模板
- 双指针算法的核心思想就是将两个循环嵌套的朴素算法的时间复杂度o(n^2^)优化成o(n)
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
while (j < i && check(i, j)) {
j ++ ;
}
}
- 常见问题分类
- 对于一个序列,用两个指针维护一段区间
- 对于两个序列,维护某种次序,比如归并排序中合并两个有序序列的操作
练习
01 最长连续不重复子序列
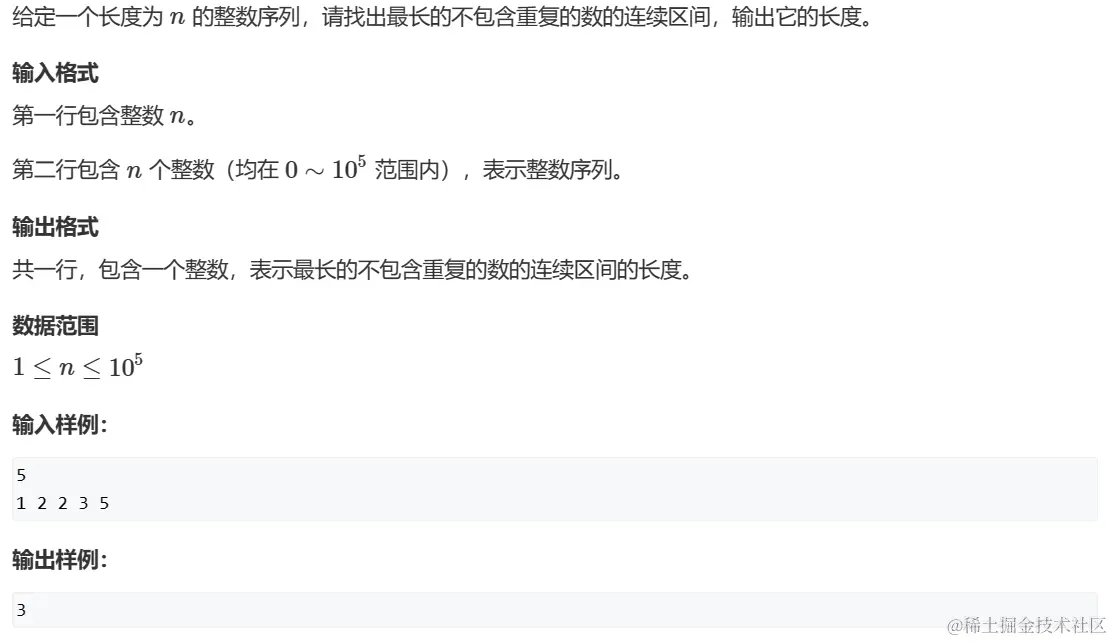
- 题解
- i指针记录序列的尾部
- j指针记录序列的头部
- 不仅i和j指针体现了双指针的算法,在check步骤中运用的滑动窗口也体现了双指针的思想
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = 100010;
public static int[] q = new int[N];
public static int[] s = new int[N];
public static int n;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
q[i] = Integer.parseInt(str1[i]);
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {
s[q[i]]++;
while (j < i && s[q[i]] > 1) {
s[q[j++]]--;
}
res = i - j + 1 > res ? i - j + 1 : res;
}
pw.println(res);
pw.close();
br.close();
}
}
02 数组元素的目标和

import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = 100010;
public static int[] A = new int[N];
public static int[] B = new int[N];
public static int m, n, x;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
x = Integer.parseInt(str1[2]);
String[] str2 = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
A[i] = Integer.parseInt(str2[i]);
}
String[] str3 = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
B[i] = Integer.parseInt(str3[i]);
}
for (int i = n - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--) {
while (j < m && A[i] + B[j] < x) {
j++;
}
if (A[i] + B[j] == x) {
pw.println(i + " " + j);
break;
}
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
}
03 判断子序列

import java.io.*;
public class Main{
public static final int N = 100010;
public static int[] a = new int[N];
public static int[] b = new int[N];
public static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
String[] str2 = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = Integer.parseInt(str2[i]);
}
String[] str3 = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
b[i] = Integer.parseInt(str3[i]);
}
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (i < n && a[i] == b[j]) {
i++;
}
}
if (i == n) {
pw.println("Yes");
} else {
pw.println("No");
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
}