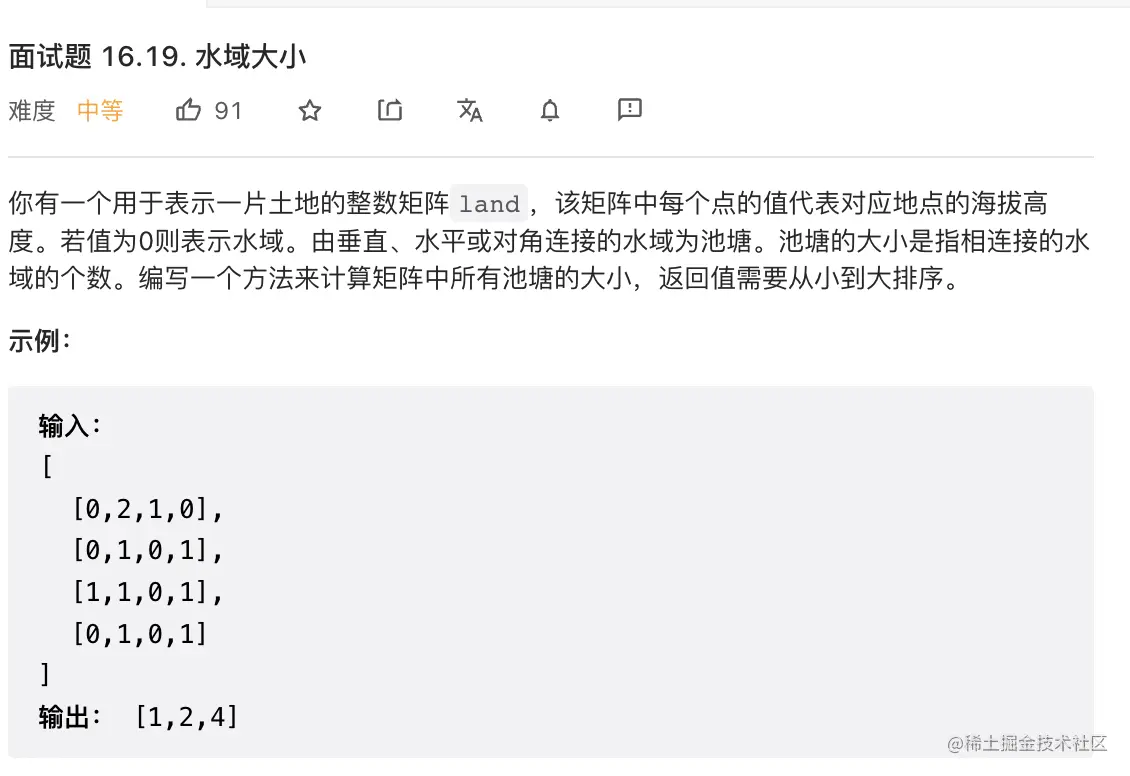
15. 水域大小
class Solution {
public int[] pondSizes(int[][] land) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (land.length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
int m = land.length;
int n = land[0].length;
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, -1, -1};
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (land[i][j] == 0) {
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
int idxI = poll[0];
int idxJ = poll[1];
if (visit[idxI][idxJ]) {
continue;
}
Queue<int[]> newQueue = new LinkedList<>();
newQueue.add(poll);
int size = 1;
while (!newQueue.isEmpty()) {
final int[] newPoll = newQueue.poll();
int x = newPoll[0];
int y = newPoll[1];
visit[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int newX = dx[i] + x;
int newY = dy[i] + y;
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || visit[newX][newY] || land[newX][newY] != 0) {
continue;
}
newQueue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
size++;
visit[newX][newY] = true;
}
}
list.add(size);
}
list.sort((x, y) -> x - y);
int[] ints = list.stream()
.mapToInt(i -> i)
.toArray();
return ints;
}
}
16. 腐烂的橘子

class Solution {
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
if (queue.size() == 0){
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
int count = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
count++;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
int x = poll[0];
int y = poll[1];
if (visit[x][y] == true) {
continue;
}
visit[x][y] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int newX = dx[j] + x;
int newY = dy[j] + y;
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || visit[newX][newY] || grid[newX][newY]!=1) {
continue;
}
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
grid[newX][newY] = 2;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
return count - 1;
}
}
17. 节点间通路

class Solution {
public boolean findWhetherExistsPath(int n, int[][] graph, int start, int target) {
int m = graph.length;
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int key = graph[i][0];
if (map.get(key) == null) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(graph[i][1]);
map.put(key, set);
} else {
Set<Integer> set = map.get(key);
set.add(graph[i][1]);
map.put(key, set);
}
}
if (map.get(start) == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
if (queue.contains(target)) {
return true;
}
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Integer poll = queue.poll();
if (map.get(poll) != null) {
queue.addAll(map.get(poll));
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
18. 地图中的最高点

class Solution {
public int[][] highestPeak(int[][] isWater) {
int m = isWater.length;
int n = isWater[0].length;
int[][] highestPeak = new int[m][n];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (isWater[i][j] == 1) {
highestPeak[i][j] = 0;
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
visit[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
int value = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
value++;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
final int[] poll = queue.poll();
int x = poll[0];
int y = poll[1];
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int newX = x + dx[j];
int newY = y + dy[j];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || visit[newX][newY] == true) {
continue;
}
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
highestPeak[newX][newY] = value;
visit[newX][newY] = true;
}
}
}
return highestPeak;
}
}
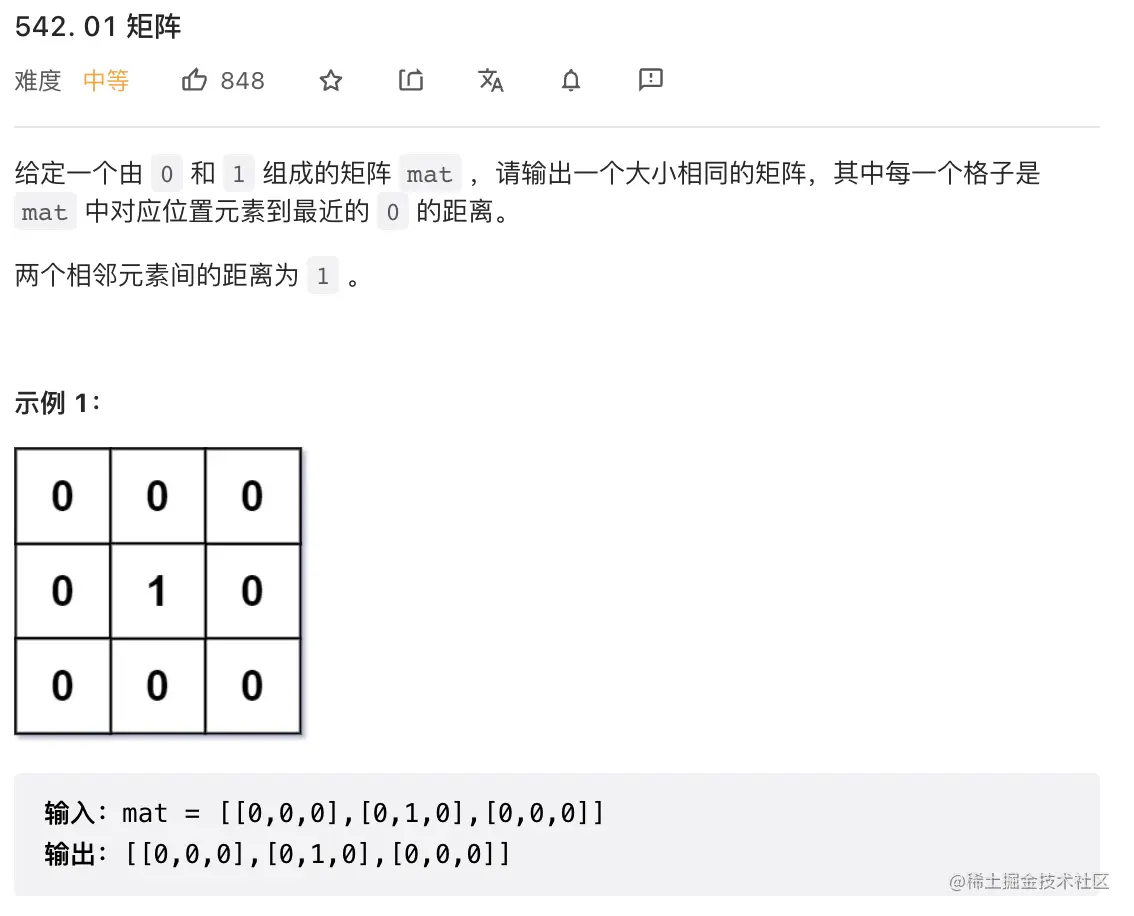
19. 01矩阵
class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int m = mat.length;
int n = mat[0].length;
int[][] len = new int[m][n];
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
len[i][j] = 0;
visit[i][j] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
int x = poll[0];
int y = poll[1];
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int newX = x + dx[j];
int newY = y + dy[j];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || visit[newX][newY]) {
continue;
}
visit[newX][newY] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
len[newX][newY] = len[x][y] + 1;
}
}
}
return len;
}
}
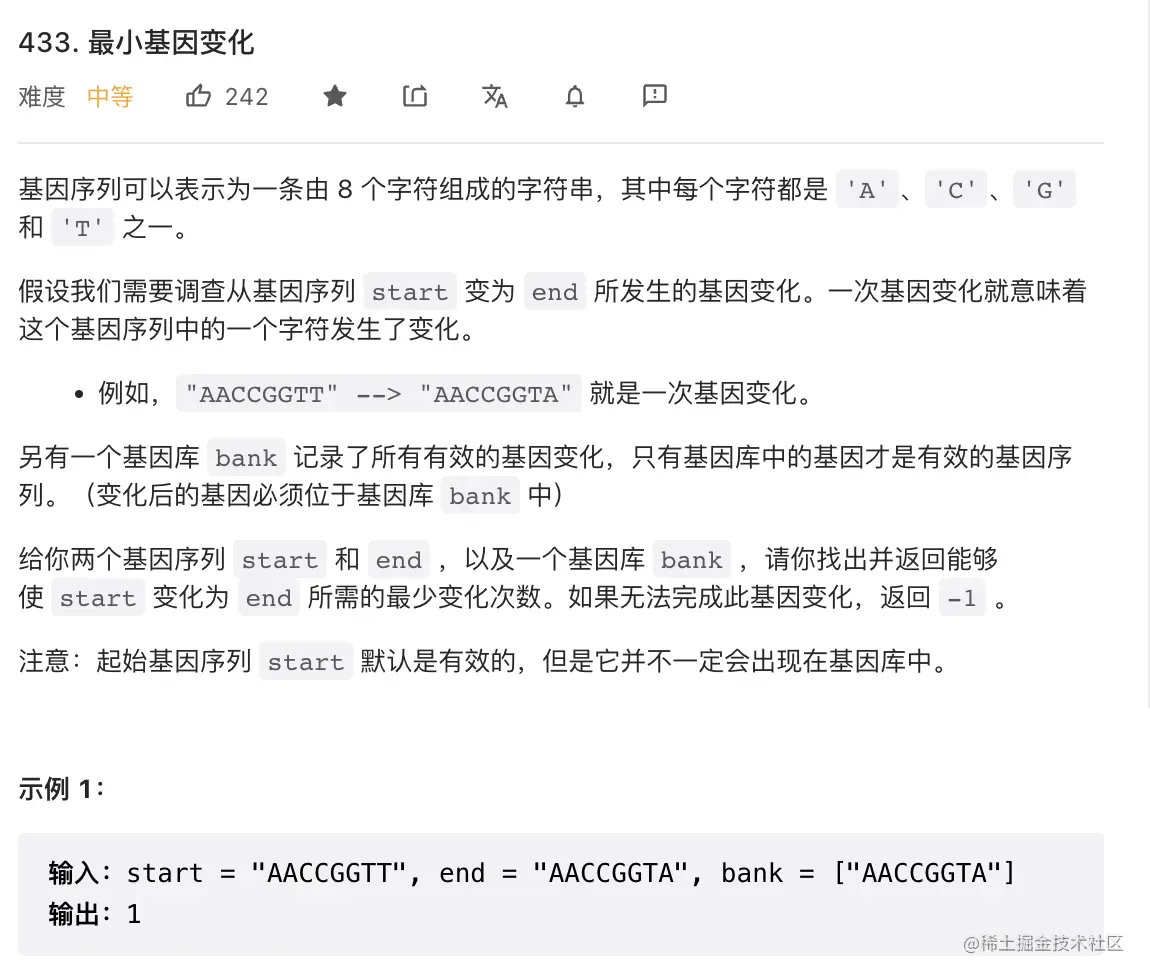
20. 最小基因变化
class Solution {
public int minMutation(String startGene, String endGene, String[] bank) {
if (bank.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (startGene.equals(endGene)) {
return 0;
}
int count = 0;
char[] chars = new char[]{'A', 'C', 'G', 'T'};
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
for (String s : bank) {
set.add(s);
}
if (!set.contains(endGene)){
return -1;
}
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(startGene);
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(startGene, "1");
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
count++;
for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) {
String poll = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (char aChar : chars) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(poll);
sb.setCharAt(i, aChar);
String s = sb.toString();
if (s.equals(endGene)) {
return count;
} else {
if (set.contains(s)) {
if (map.get(s) != null) {
continue;
} else {
map.put(s, "1");
queue.add(s);
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
21. 课程表

class Solution {
public static boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] prerequisite : prerequisites) {
int x = prerequisite[0];
int y = prerequisite[1];
if (map.get(x) == null) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(y);
map.put(x, list);
} else {
List<Integer> list = map.get(x);
list.add(y);
map.put(x, list);
}
}
boolean[] visit = new boolean[numCourses];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (map.get(i) == null) {
queue.add(i);
}
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer poll = queue.poll();
visit[poll] = true;
for (Integer integer : map.keySet()) {
if (map.get(integer).contains(poll)) {
List<Integer> list = map.get(integer);
list.remove(poll);
if (list.size() == 0 && visit[integer] == false) {
queue.add(integer);
set.add(integer);
} else if (visit[integer] == false) {
map.put(integer, list);
}
}
}
}
map.keySet().removeAll(set);
if (map.keySet().isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
22. 课程表II
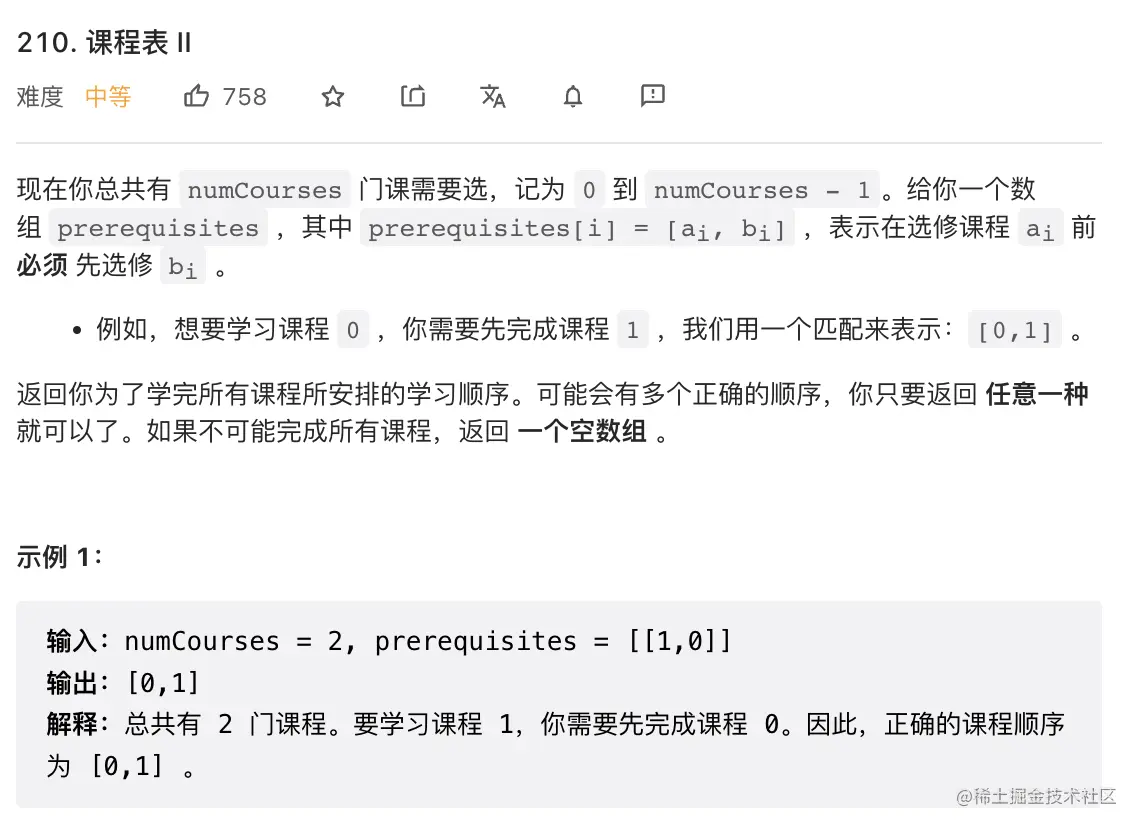
class Solution {
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] prerequisite : prerequisites) {
int x = prerequisite[0];
int y = prerequisite[1];
if (map.get(x) == null) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(y);
map.put(x, list);
} else {
List<Integer> list = map.get(x);
list.add(y);
map.put(x, list);
}
}
boolean[] visit = new boolean[numCourses];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (map.get(i) == null) {
queue.add(i);
}
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer poll = queue.poll();
visit[poll] = true;
result.add(poll);
for (Integer integer : map.keySet()) {
if (map.get(integer).contains(poll)) {
List<Integer> list = map.get(integer);
list.remove(poll);
if (list.size() == 0 && visit[integer] == false) {
queue.add(integer);
set.add(integer);
} else if (visit[integer] == false) {
map.put(integer, list);
}
}
}
}
int n = result.size();
if(n == numCourses){
int[] res = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res[i] = result.get(i);
}
return res;
}else {
return new int[0];
}
}
}
23. 飞地的数量
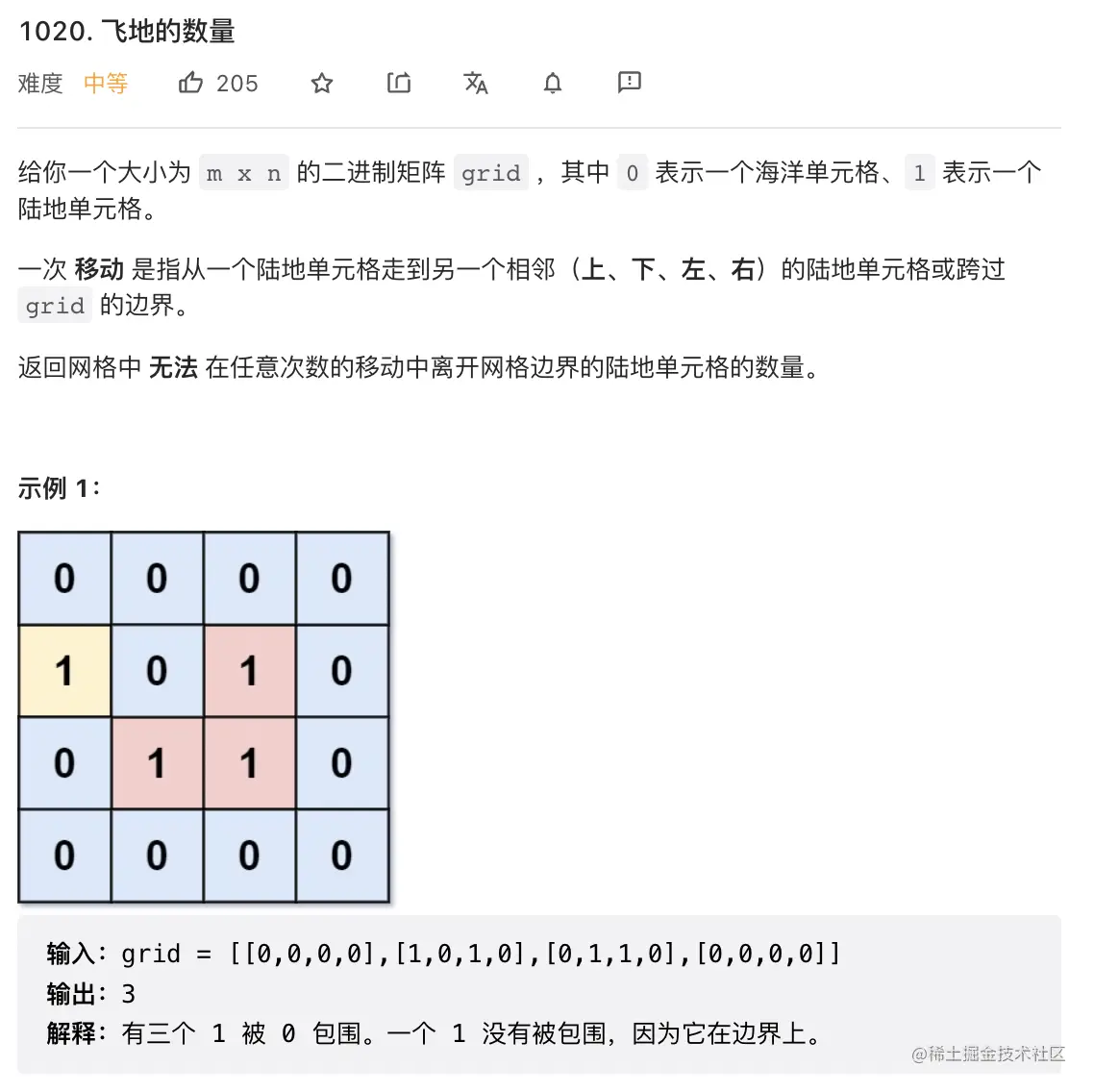
class Solution {
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) {
queue.add(new int[]{i, 0});
}
if (grid[i][n - 1] == 1) {
queue.add(new int[]{i, n - 1});
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] == 1) {
queue.add(new int[]{0, j});
}
if (grid[m - 1][j] == 1) {
queue.add(new int[]{m - 1, j});
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
int x = poll[0];
int y = poll[1];
if (visit[x][y]){
continue;
}
visit[x][y] = true;
grid[x][y] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = x + dx[i];
int newY = y + dy[i];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || grid[newX][newY] == 0 || visit[newX][newY]) {
continue;
} else {
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
sum++;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
}
24. 统计封闭岛屿的数目
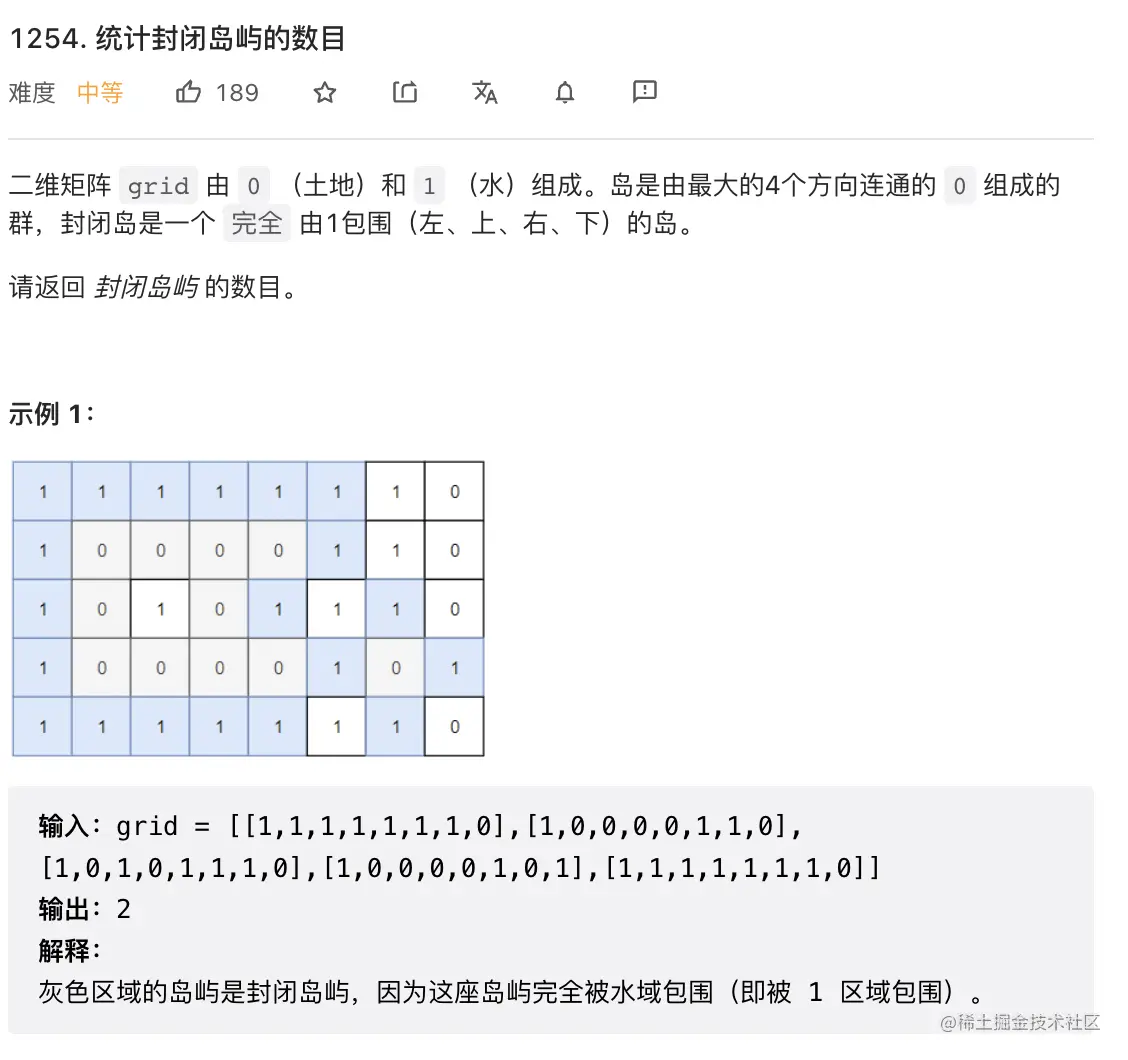
class Solution {
public int closedIsland(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] dx = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0};
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 0) {
queue.add(new int[]{i, 0});
}
if (grid[i][n - 1] == 0) {
queue.add(new int[]{i, n - 1});
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] == 0) {
queue.add(new int[]{0, j});
}
if (grid[m - 1][j] == 0) {
queue.add(new int[]{m - 1, j});
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = queue.poll();
int x = poll[0];
int y = poll[1];
if (visit[x][y]) {
continue;
}
visit[x][y] = true;
grid[x][y] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = x + dx[i];
int newY = y + dy[i];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || grid[newX][newY] == 1 || visit[newX][newY]) {
continue;
} else {
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0 && visit[i][j] == false) {
sum++;
Queue<int[]> newQueue = new LinkedList<>();
newQueue.add(new int[]{i, j});
while (!newQueue.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = newQueue.poll();
int x = poll[0];
int y = poll[1];
if (visit[x][y]){
continue;
}
visit[x][y] = true;
grid[x][y] = 1;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int newX = x + dx[k];
int newY = y + dy[k];
if (newX < 0 || newX >= m || newY < 0 || newY >= n || grid[newX][newY] == 1 || visit[newX][newY]) {
continue;
} else {
newQueue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
}
}
}
}
return sum;
}
}
25. 最短的桥
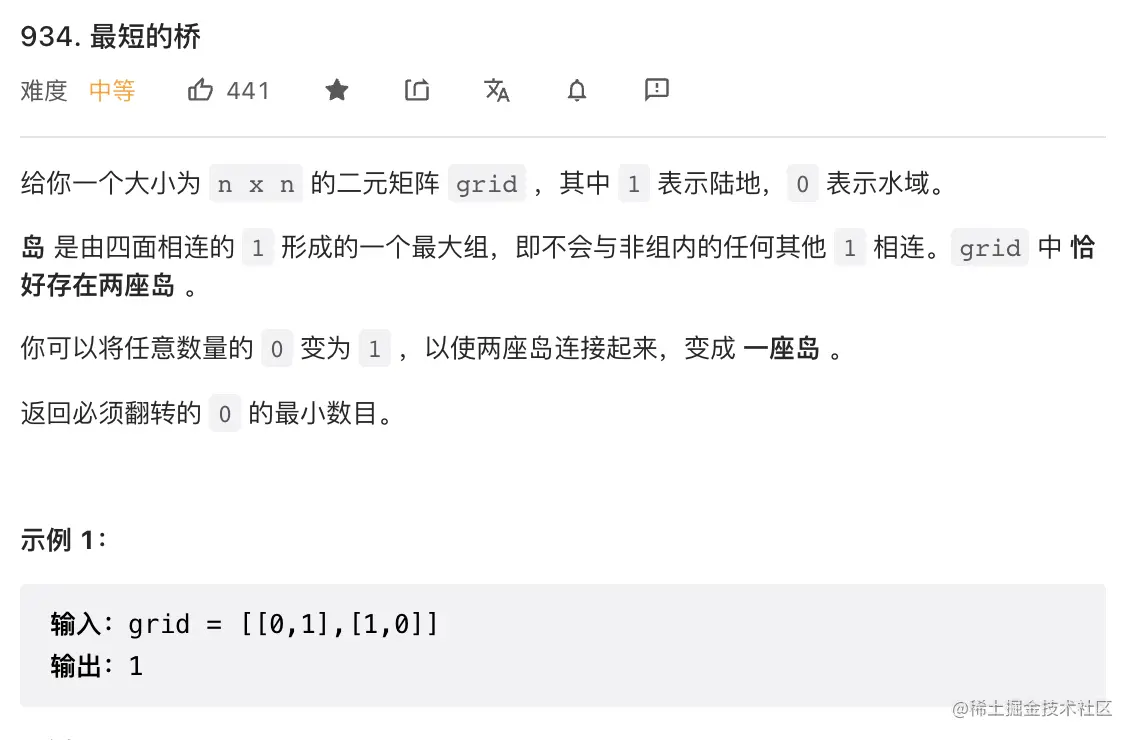
class Solution {
public int shortestBridge(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
List<int[]> island = new ArrayList<int[]>();
Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<int[]>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
grid[i][j] = -1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = queue.poll();
int x = cell[0], y = cell[1];
island.add(cell);
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nx = x + dirs[k][0];
int ny = y + dirs[k][1];
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < n && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
queue.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
grid[nx][ny] = -1;
}
}
}
for (int[] cell : island) {
queue.offer(cell);
}
int step = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int sz = queue.size();
for (int k = 0; k < sz; k++) {
int[] cell = queue.poll();
int x = cell[0], y = cell[1];
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = x + dirs[d][0];
int ny = y + dirs[d][1];
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < n && ny < n) {
if (grid[nx][ny] == 0) {
queue.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
grid[nx][ny] = -1;
} else if (grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
return step;
}
}
}
}
step++;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}