值和引用类型
哪些类型是值类型?哪些类型是引用类型
- 值类型:String Number Boolean Symbol
- 引用类型 JSON Array null
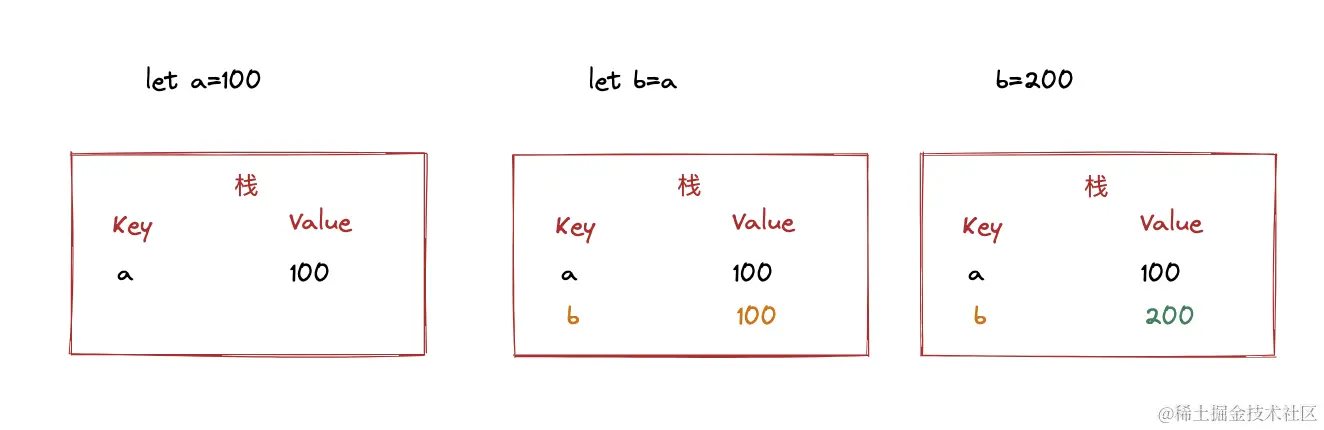
演示值与引用类型的堆栈
值类型
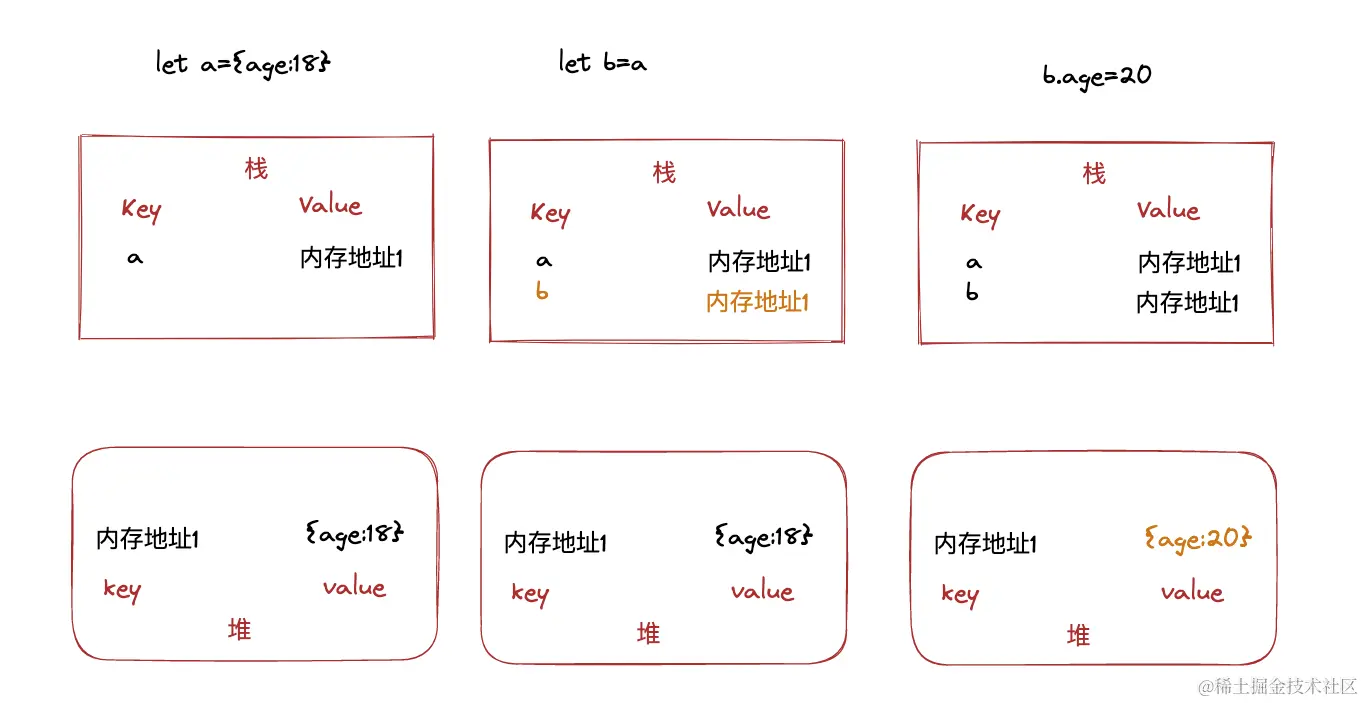
引用类型
变种提问
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// //内存地址不同
let a = 100
let b = a
b = 200
console.log(a); //100
//指向同一个内存地址
let a1 = {age:18}
let b1 = a1
b1.age = 20
console.log(a1);//20
//变种提问
const a = {x:100,y:200}
const b = a
let c = a.x
b.x = 300
console.log(a);//300因为内存地址相同
</script>
</body>
</html>
手写深拷贝
如何实现深拷贝
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj))
- 不能存放函数 时间对象 正则....
- 递归 lodash.cloneDeep 推荐
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const obj1 = {
name:'张三',
age:18,
address:{
city:'北京'
},
hobby:['打篮球','踢足球'],
fn:function(){
console.log(12321);
}
}
const obj2 = deepclone(obj1)
//内存指向不同源数据不会改变
obj2.age = 20
obj2.address.city = "上海"
console.log(obj1);
console.log(obj2);
function deepclone(obj){
if(typeof obj !=='object'||obj==null){
return obj
}
let res = obj instanceof Array ?[]:{}
for(let key in obj){
//object.hasOwnProper('属性名') 方法用于判断否个对象中是否有指定的属性
if(obj.hasOwnProperty(key)){
res[key] = deepclone(obj[key])
}
}
return res
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
何时使用==何时使用===
== 隐式类型转换
100 == '100'
0 == ''
0 == false
false == ''
null == undefined
只有使用 == null使用双等
if (obj === null || obj === undefined) {
}
示例代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//隐式转换类型
console.log(100 == "100");
console.log(0 == "");
console.log(0 == false);
console.log("" == false);
console.log(null == undefined);
let obj = {age:18}
//只有判断obj == null时才用双等
console.log(obj == null);
console.log(obj === null || obj === undefined);
</script>
</body>
</html>
哪些是truly变量哪些是falsely变量
什么是truly变量 什么是falsely变量
- truly:!!val === true
- falsely变量:!!val===false
除了falsely变量都是 truly变量
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//truly变量:两次取反后结果是true就是truly变量
//falsely变量:两次取反后结果是false就是falsely变量
/*
空字符串
数字0
null
undefined
NaN
注:以上全是falsely变量,其余的全是truly变量
*/
console.log(!!"" === false);
console.log(!!NaN === false);
console.log(!!0 === false);
console.log(!!undefined === false);
console.log(!!null === false);
</script>
</body>
</html>
原型和原型链
复习class基础语法
- class
- construct
- extends
- super
- instanceof
什么是原型
- 每个class类都有一个prototype 每个实例都有隐式 proto
- 实例的__proto___都指向对应class类的prototype
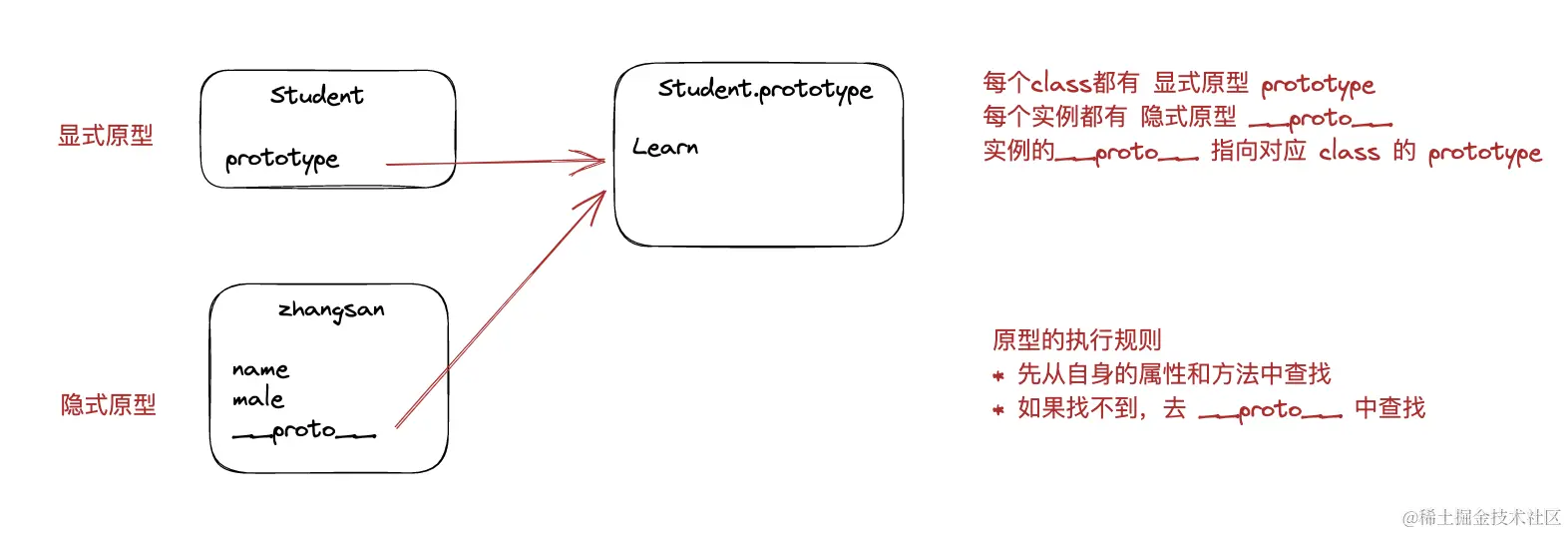
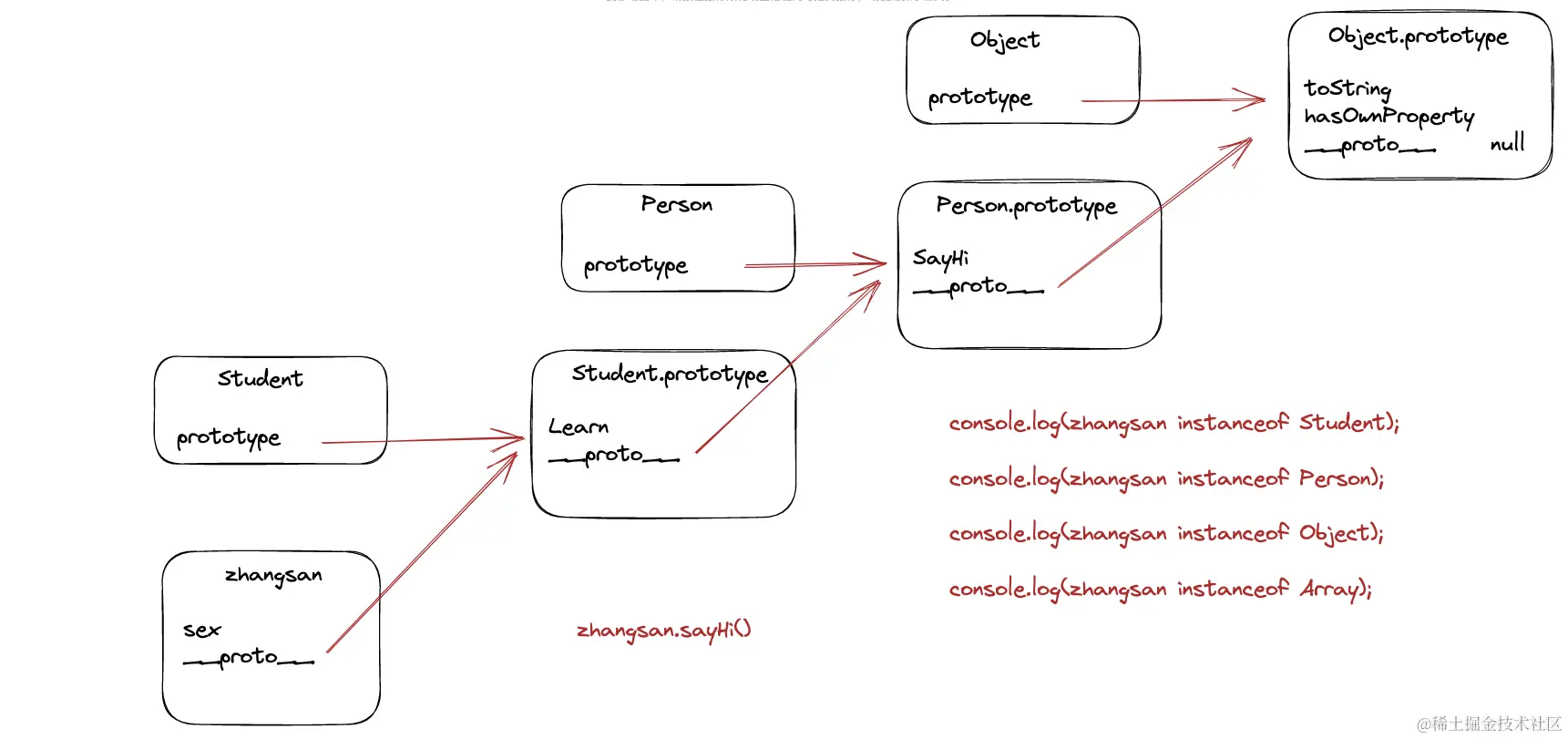
什么是原型链
- 每一个对象都有一个
隐式原型,指的就是__proto__,也就是通过它往上查找原型上的属性和方法,如果还没有那么会继续向上查找,直到找到最顶层的Object对象,它的__proto__是Null,这样一层一层通过__proto__向上查找的过程就是原型链
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//声明类
class Person{
constructor(name,age){
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
sayHello(){
console.log(`你好${this.name}`);
console.log(`你好${this.name}${this.age}岁`);
}
}
//实例化类
let zhangsan = new Person('zhangsan',18)
console.log(zhangsan.name);
console.log(zhangsan.age);
zhangsan.sayHello()
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//声明类
class Proson{
constructor(name,age){
this.name=name;
this.age = age
}
sayHello(){
console.log(`你好${this.name}`);
}
}
//继承父级类
class Student extends Proson{
//继承父级类子级的constructor中必须要有父级的参数,也可以有自己的参数和方法
constructor(name,age,sex){
//super方法 调用父级类
super(name,age)
this.sex = sex
}
fn(){
console.log(`你好${this.name}${this.sex}`);
}
}
//实例化
let zhangsan = new Student("zhangsan",18,"男")
zhangsan.sayHello()
zhangsan.fn()
//instanceof方法用来判断一个构造函数的prototype属性是否在另一个要检测对象的原型链上
console.log(zhangsan instanceof Proson);//true
console.log(zhangsan instanceof Student);//true
console.log(zhangsan instanceof Object);//true
console.log(Proson instanceof Object);//true
console.log(zhangsan instanceof Array);//false
</script>
</body>
</html>