what is continuation
刚开始学continuation真的头大,关于这个continuation定义,说什么的都有,什么继续点,control flow | func的call back
后来看到一段话才有点明白
a continuation is a return point,a call stack, a the remainder of the program,viewed as a function
continuation可以是什么继续点,control flow或者func的call back,但是它都是function。function是什么?我的理解是对计算过程procedure的抽象,换言之continuation就是procedure,不过是整个procedure的一部分。
不理解也没关系,举个例子就懂了,现在有一个procedure或者说函数 A
(+ 1 (* 2 3))
答案是7,很简单。这个计算分成两部分,a‘(+ 1 x)和a'’(* 2 3)两部分计算
对于a‘来说它的continuation就是a'’,就是两件事:处理和返回
也可以举一个现实的例子:二楼的厨师要给我做饭,但是他不知道我要吃什么?于是他给我打了个电话,然后我告诉他我喜欢红烧鸡翅,然后他就开始烤鸡翅了。(有没有感觉这个事情很蠢,为什么要这么做呢?因为事情的关键控制权在我,在这个里层的我,所以他要等我返回)
然后就可以优化了:我告诉厨师想吃红烧鸡翅,然后厨师就可以工作了。(这就是cps ,实现控制反转),但是关于cps我们先按下不表
在scheme中可以用call/cc来支持continuation这个特性,并且continuation可以作为第一等公民(first class),也就是可以作为函数的参数和返回值。
(call/cc *expr*) does the following:
-
Captures the current continuation.
-
Constructs a function
Cthat takes one argument, and applies the current continuation with that argument value. -
Passes this function as an argument to
*expr*--- i.e., it invokes(*expr* C). -
Returns the result of evaluating
(*expr* C), unless*expr*callsC, in which case the value that is passed toCis returned.
搞不懂没关系,语法上反正就是先call/cc 再来一个匿名函数f,这个函数的参数k,这个k就是continuation。
在行为上:call/cc会先在函数中占着一个坑(hole),在去捕获下一个procedure作为continuation,然后把capture的procedure的值填回到原来的hole,再继续原本函数的执行。(有点懵,没事看下面的例子)
continuation as first class in scheme
(define a 5)
(define (add1)
(+ 1
(call/cc
(lambda (k)
(set! a k)))))
-> a
-> 5
-> (add1)
->error
-> a
-> procedure
-> (a 1)
-> 2
-> (a (+ 2 3))
-> 6
刚开时a还是5,运行add1后,可以看到我们把k赋给了a,a就是continuation了,还有一件事整个
(call/cc
(lambda (k)
(set! a k))))
都会变成hole。然后执行(a (+ 2 3)),就会capture这个(+ 2 3)procedure然后就会把这个procedure的值5填回到hole,再继续原来函数的执行就是(+ 1 5),结果是6
反正call/cc就干两件事,先把后面的procedure抽象成continuation,再去capture他,算出值再把值填到hole,继续func的计算(注意是继续有关call/c及其之后的计算),在回去时env也切换到原来的env时
再去看那个厨师的例子,其实和这个概念是一样的
还有一件事:如果fn中没有调用continuation,则(call/cc ...)的值就是函数的返回值。
上面关于只会继续有关call/c及其之后的计算,可能是一个空洞的概念。我们可以举个例子
(define a 5)
(define (add1)
(display "cant go here")
(+ 1
(call/cc
(lambda (k)
(set! a k))))
(display "hi")
)
->(add1)
->error
->(a 1)
->hi
让chatgpt来解释什么是continuation
 感觉就是我想讲的
感觉就是我想讲的
(新加的):今天去看了eopl,上面说continuation
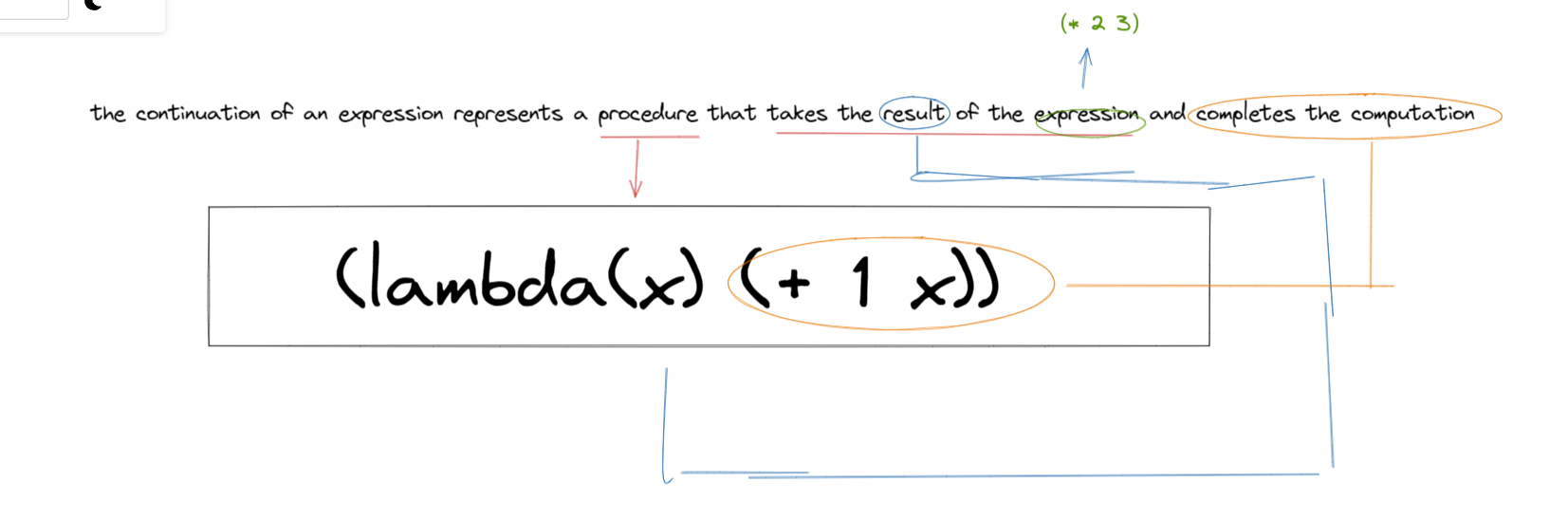
the continuation of an expression represents a procedure that takes the result of the expression and completes the computation
我只能说这句话杀死比赛了
难怪在( + 1 (* 2 3))中(+ 1)的continuation是
(lambda(x) (+ 1 x))
a small test
((call/cc (lambda (cont) cont)) (lambda (x) "hi"))
-> hi
不知道如何下手?先抽象成(f a),就要解析f和a了。
先看f:他没有调用continuation,所以回返回cont(就是一个continuation),a就是一个函数
接下来就是执行f(a)了:cont会capture然后填充到hole,再继续计算
于是代码变成了现在这样
((lambda (x) "hi") (lambda (x) "hi"))
自然结果是hi(在scheme中函数也是first class的)
yin yang
(let* ((yin ((lambda (foo) (display "@") foo)
(call/cc (lambda (bar) bar))))
(yang ((lambda (foo) (display "*") foo)
(call/cc (lambda (bar) bar)))))
(yin yang))
-> @*@**@***@****@*****@******
感觉有点晕没关系,let we do it
让我们一行一行的来看:
1.lambda (foo) (display "@") foo 就打印一个@
2.yin被赋值为c1(continuation 1)
3.(lambda (foo) (display "*") foo 打印出 *
4.yang被赋值为c2(continuation 2)
5.(yin yang),就像small test一样,分别解析yin yang,并且由于第一行和第三行的原因,会打印出@ *
现在 yin:c1 yang:c2 ->(terminal |之后表示是新产生的)| @ *
现在就变成了(c1 c2)
代码就会变成这样(不要在意括号)
yin ((lambda (foo) (display "@") foo
lambda (foo) (display "*") foo
(call/cc (lambda (bar) bar))
yang (call/cc (lambda (bar) bar)
(yin yang)
刚开始我还在想他为什么会继续计算下去呢?后来觉得是因为他们都在let*中。
现在 yin :c2(为什么yin是c2吗?因为c1 apture的c2) yang:c 3(为什么yang是c3吗?重新生成的) -> :@ *| @ *(为什么不是@ * *呢?不是解析yang也会打印 * 吗? 因为yang现在还是一个continuation)
计算(c2 c3)
代码就会变成这样(不要在意括号)
yang ((lambda (foo) (display "*") foo)
(call/cc (lambda (bar) bar)
(yin yang)
yin:c1(为什么yin是c1吗?因为在c2下yin就是c1) yang:c3 -> @ * @ *| *
(c1 c3)
代码就会变成这样(不要在意括号)
yin ((lambda (foo) (display "@") foo
lambda (foo) (display "*") foo
(call/cc (lambda (bar) bar))
yang (call/cc (lambda (bar) bar)
(yin yang)
yin: c3 yang:c4 ->@ * @ * * | @ *
(c3 c4)
代码就会变成这样(不要在意括号)
yang ((lambda (foo) (display "*") foo)
(call/cc (lambda (bar) bar)
(yin yang)
yin:c2(为什么yin是c2吗?因为在c3下yin就是c2) yang:c4 -> @ * @ * * @ * |*
(c2 c4)
代码就会变成这样(不要在意括号)
yang ((lambda (foo) (display "*") foo)
(call/cc (lambda (bar) bar)
(yin yang)
yin:c1(为什么yin是c1吗?因为在c2下yin就是c1) yang:c4 -> @ * @ * * @ * * | *
(c1 c4)
代码就会变成这样(不要在意括号)
yin ((lambda (foo) (display "@") foo
lambda (foo) (display "*") foo
(call/cc (lambda (bar) bar))
yang (call/cc (lambda (bar) bar)
(yin yang)
yin:c4(为什么yin是c4吗?因为c1 apture的c4) yang:c5(重新生成的) ->@ * @ * * @ * * * | @ *
(c4 c5)
......
总结下来,关于yin有两种情况:1 capture新的continuation 2. 是一个continuation apply 一个continuation
yang也有两种情况:1. 旧的传递的 2.重新生成的
参考资料
1.柯里化的前生今世(七):first-class continuation(柯里化的前生今世(七):first-class continuation - 知乎 (zhihu.com))
2.scheme心得(1) continuation与阴阳谜题(scheme心得(1) continuation与阴阳谜题 - CodeAntenna)