设计原则与常用的设计模式
项目地址
设计原则:先设计,后模式
- 即按照一种思路或者标准来实现功能
- 功能相同,可以有不同设计方案来实现
- 伴随着需求增加,设计的作用才能体现出来
SOLID 五大设计原则
S - 单一职责原则
- 一个程序只做好一件事
- 如果功能过于复杂就拆分开,每个部分保持独立
O - 开放封闭原则
- 对拓展开放,对修改封闭
- 增加需求时,拓展新代码来解决,而非改动
L - 李氏置换原则
- 子类能覆盖父类
- 父类能出现的地方子类就能出现
- 前端应用较少
I - 接口独立原则
- 保持接口的单一独立,避免出现“胖接口”
- 类似于单一职责原则,这里更关注接口
D - 依赖倒置原则
- 面向接口编程,依赖于抽象而不依赖于实例
- 使用方只关注接口而不关注具体类的实现
设计原则总结
- SO 体现较多,详细研究
- LID 体现较少,但也要了解其用意
示例:用 Promise 来说明
- 单一职责原则:每个
then中的逻辑只做好一件事
- 开放封闭原则:对拓展开放、对修改封闭(如果新增需求,拓展
then)
function loadImg(src: string) {
const promise = new Promise<HTMLImageElement>((resolve, reject) => {
const img = document.createElement('img');
img.onload = function () {
resolve(img);
};
img.onerror = function () {
reject('图片加载失败');
};
img.src = src;
});
return promise;
}
const src = 'https://t7.baidu.com/it/u=1595072465,3644073269&fm=193&f=GIF';
const res = loadImg(src);
res
.then((img: HTMLImageElement) => {
console.log('width: ', img.width);
return img;
})
.then((img) => {
console.log('height: ', img.height);
return img;
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
export {};
23 种设计模式
| 类型 | 模式 |
|---|
| 创建型 | 工厂模式(简单工厂(建造者模式),工厂方法模式,抽象工厂模式)、单例模式、原型模式 |
| 组合型 | 适配器模式、装饰器模式、代理模式、外观模式、桥接模式、组合模式、享元模式 |
| 行为型-1 | 策略模式、模版方式模式、观察者模式、迭代器模式、职责连模式、命令模式 |
| 行为型-2 | 备忘录模式、状态模式、访问者模式、中介者模式、解释器模式 |
经典题目
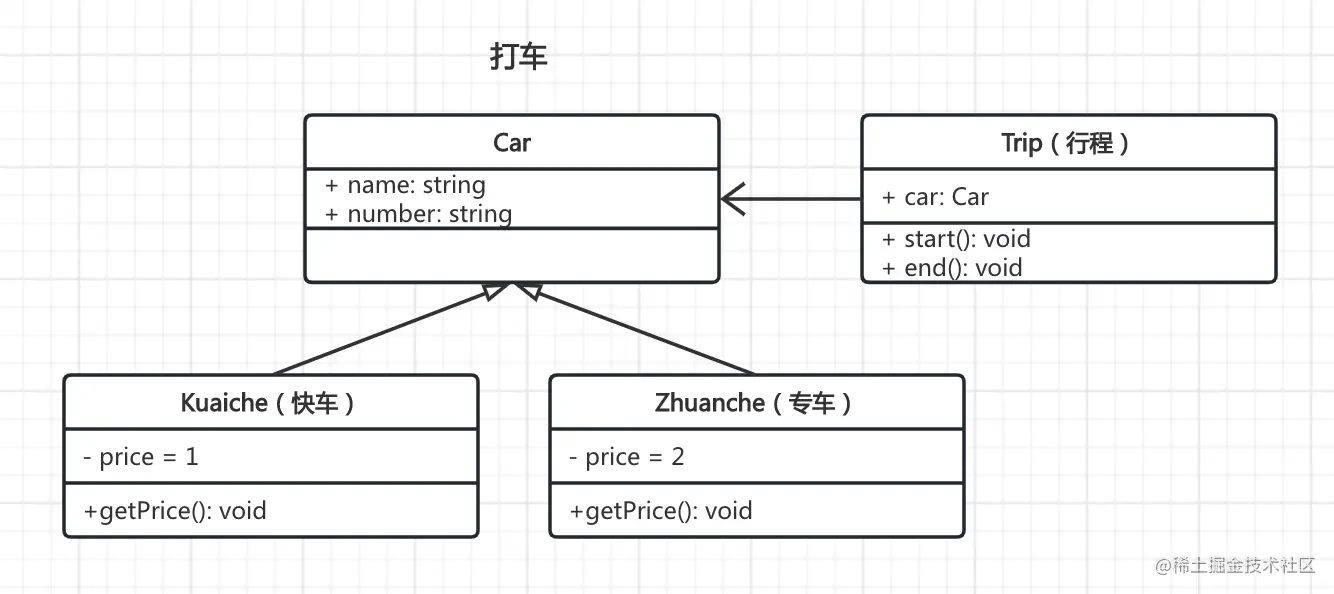
第一题
- 打车时,可以打专车或者快车。任何车都有车牌号和名称
- 不同车价格不同,快车每公里 1 元,专车每公里 2 元
- 行程开始时,显示车辆信息
- 行程结束时,显示打车金额(假定行程就 5 公里)
画出 UML 类图
代码演示
class Car {
name: string;
number: string;
constructor(name: string, number: string) {
this.name = name;
this.number = number;
}
}
class Kuaiche extends Car {
private price = 1;
constructor(name: string, number: string) {
super(name, number);
}
getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
}
class Zhuanche extends Car {
private price = 2;
constructor(name: string, number: string) {
super(name, number);
}
getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
}
type CarType = Kuaiche | Zhuanche;
class Trip {
car: CarType;
constructor(car: CarType) {
this.car = car;
}
start() {
console.log(`行程开始,车辆型号:${this.car.name},车牌号:${this.car.number}`);
}
end() {
console.log(`行程结束,价格:${this.car.getPrice() * 5}`);
}
}
const car = new Kuaiche('Toyota', '粤A0001');
const trip = new Trip(car);
trip.start();
trip.end();
export {};
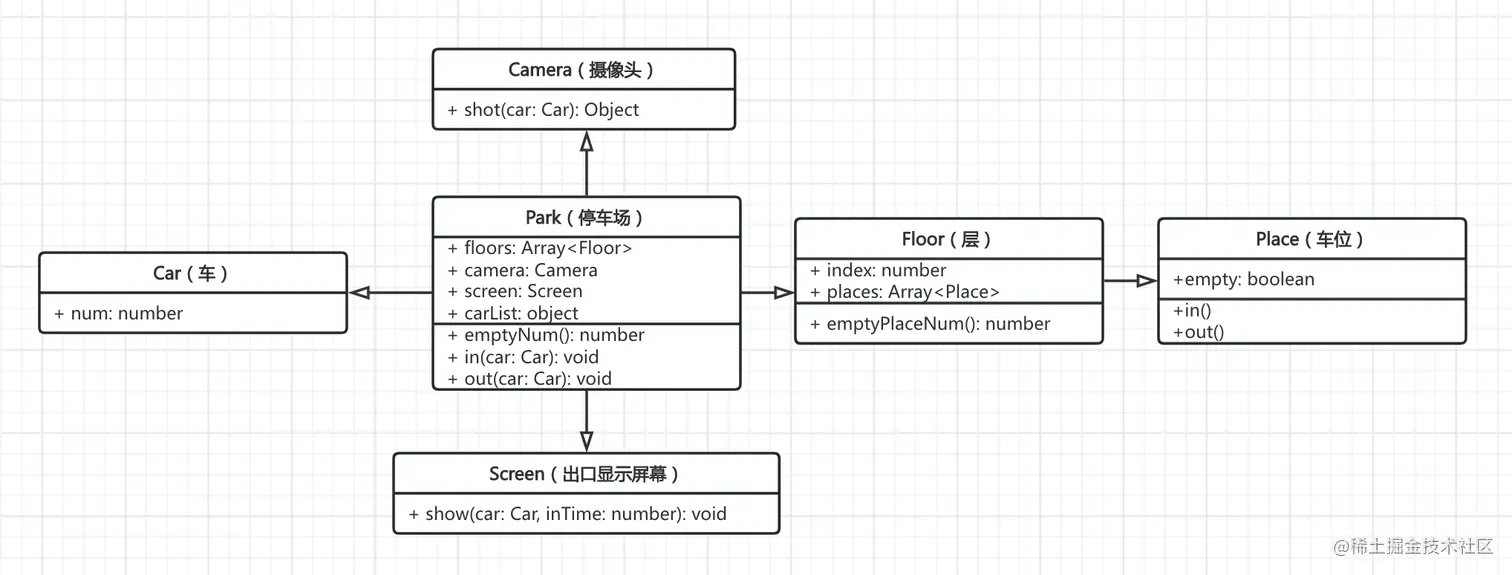
第二题
- 某停车场,分 3 层,每层 100 车位
- 每个车位都能监控到车辆的驶入和离开
- 车辆进入前,显示每层的空余车位数量
- 车辆进入时,摄像头可识别车牌号和时间
- 车辆出来时,出口显示器显示车牌号和停车时长
UML 类图
代码演示
class Place {
empty: boolean;
constructor() {
this.empty = true;
}
in() {
this.empty = false;
}
out() {
this.empty = true;
}
}
class Floor {
index: number;
places: Place[];
constructor(index: number, places: Place[]) {
this.index = index;
this.places = places || [];
}
emptyPlaceNum() {
let num = 0;
this.places.forEach((p) => {
if (p.empty) {
num = num + 1;
}
});
return num;
}
}
class Car {
num: number;
constructor(num: number) {
this.num = num;
}
}
class Camera {
shot(car: Car) {
return {
num: car.num,
inTime: Date.now(),
};
}
}
class Screen {
show(car: Car, inTime: number) {
console.log('车牌号:', car.num);
console.log('停车时间:', Date.now() - inTime);
}
}
class Park {
floors: Floor[];
camera: Camera;
screen: Screen;
carList: any;
constructor(floors: Floor[]) {
this.floors = floors || [];
this.camera = new Camera();
this.screen = new Screen();
this.carList = {};
}
in(car: Car) {
const info = this.camera.shot(car);
const i = parseInt((Math.random() * 100) % 100);
const place = this.floors[0].places[i];
place.in();
info.place = place;
this.carList[car.num] = info;
}
out(car: Car) {
const info = this.carList[car.num];
const place = info.place;
place.out();
this.screen.show(car, info.inTime);
delete this.carList[car.num];
}
emptyNum() {
return this.floors
.map((floor) => {
return `${floor.index} 层还有 ${floor.emptyPlaceNum()} 个空闲车位`;
})
.join('\n');
}
}
const floors = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
const places = [];
for (let j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
places[j] = new Place();
}
floors[i] = new Floor(i + 1, places);
}
const park = new Park(floors);
const car1 = new Car(100);
const car2 = new Car(200);
const car3 = new Car(300);
console.log('第一辆车进入');
console.log(park.emptyNum());
park.in(car1);
console.log('第二辆车进入');
console.log(park.emptyNum());
park.in(car2);
console.log('第一辆车离开');
console.log(park.emptyNum());
park.out(car1);
console.log('第二辆车离开');
console.log(park.emptyNum());
park.out(car2);
console.log('第三辆车进入');
console.log(park.emptyNum());
park.in(car3);
console.log('第三辆车离开');
console.log(park.emptyNum());
park.out(car3);
export {};