定位方式
| 定位方式 | 属性值 |
|---|
| 静态定位 | static |
| 相对定位 | relative |
| 绝对定位 | absolute |
| 固定定位 | fixed |
偏移值
- 偏移值分为两个方向,水平和垂直方向各选一个使用即可
- 选取原则一般是就近原则
| 方向 | 属性名 | 属性值 | 含义 |
|---|
| 水平 | left | 数字+px | 距离左边的距离 |
| 水平 | right | 数字+px | 距离右边的距离 |
| 垂直 | top | 数字+px | 距离上边的距离 |
| 垂直 | bottom | 数字+px | 距离下边的距离 |
一、静态定位
- 介绍:静态定位是默认值
- 代码:position : static ;
- 注意:静态定位不能通过方位属性进行移动
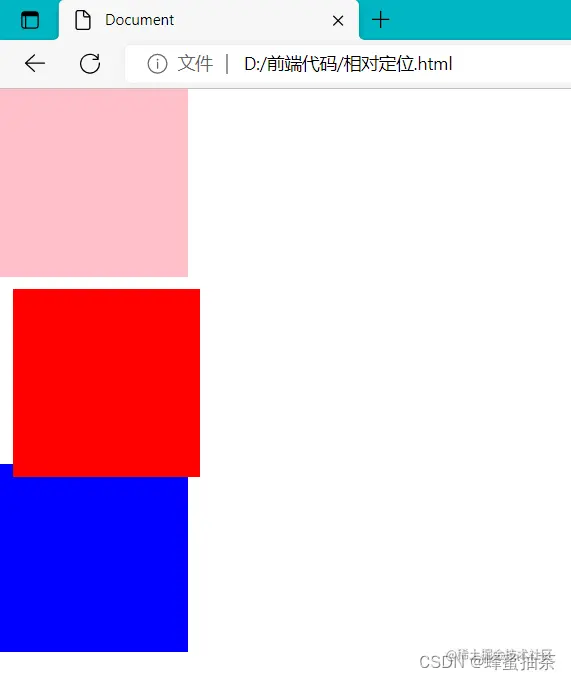
二、相对定位
- 介绍:自恋型定位,相对于自己之前的位置进行移动
- 代码:position : relative ;
- 注意:
- 需要配合方位属性实现移动
- 相对于自己原来位置进行移动
- 在页面中占位置→没有脱标(原位置不变)
- 场景:小范围的移动、配合绝对定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: o;
}
div {
height: 150px;
width: 150px;
}
.a {
background-color: pink;
}
.b {
position: relative;
background-color: red;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
.c {
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="c"></div>
</body>
</html>
- 效果
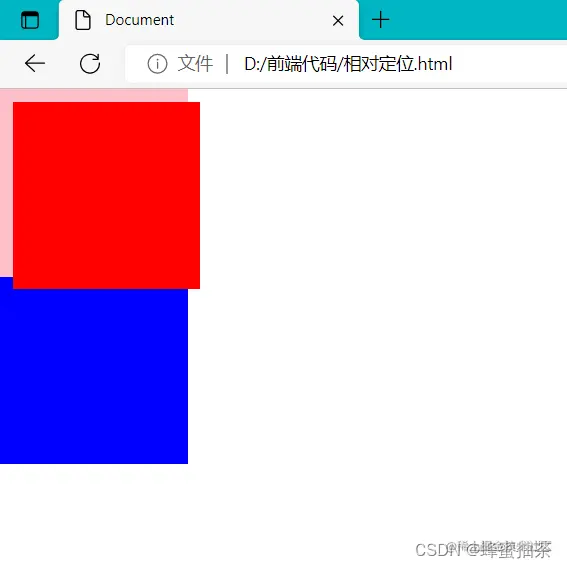
三、绝对定位
- 介绍:拼爹型定位,相对于非静态定位的父元素进行定位移动
- 代码:position : absolute ;
- 注意:
- 需要配合方位属性实现移动
- 默认相对于浏览器可视区域进行移动
- 在页面中不占位置→已经脱标
- 场景:配合绝对定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: o;
}
div {
height: 150px;
width: 150px;
}
.a {
background-color: pink;
}
.b {
position: absolute;
background-color: red;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
.c {
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="c"></div>
</body>
</html>
绝对定位相对于谁移动?
- 祖先元素中==没有==定位→默认相对于浏览器进行移动
- 祖先元素中==有==定位→相对于 最近的 有定位 的祖先元素进行移动
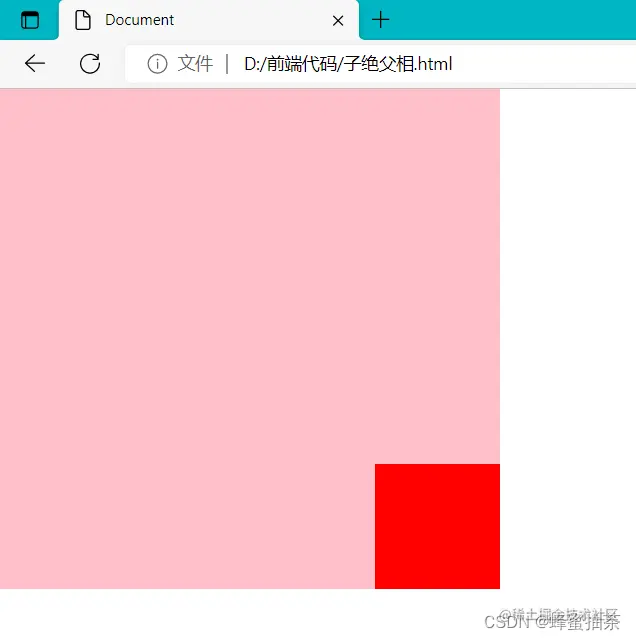
四、子绝父相
- 场景:让子元素相对于父元素进行自由移动
- 含义:
- 父元素是相对定位,则对网页布局影响最小
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: o;
}
.father {
height: 400px;
width: 400px;
background-color: pink;
position: relative;
}
.son {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
right: 0px;
bottom: 0px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
五、固定定位
- 介绍:相对于浏览器进行定位移动
- 代码:position : fixed ;
- 注意:
- 需要配合方位属性实现移动
- 相对于浏览器可视区域进行移动
- 在页面中不占位置→已脱标
- 场景:让盒子固定在屏幕中的某个位置 ,滑动页面时依然在固定的位置
六、更改定位元素的层级
- 场景:改变定位元素的层级
- 属性名:z-index
- 属性值:数字
z-index: 999;