上一篇:Elasticsearch8.5.3源码分析(3)-Get数据读取过程 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
总述
创建和更新文档的API和对应的处理类如下:
| API Path | Method | RestHandler | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| /{index}/_update/{id} | POST | RestUpdateAction | 编写脚本更新文档,支持部分更新 |
| /{index}/_doc/{id} | POST | RestIndexAction | 创建或全量更新文档 |
| /{index}/_doc/{id} | PUT | RestIndexAction | 创建或全量更新文档 |
| /{index}/_create/{id} | POST | RestIndexAction.CreateHandler | 创建文档 |
| /{index}/_create/{id} | PUT | RestIndexAction.CreateHandler | 创建文档 |
| /{index}/_doc | POST | RestIndexAction.AutoIdHandler | 系统自动生成文档主键ID |
| /_bulk | POST | RestBulkAction | 任意索引批处理 |
| /_bulk | PUT | RestBulkAction | 任意索引批处理 |
| /{index}/_bulk | POST | RestBulkAction | 指定索引批处理 |
| /{index}/_bulk | PUT | RestBulkAction | 指定索引批处理 |
这里以文档创建API 'POST /{index}/_create/{id}' 来分析数据写入的流程。其它API大同小异。
写数据协调过程
图中标注了流程中的核心方法。
- HTTP Rest API请求由RestController统一接收,然后根据路径匹配转发给相应用的RestHandler接口实现类处理。
- NodeClient:拿到RestHandler对应的TransportAction。通过TaskManager注册并执行TransportAction。
- TransportBulkAction.doInternalExecute方法负责创建索引。
- BulkOperation.doRun 将请求按分片分组,同一个分片的请求,合并成一个。
- ReroutePhase.doRun 根据主分片所处节点,将请求重新路由分发。
TransportBulkAction.doExecute
检查索引内存压力,并用新的线程来处理请求
protected void doExecute(Task task, BulkRequest bulkRequest, ActionListener<BulkResponse> listener) {
final int indexingOps = bulkRequest.numberOfActions();
final long indexingBytes = bulkRequest.ramBytesUsed();
final boolean isOnlySystem = isOnlySystem(bulkRequest, clusterService.state().metadata().getIndicesLookup(), systemIndices);
//统计并检测索引内存压力,超出indexing_pressure.memory.limit配置的值,则拒绝新的请求。
final Releasable releasable = indexingPressure.markCoordinatingOperationStarted(indexingOps, indexingBytes, isOnlySystem);
//在返回响应前,释放压力数据
final ActionListener<BulkResponse> releasingListener = ActionListener.runBefore(listener, releasable::close);
final String executorName = isOnlySystem ? Names.SYSTEM_WRITE : Names.WRITE;
threadPool.executor(Names.WRITE).execute(new ActionRunnable<>(releasingListener) {
@Override
protected void doRun() {
doInternalExecute(task, bulkRequest, executorName, releasingListener);
}
});
}
TransportBulkAction.doInternalExecute
doInternalExecute(Task task, BulkRequest bulkRequest, String executorName, ActionListener<BulkResponse> listener)
所有的创建更新文档的请求,最终都会经过TransportBulkAction.doInternalExecute处理。所以这里BulkRequest参数包含一个或多个文档操作请求。
该方法核心功能是尝试创建请求中需要的所有索引(如果没有预先创建索引)。
第一步:遍历bulkRequest.requests收集需要创建的索引.
删除请求不应尝试创建索引(如果索引不存在),除非使用外部版本控制
final Map<String, Boolean> indices = bulkRequest.requests.stream()
.filter(
request -> request.opType() != DocWriteRequest.OpType.DELETE
|| request.versionType() == VersionType.EXTERNAL
|| request.versionType() == VersionType.EXTERNAL_GTE
)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(DocWriteRequest::index, DocWriteRequest::isRequireAlias, (v1, v2) -> v1 || v2));
第二步:筛选索引列表以查找当前不存在的索引
只有目标不是别名时,才自动创建
final Map<String, IndexNotFoundException> indicesThatCannotBeCreated = new HashMap<>();
Set<String> autoCreateIndices = new HashSet<>();
ClusterState state = clusterService.state();
for (Map.Entry<String, Boolean> indexAndFlag : indices.entrySet()) {
final String index = indexAndFlag.getKey();
// hasIndexAbstraction判断指定的索引、数据流或别名是否存在
boolean shouldAutoCreate = indexNameExpressionResolver.hasIndexAbstraction(index, state) == false;
//indexAndFlag.getValue()为目标索引是否为别名
if (shouldAutoCreate && (indexAndFlag.getValue() == false)) {
autoCreateIndices.add(index);
}
}
第三步:创建所有缺失的索引。在索引创建返回成功后才开始批量操作
if (autoCreateIndices.isEmpty()) {
//如果不需要创建索引,则直接执行批操作
executeBulk(task, bulkRequest, startTime, listener, executorName, responses, indicesThatCannotBeCreated);
} else {
//设置索引数量计数器
final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(autoCreateIndices.size());
for (String index : autoCreateIndices) {
//异步创建索引
createIndex(index, bulkRequest.timeout(), new ActionListener<>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(CreateIndexResponse result) {
//每创建一个索引,计数器减1.直到所有索引创建完毕,才执行批处理
if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
threadPool.executor(executorName).execute(new ActionRunnable<>(listener) {
@Override
protected void doRun() {
executeBulk(
task,
bulkRequest,
startTime,
listener,
executorName,
responses,
indicesThatCannotBeCreated
);
}
});
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
//创建索引失败,抛出异常
//异常为IndexNotFoundException则将索引存入indicesThatCannotBeCreated
//异常为ResourceAlreadyExistsException则将该索引涉及的相关request置为null
// bulkRequest.requests.set(i, null);
//然后执行判断计数器,满足条件执行executeBulk
}
});
}
}
BulkOperation.doRun
先检查集群状态,如果状态异常直接返回。
然后遍历bulkRequest.requests,做一些校验将满足如下条件的request抛弃:
- 创建索引抛出IndexNotFoundException异常的
- 创建索引抛出ResourceAlreadyExistsException异常的
- request需要别名,但是metadata未定义别名的。
- 索引状态为closed的
- ...
校验完成后,就是关键逻辑了,见代码: 此处将所有request先按路由规则获取shardId,然后以shardId为key存入requestsByShard中,将相同shardId的请求,放到同一个List中。
Map<ShardId, List<BulkItemRequest>> requestsByShard = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < bulkRequest.requests.size(); i++) {
//此处校验逻辑代码略
//通过IndexRouting类路由分片,拿到分片ID.
IndexRouting indexRouting = concreteIndices.routing(concreteIndex);
//如果doc没有指定ID,此处会生成一个随机ID
docWriteRequest.process(indexRouting);
int shardId = docWriteRequest.route(indexRouting);
//将所有请求按分片分组
List<BulkItemRequest> shardRequests = requestsByShard.computeIfAbsent(
new ShardId(concreteIndex, shardId),
shard -> new ArrayList<>()
);
shardRequests.add(new BulkItemRequest(i, docWriteRequest));
}
然后将同一个Shard的请求,组装成一个BulkShardRequest对象,调用client.executeLocally方法执行。
所有请求执行完成后,返回相应的执行结果信息。
//请求计数器
final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(requestsByShard.size());
String nodeId = clusterService.localNode().getId();
for (Map.Entry<ShardId, List<BulkItemRequest>> entry : requestsByShard.entrySet()) {
final ShardId shardId = entry.getKey();
final List<BulkItemRequest> requests = entry.getValue();
//构建BulkShardRequest,针对同一个分片的请求,组合成一个BulkShardRequest
BulkShardRequest bulkShardRequest = new BulkShardRequest(
shardId,
bulkRequest.getRefreshPolicy(),
requests.toArray(new BulkItemRequest[requests.size()])
);
bulkShardRequest.waitForActiveShards(bulkRequest.waitForActiveShards());
bulkShardRequest.timeout(bulkRequest.timeout());
bulkShardRequest.routedBasedOnClusterVersion(clusterState.version());
if (task != null) {
bulkShardRequest.setParentTask(nodeId, task.getId());
}
client.executeLocally(TransportShardBulkAction.TYPE, bulkShardRequest, new ActionListener<>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(BulkShardResponse bulkShardResponse) {
for (BulkItemResponse bulkItemResponse : bulkShardResponse.getResponses()) {
// 拼装响应信息
}
//每执行一个request,计数器减1
//所有request执行完毕,调用返回Response的方法
if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
finishHim();
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
// create failures for all relevant requests
for (BulkItemRequest request : requests) {
// 拼装响应信息
}
//每执行一个request,计数器减1
//所有request执行完毕,调用返回Response的方法
if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
finishHim();
}
}
private void finishHim() {
//向客户端发送响应信息
listener.onResponse(
new BulkResponse(responses.toArray(new BulkItemResponse[responses.length()]), buildTookInMillis(startTimeNanos))
);
}
});
}
ReroutePhase.doRun
//设置任务执行阶段
setPhase(task, "routing");
// ...
//校验集群状态,此处代码略
// ...
//获取主分片索引路由信息,如:id,状态,版本等
final ShardRouting primary = state.getRoutingTable().shardRoutingTable(request.shardId()).primaryShard();
// ...
//状态检测,此处代码略
// ...
//获取主分片集群节点信息
final DiscoveryNode node = state.nodes().get(primary.currentNodeId());
//判断主分片节点是否当前节点
if (primary.currentNodeId().equals(state.nodes().getLocalNodeId())) {
//主分片在当前节点
performLocalAction(state, primary, node, indexMetadata);
} else {
//主分片不在当前节点,执行远程调用
performRemoteAction(state, primary, node);
}
主分片位于本地节点,执行performLocalAction,将数据写入本地磁盘
private void performLocalAction(ClusterState state, ShardRouting primary, DiscoveryNode node, IndexMetadata indexMetadata) {
setPhase(task, "waiting_on_primary");
performAction(
node,
transportPrimaryAction,
true,
new ConcreteShardRequest<>(
request,
primary.allocationId().getId(),
indexMetadata.primaryTerm(primary.id()),
true,
initiatedByNodeClient
)
);
}
主分片位于远程节点上,执行performRemoteAction,将请求路由至远程节点。
private void performRemoteAction(ClusterState state, ShardRouting primary, DiscoveryNode node) {
setPhase(task, "rerouted");
performAction(node, actionName, false, request);
}
Transport.Connection.sendRequest
TransportService最终在sendRequestInternal方法中调用Transport.Connection接口的sendRequest方法。
Transport.Connection类的实例由如下方法获取,判断是否本地节点,是就返回localNodeConnection。
public Transport.Connection getConnection(DiscoveryNode node) {
if (isLocalNode(node)) {
return localNodeConnection;
} else {
return connectionManager.getConnection(node);
}
}
localNodeConnection是一个匿名类,实现了Transport.Connection接口
如果不是本地节点就从连接管理器获取远程节点的连接,连接管理器返回的是TcpTransport.NodeChannels,为Transport.Connection接口的实现类。
分发请求至远程节点
集群中的节点通信通过Netty组件实现。
写请求发送到目标节点后,InboundHandler调用Tranport.RequestHandlers类的getHandler方法,获取对应类型的TransportAction处理类,这里为TransportReplicationAction。
然后调用TransportReplicationAction.handleOperationRequest方法介入ReroutePhase:
private void handleOperationRequest(final Request request, final TransportChannel channel, Task task) {
Releasable releasable = checkOperationLimits(request);
ActionListener<Response> listener = ActionListener.runBefore(
new ChannelActi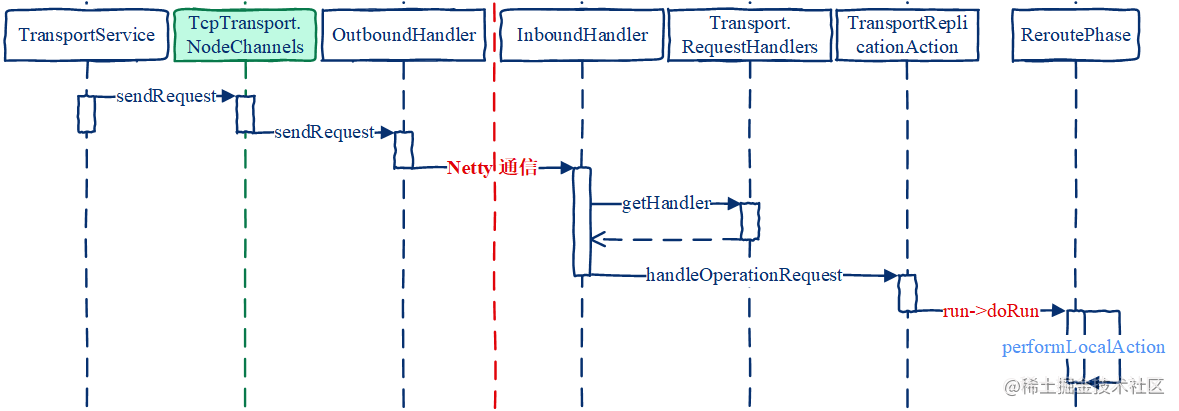onListener<>(channel, actionName, request),
releasable::close
);
runReroutePhase(task, request, listener, false);
}
对比前面从RestHandler进入时调用的TransportReplicationAction.doExecute方法:
protected void doExecute(Task task, Request request, ActionListener<Response> listener) {
assert request.shardId() != null : "request shardId must be set";
runReroutePhase(task, request, listener, true);
}
两个方法都是调用的runReroutePhase方法,但是最后一个标识来源是否为NodeClient的参数,一个传True,一个传的False.
private void runReroutePhase(Task task, Request request, ActionListener<Response> listener, boolean initiatedByNodeClient) {
try {
new ReroutePhase((ReplicationTask) task, request, listener, initiatedByNodeClient).run();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
listener.onFailure(e);
}
}
后续的处理过程就是执行本地Action逻辑一样了,最终都会执行performLocalAction方法。