单项数据绑定
原/简写法
双向数据绑定 应用于表单元素
el的2种写法
data的2种写法
对象式 函数式 (组件的时候必须用函数式)
new Vue 实例对象
vue管理的函数不能写箭头函数(比如data函数),否则this不是vue实例,而是window
MVVM 【p10】
M:model 模型对应data V:视图 VM: 视图模型(ViewModel) 经常用vm代表vue实例对象
console.log(vm);
能看见vm身上所有的属性 data中所有的属性,最后都出现在了vm身上
vm身上所有的属性 及 Vue原型上所有属性,在Vue模板中都可以直接使用。
事件处理 如何传参@click="demo($event,a,b)"
1.使用v-on:xxx 或 @xxx 绑定事件,其中xxx是事件名;
2.事件的回调需要配置在methods对象中,最终会在vm上;
3.methods中配置的函数,不要用箭头函数!否则this就不是vm了;
4.methods中配置的函数,都是被Vue所管理的函数,this的指向是vm 或 组件实例对象;
5.@click="demo" 和 @click="demo($event)" 效果一致,但后者可以传参;
事件修饰符 可以连续写
1.prevent:阻止默认事件(常用)
2.stop:阻止事件冒泡(常用)
3.once:事件只触发一次(常用)
4.capture:使用事件的捕获模式
5.self:只有event.target是当前操作的元素时才触发事件
6.passive:事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕
键盘事件 最好用名称绑定事件 编码可能不同呢
常用的别名
回车 => enter
删除 => delete (捕获“删除”和“退格”键)
退出 => esc
空格 => space
换行 => tab (特殊,必须配合keydown去使用)
上 => up
下 => down
左 => left
右 => right
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup="showInfo($event)">
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.enter="showInfo($event)">
<input type="text" placeholder="按下caps-lock提示输入" @keyup.caps-lock="showInfo($event)">
tips
- 所被Vue管理的函数,最好写成普通函数,这样this的指向才是vm 或 组件实例对象。
- 所有不被Vue所管理的函数(定时器的回调函数、ajax的回调函数等、Promise的回调函数),最好写成箭头函数,
这样this的指向才是vm 或 组件实例对象。
css跟style绑定样式 案例
字符串:类名不确定
对象:多个样式,个数、名字不确定
数组:多个样式,个数、名字确定,但不知道用不用
:style="{fontSize: xxx}"其中xxx是动态值。
:style="[a,b]"其中a、b是样式对象。
<div id="demo">
<p :class="classStr">class1+class2使用字符串变量</p>
<button @click="checkClass">点击切换样式</button>
<p :class="classArr">绑定多个样式,个数名字不确定</p>
<p :class="classObj">要绑定多个样式,个数确定,名字也确定,但不确定用不用</p>
<p :style="{fontSize:sizeValue}">{fontSize:sizeValue}</p>
<p :style="[a,b]">:style="[a,b]"其中a、b是样式对象</p>
</div>
<script type='text/javascript'>
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
classStr:'',
classArr:['class1','class2'],
classObj:{
class1:true,
class2:false,
class3:true
},
sizeValue:'30px',
a:{fontSize:'20px'},
b:{color:'#911005'},
},
methods: {
checkClass(){
const index = Math.floor(Math.random(0,1)*2)+1;
this.classStr = `class${index}`;
console.log(index,this.classStr)
}
},
})
</script>
条件渲染 列表渲染 key原理
- 条件渲染 v-if (template) v-show
v-if v-else-if v-else 切换频率低的时候使用 直接移除dom 要求结构不能被打断
v-show 高频切换 仅使用样式隐藏
v-if 元素可能无法获取到 v-show可以
对结构破坏,为了v-if在外层加div 可以使用template去替代,就不会有多余的元素了
/* v-for="(item,index) in xxx" :key="index" 遍历对象 数组 字符串 指定次数 */
<div id="demo">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in persons" ::key="index">{{p.id}}{{p.name}}{{p.age}}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="(c,index) in car" ::key="index">{{c}}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="(str,index) in str" ::key="index">{{str}}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="(number,index) of 5" :key="index">
{{index}}-{{number}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type='text/javascript'>
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
persons: [{
id: '001',
name: '张三',
age: 18
},
{
id: '002',
name: '李四',
age: 19
},
{
id: '003',
name: '王五',
age: 20
}
],
car: {
name: '奥迪A8',
price: '70万',
color: '黑色'
},
str: 'hello'
}
})
</script>
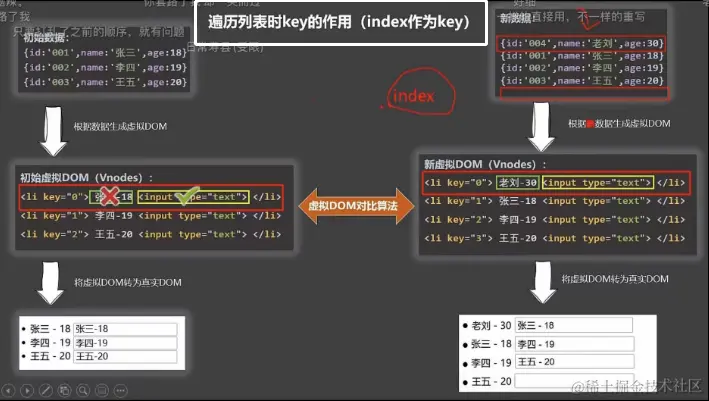
【用index作为key】
1.如果对数据进行破坏顺序的操作 会导致数据残留导致dom渲染错乱
因为index重新排序01234 虚拟dom保持之前index相同的dom(比如这里的input结构并没有不同所以会保留原来的dom)
2.并且数据没有复用 所以效率低
因为0123对应的文本 张三李四王五都变了 所以会重新渲染数据
ps:如果不写key那么vue补的key就是循环的那个index作为key
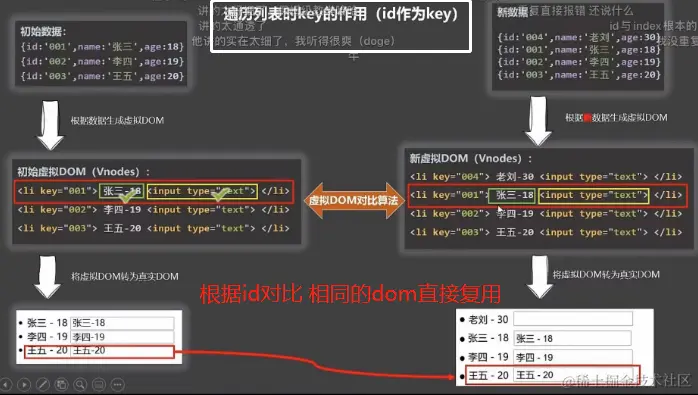
【用唯一标识作为key】
新虚拟dom取出第一个id 去旧的虚拟dom找id diff算法 找不到的话就重新生成 找的到的话就复用
所以效率高 且不会数据错乱 key值是唯一标识id
ps:身份证号等唯一标识
列表渲染 过滤(watch computed) 排序 案例
<div id="demo">
<input type="text" v-model="keyWord">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in filterPerson">{{item.id}}{{item.name}}{{item.age}}{{item.sex}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type='text/javascript'>
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
keyWord: '',
persons: [{
id: '001',
name: '马冬梅',
age: 19,
sex: '女'
},
{
id: '002',
name: '周冬雨',
age: 20,
sex: '女'
},
{
id: '003',
name: '周杰伦',
age: 21,
sex: '男'
},
{
id: '004',
name: '温兆伦',
age: 22,
sex: '男'
}
],
filterPerson: []
},
watch: {
keyWord: {
immediate: true,
handler(key) {
const person = this.persons.filter((item) => {
return item.name.includes(key)
})
this.filterPerson = person;
console.log(person)
}
}
},
})
</script>
<div id="demo">
<input type="text" v-model="keyWord">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in filterPerson">{{item.id}}{{item.name}}{{item.age}}{{item.sex}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type='text/javascript'>
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
keyWord: '',
persons: [{
id: '001',
name: '马冬梅',
age: 19,
sex: '女'
},
{
id: '002',
name: '周冬雨',
age: 20,
sex: '女'
},
{
id: '003',
name: '周杰伦',
age: 21,
sex: '男'
},
{
id: '004',
name: '温兆伦',
age: 22,
sex: '男'
}
],
},
computed: {
filterPerson() {
return this.persons.filter((item) => {
return item.name.indexOf(this.keyWord) !== -1;
})
}
}
})
</script>
<div id="root">
<h2>人员列表</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入名字" v-model="keyWord">
<button @click="sortType = 2">年龄升序</button>
<button @click="sortType = 1">年龄降序</button>
<button @click="sortType = 0">原顺序</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) of filPerons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}-{{p.sex}}
<input type="text">
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
keyWord: '',
sortNum:0,
persons: [{
id: '001',
name: '马冬梅',
age: 19,
sex: '女'
},
{
id: '002',
name: '周冬雨',
age: 20,
sex: '女'
},
{
id: '003',
name: '周杰伦',
age: 21,
sex: '男'
},
{
id: '004',
name: '温兆伦',
age: 22,
sex: '男'
}
],
},
computed: {
filterPerson() {
const arr = this.persons.filter((item) => {
return item.name.indexOf(this.keyWord) !== -1;
})
if(this.sortNum){
arr.sort((p1,p2)=>{
return this.sortNum === 1 ? p2.age-p1.age : p1.age-p2.age
})
}
return arr
}
}
})
</script>
收集表单+过滤器
收集表单数据:
若:<input type="text"/>,则v-model收集的是value值,用户输入的就是value值。
若:<input type="radio"/>,则v-model收集的是value值,且要给标签配置value值。
若:<input type="checkbox"/>
1.没有配置input的value属性,那么收集的就是checked(勾选 or 未勾选,是布尔值)
2.配置input的value属性:
(1)v-model的初始值是非数组,那么收集的就是checked(勾选 or 未勾选,是布尔值)
(2)v-model的初始值是数组,那么收集的的就是value组成的数组
备注:v-model的三个修饰符:
lazy:失去焦点再收集数据 v-model.lazy="userInfo.other"
number:输入字符串转为有效的数字 type="number" v-model.number="userInfo.age"
trim:输入首尾空格过滤 v-model.trim="userInfo.account"
- 1.收集表单
- 表单元素checkbox radio 没有输入框的
- 需要配置个默认的value值,才能双向绑定
- 如果是单选框只需要是否选择就不用配置 value 直接就给个'' 会返回true和false
<div id="demo">
<form @submit.prevent="demo">
账号:<input type="text" v-model.trim="userInfo.account"> <br /><br />
密码:<input type="password" v-model="userInfo.password"> <br /><br />
年龄:<input type="number" v-model.number="userInfo.age"> <br /><br />
性别:
男<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="userInfo.sex" value="male">
女<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="userInfo.sex" value="female"> <br /><br />
爱好:
学习<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.hobby" value="study">
打游戏<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.hobby" value="game">
吃饭<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.hobby" value="eat">
<br /><br />
所属校区
<select v-model="userInfo.city">
<option value="">请选择校区</option>
<option value="beijing">北京</option>
<option value="shanghai">上海</option>
<option value="shenzhen">深圳</option>
<option value="wuhan">武汉</option>
</select>
<br /><br />
其他信息:
<textarea v-model.lazy="userInfo.other"></textarea> <br /><br />
<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.agree">阅读并接受<a href="http://www.atguigu.com">《用户协议》</a>
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</div>
<script type='text/javascript'>
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
userInfo: {
account: '',
password: '',
age: 18,
sex: 'female',
hobby: [],
city: 'beijing',
other: '',
agree: ''
}
},
methods: {
demo() {
console.log(JSON.stringify(this.userInfo))
}
}
})
</script>
定义:对要显示的数据进行特定格式化后再显示(适用于一些简单逻辑的处理)。
语法:
1.注册过滤器:Vue.filter(name,callback) 或 new Vue{filters:{}}
2.使用过滤器:{{ xxx | 过滤器名}} 或 v-bind:属性 = "xxx | 过滤器名"
备注:
1.过滤器也可以接收额外参数、多个过滤器也可以串联
2.并没有改变原本的数据, 是产生新的对应的数据
<div id="demo">
<p>{{newtime}}</p>
<p>{{getTime()}}</p>
<p>{{time | timeFormater}}</p>
<p>{{time | timeFormater('YYYY_MM_DD') | mySlice}}</p>
</div>
<div id="root">
<h2>{{msg | mySlice}}</h2>
</div>
<script type='text/javascript'>
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.filter('mySlice', function (value) {
return value.slice(0, 4)
})
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
time: 1621561377603,
msg: '你好,尚硅谷'
},
computed: {
newtime() {
return dayjs(this.time).format('YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss')
}
},
methods: {
getTime() {
return dayjs(this.time).format('YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss')
}
},
filters: {
timeFormater(value, str = 'YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss') {
return dayjs(value).format(str)
},
mySlice(value) {
return value.slice(0, 4)
}
}
})
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
msg: 'hello,atguigu!'
}
})
</script>
vue指令
new Vue({
directives:{指令名:配置对象} 或
directives{指令名:回调函数}
})
<div id="demo">
<div>
<p>当前n是 <span v-text="n"></span></p>
<p>放大10倍后的n值是 <span v-big="n"></span></p>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
</div>
<input type="text" v-fbind:value="n">
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
el: "#demo",
data: {
n: 1,
},
directives: {
"big":function(element, binding) {
console.log(element, binding, binding.value, "sss");
element.innerText = binding.value * 10;
},
fbind:{
bind(element,binding){
console.log('bind')
element.value=binding.value
},
inserted(element,binding){
console.log('inserted')
element.focus()
},
update(element,binding){
console.log('update')
element.focus()
element.value=binding.value
},
}
},
});
</script>
就是一个命名的问题 定义的时候用-分隔 v-big-number
directives里面则是 'big-number': function (element, binding){}
<div id="demo">
<div>
<p>当前n是 <span v-text="n"></span></p>
<p>放大10倍后的n值是 <span v-big-number="n"></span></p>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
el: "#demo",
data: {
n: 1,
},
directives: {
'big-number': function (element, binding) {
console.log('big',this);
console.log(element, binding, binding.value, "sss");
element.innerText = binding.value * 10;
},
},
});
</script>
Vue.directive(指令名,配置对象) 或 Vue.directive(指令名,回调函数)
Vue.directive('fbind',{
bind(element,binding){
element.value = binding.value
},
inserted(element,binding){
element.focus()
},
update(element,binding){
element.value = binding.value
}
})
VueComponent 构造函数 【p58听不懂】
一个重要的内置关系 【p59听不懂】