- 单链表中最常用的是邻接表
- 邻接表就是n个单链表
- 邻接表最主要的用途就是存储树与图
- 这里主要用数组来模拟链表,也叫静态链表
模板一
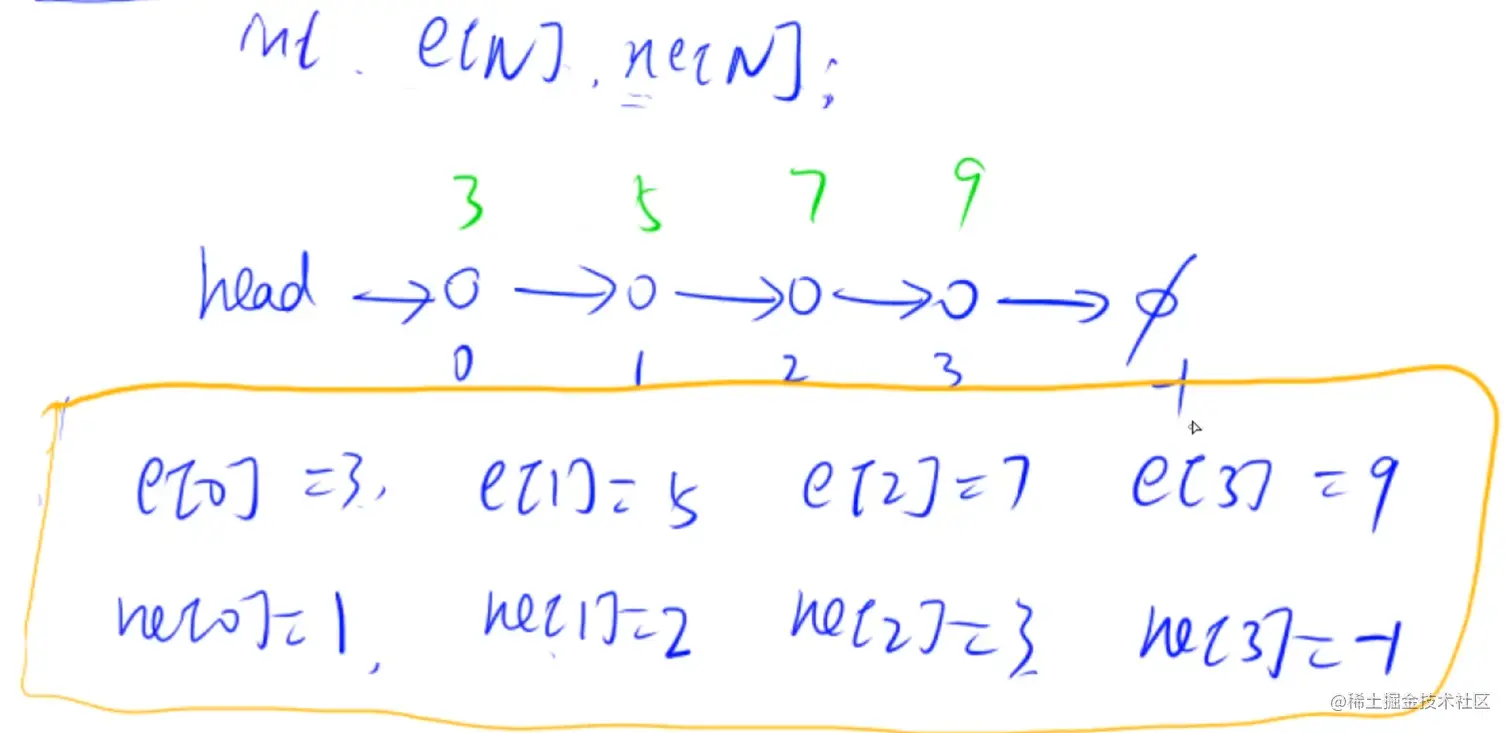
- 注意,这里面的k - 1代表第k个插入的元素,因为idx是从0开始的
- C++
int head, e[N], ne[N], idx;
void init()
{
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
void insert_to_head(int a)
{
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = head, head = idx ++ ;
}
void insert(int k, int a)
{
e[idx] = a;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx ++;
}
void remove_head()
{
head = ne[head];
}
void remove(int k) {
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
cout << e[i] << ' ';
}
public static int head, idx;
public static int[] e = new int[N];
public static int[] ne = new int[N];
public static void init() {
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
public static void insert_to_head(int a) {
e[idx] = a;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx++;
}
public static void insert(int k, int a) {
e[idx] = a;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
public static void remove_head() {
head = ne[head];
}
public static void remove(int k) {
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]]
}
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
pw.print(e[i] + " ");
}
模板二
- 改良版:将head存入ne[0]中,这样可以将添加和删除方法进行优化
- 注意:改良版中的k指的是第k个加入链表中的元素
- C++
int e[N], ne[N], idx;
void init()
{
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
void insert_to_head(int a)
{
e[idx] = a;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx ++;
}
void insert(int k, int a)
{
e[idx] = a;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx ++;
}
void remove_head()
{
head = ne[head];
}
void remove(int k) {
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
cout << e[i] << ' ';
}
public static int idx;
public static int[] e = new int[N];
public static int[] ne = new int[N];
public static void init() {
ne[0] = -1;
idx = 1;
}
public static void insert(int k, int a) {
e[idx] = a;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
public static void insert_to_head(int a) {
insert(0, a);
}
public static void remove(int k) {
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]]
}
public static void remove_head() {
remove(0);
}
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
pw.print(e[i] + " ");
}
练习
01 单链表

import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = 100010;
public static int M;
public static int head = -1;
public static int idx = 0;
public static int[] e = new int[N];
public static int[] ne = new int[N];
public static void insert_to_head(int x) {
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx++;
}
public static void insert(int k, int x) {
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
public static void remove_head() {
head = ne[head];
}
public static void remove(int k) {
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
M = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
while (M-- > 0) {
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
if (str1[0].equals("H")) {
insert_to_head(Integer.parseInt(str1[1]));
} else if (str1[0].equals("I")) {
insert(Integer.parseInt(str1[1]) - 1, Integer.parseInt(str1[2]));
} else {
int k = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
if (k == 0) {
remove_head();
} else {
remove(k - 1);
}
}
}
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
pw.print(e[i] + " ");
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = 100010;
public static int M;
public static int[] e = new int[N];
public static int[] ne = new int[N];
public static int idx;
public static void init() {
idx = 1;
ne[0] = -1;
}
public static void insert(int k, int x) {
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
public static void remove(int k) {
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
M = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
init();
while (M-- > 0) {
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
if (str1[0].equals("H")) {
insert(0, Integer.parseInt(str1[1]));
} else if (str1[0].equals("I")) {
insert(Integer.parseInt(str1[1]), Integer.parseInt(str1[2]));
} else {
remove(Integer.parseInt(str1[1]));
}
}
for (int i = ne[0]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
pw.print(e[i] + " ");
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
}