- 将两个集合合并
- 询问两个元素是否在一个集合当中
- 并查集可以在近乎O(1)的时间内完成这两个操作
- 基本原理:每个集合用一棵树来表示,树根的编号就是整个集合的编号,每个节点存储它的父节点,p[x]表示x的父节点
- 如何判断树根?
- 如何求x的集合编号?
while (p[x] != x) {x = p[x]};
- 如何合并两个集合?
- px是x的集合编号,py是y的集合编号,
p[x] = y
- 优化:路径压缩
模板
朴素并查集
int p[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
p[find(a)] = find(b);
维护size的并查集
int p[N], size[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
size[find(b)] += size[find(a)];
p[find(a)] = find(b);
维护到祖宗节点距离的并查集
int p[N], d[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x)
{
int u = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[p[x]];
p[x] = u;
}
return p[x];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
d[i] = 0;
}
p[find(a)] = find(b);
d[find(a)] = distance;
练习
01 集合合并

import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = 100010;
public static int[] p = new int[N];
public static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
}
while (m-- > 0) {
String[] str2 = br.readLine().split(" ");
if (str2[0].equals("M")) {
p[find(Integer.parseInt(str2[1]))] = find(Integer.parseInt(str2[2]));
} else {
if (find(Integer.parseInt(str2[1])) == find(Integer.parseInt(str2[2]))) {
pw.println("Yes");
} else {
pw.println("No");
}
}
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
public static int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}
02 连通块中点的数量

import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = 100010;
public static int[] p = new int[N];
public static int size[] = new int[N];
public static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
while (m-- > 0) {
String[] str2 = br.readLine().split(" ");
if (str2[0].equals("C")) {
int a = Integer.parseInt(str2[1]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(str2[2]);
if (find(a) != find(b)) {
size[find(b)] += size[find(a)];
p[find(a)] = find(b);
}
} else if (str2[0].equals("Q1")) {
int a = Integer.parseInt(str2[1]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(str2[2]);
if (find(a) == find(b)) {
pw.println("Yes");
} else {
pw.println("No");
}
} else {
int a = Integer.parseInt(str2[1]);
pw.println(size[find(a)]);
}
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
public static int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}
03 食物链


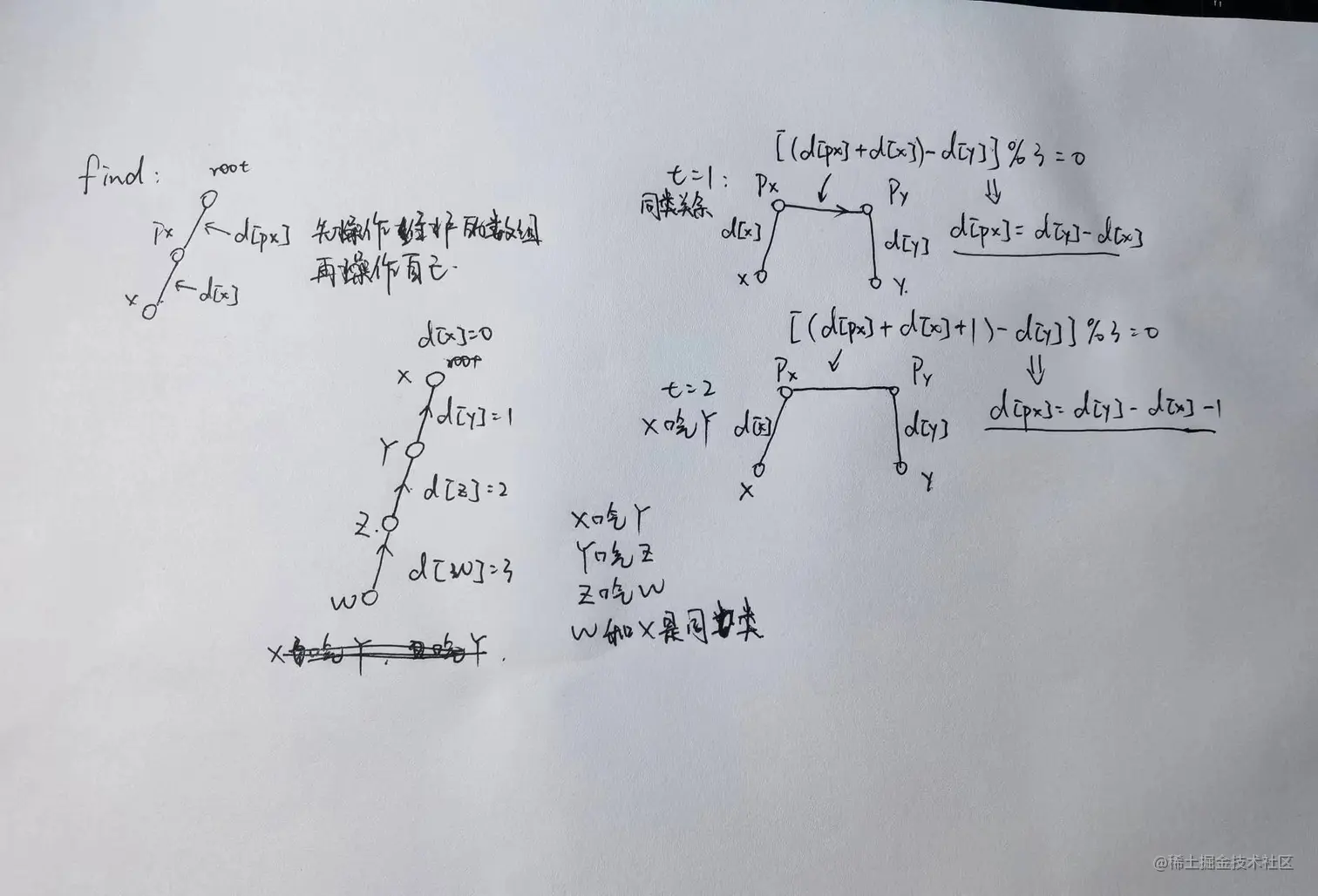
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = 50010;
public static int[] p = new int[N];
public static int[] d = new int[N];
public static int n, k;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
k = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
d[i] = 0;
}
int res = 0;
while (k-- > 0) {
String[] str2 = br.readLine().split(" ");
int t = Integer.parseInt(str2[0]);
int x = Integer.parseInt(str2[1]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(str2[2]);
if (x > n || y > n) {
res++;
} else {
int px = find(x);
int py = find(y);
if (t == 1) {
if (px == py && (d[y] - d[x]) % 3 != 0) {
res++;
} else if (px != py) {
p[px] = p[y];
d[px] = d[y] - d[x];
}
} else {
if (px == py && (d[y] - d[x] - 1) % 3 != 0) {
res++;
} else if (px != py) {
p[px] = p[y];
d[px] = d[y] - d[x] - 1;
}
}
}
}
pw.println(res);
pw.close();
br.close();
}
public static int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
int t = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[p[x]];
p[x] = t;
}
return p[x];
}
}