模板
一维差分
- 给出一个数组S构造出它的差分数组a使得
S[i] = a[1] + … +a[i]
- 此时我们如果想在原数组S的某个区间上进行批量的数据修改,可以只在其差分数组中修改区间端点的值就行
- 这样时间复杂度就由o(n)降到了o(1)
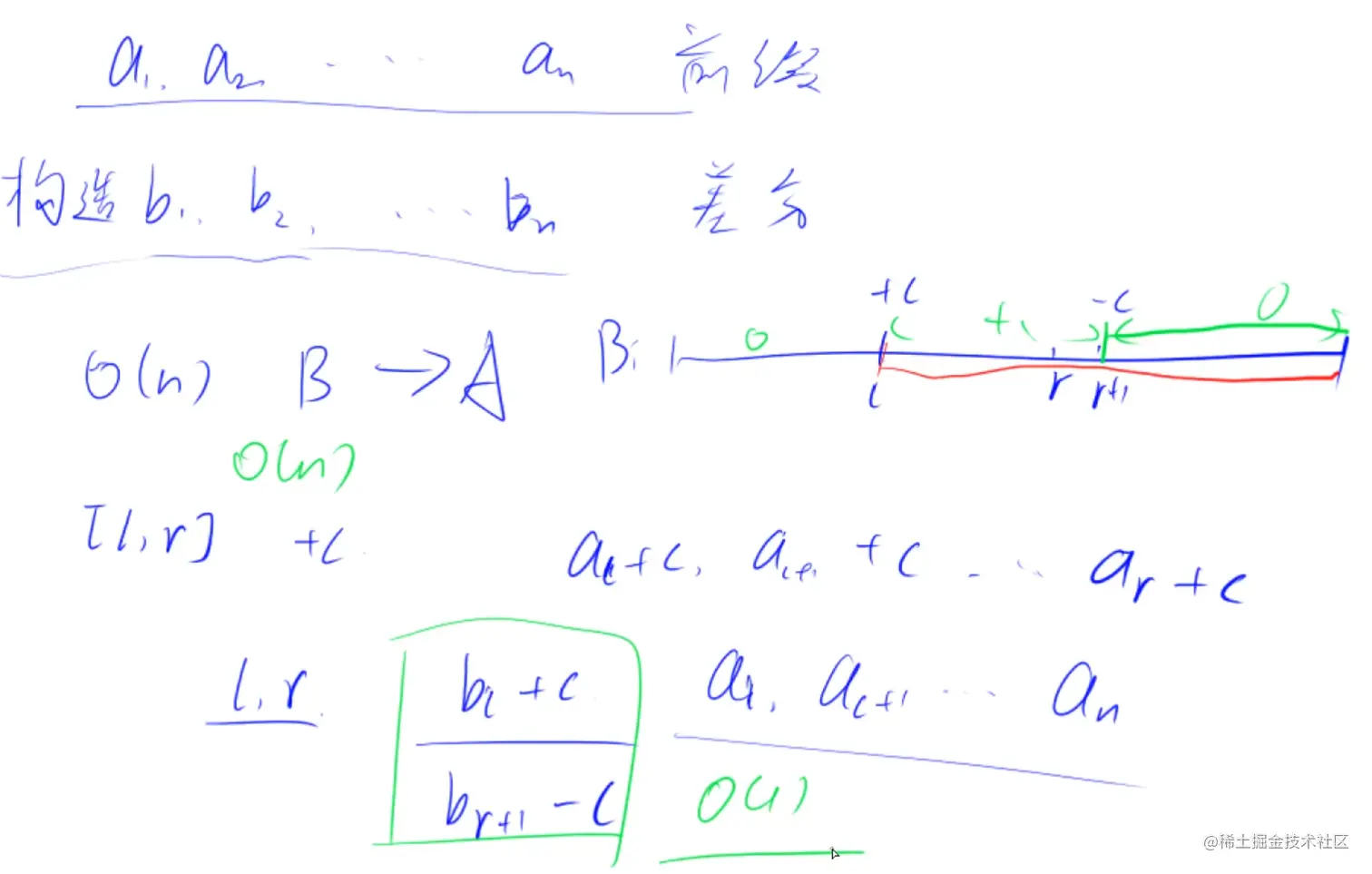
构造差分数组:a[i] = S[i] - S[i - 1]
给区间[l, r]中的每个数加上c:a[l] += c, a[r + 1] -= c
或者构造一个insert方法:
public static void insert(int l, int r, int c) {
a[l] += c;
a[r + 1] -= c;
}
这个方法还可以巧妙地构造差分数组:
insert(i, i, S[i]);
二维差分

构造差分矩阵:a[i][j] = S[i][j] - S[i - 1][j] - S[i][j - 1] + S[i - 1][j - 1]
给以(x1, y1)为左上角,(x2, y2)为右下角的子矩阵中的所有元素加上c:
S[x1, y1] += c, S[x2 + 1, y1] -= c, S[x1, y2 + 1] -= c, S[x2 + 1, y2 + 1] += c
或者构造一个insert方法:
public static void insert(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int c) {
S[x1, y1] += c;
S[x2 + 1, y1] -= c;
S[x1, y2 - 1] -= c;
S[x2 + 1, y2 += 1] += c;
}
这个方法还可以巧妙地构造差分数组:
insert(i, j, i, j, S[i][j]);
练习
01 差分

import java.io.*;
public class Main{
public static final int N = 100010;
public static int[] S = new int[N];
public static int[] a = new int[N];
public static int n;
public static int m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
String[] str2 = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
S[i] = Integer.parseInt(str2[i - 1]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
insert(i, i, S[i]);
}
while (m-- > 0) {
String[] str3 = br.readLine().split(" ");
int l = Integer.parseInt(str3[0]);
int r = Integer.parseInt(str3[1]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(str3[2]);
insert(l, r, c);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
S[i] = S[i - 1] + a[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
pw.print(S[i] + " ");
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
public static void insert(int l, int r, int c) {
a[l] += c;
a[r + 1] -= c;
}
}
02 差分矩阵

import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = 1010;
public static int[][] a = new int[N][N];
public static int[][] S = new int[N][N];
public static int n, m, q;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String[] str1 = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
q = Integer.parseInt(str1[2]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
String[] str2 = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
S[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(str2[j - 1]);
insert(i, j, i, j, S[i][j]);
}
}
while (q-- > 0) {
String[] str3 = br.readLine().split(" ");
int x1 = Integer.parseInt(str3[0]);
int y1 = Integer.parseInt(str3[1]);
int x2 = Integer.parseInt(str3[2]);
int y2 = Integer.parseInt(str3[3]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(str3[4]);
insert(x1, y1, x2, y2, c);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
S[i][j] = S[i - 1][j] + S[i][j - 1] - S[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i][j];
pw.print(S[i][j] + " ");
}
pw.println();
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
public static void insert(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int c) {
a[x1][y1] += c;
a[x2 + 1][y1] -= c;
a[x1][y2 + 1] -= c;
a[x2 + 1][y2 + 1] += c;
}
}