队列 Queue
符合 先进先出的数据结构
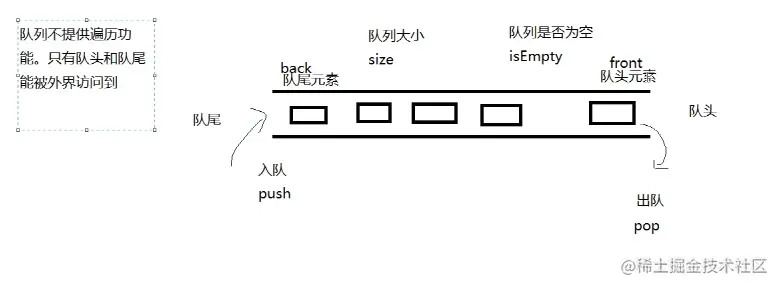
术语:
入队 push
出队 pop
返回队列大小 size
判断是否为空 isEmpty
队头元素 front
队尾元素 back
队列的顺序存储
利用数组模拟出 先进先出的数据结构
接口:
初始化队列 init
入队 push
出队 pop
返回队列大小 size
判断是否为空 isEmpty
队头元素 front
队尾元素 back
销毁队列 destroy
示例
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "SeqQueue.h"
#include "DynamicArray.h"
seqQueue initSeqQueue()
{
struct dynamicArray * arr = initDynamicArray(MAX);
return arr;
}
void pushSeqQueue(seqQueue queue, void* data)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (data == NULL)
{
return;
}
struct dynamicArray* myQueue = queue;
if (myQueue->mSize == MAX)
{
return;
}
insertDynamicArray(myQueue, myQueue->mSize, data);
}
void popSeqQueue(seqQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return;
}
struct dynamicArray* myQueue = queue;
if (myQueue->mSize <= 0)
{
return;
}
removeByPosDynamicArray(myQueue, 0);
}
int sizeSeqQueue(seqQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
struct dynamicArray* myQueue = queue;
return myQueue->mSize;
}
int isEmptySeqQueue(seqQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
struct dynamicArray* myQueue = queue;
if (myQueue->mSize ==0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void* frontSeqQueue(seqQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct dynamicArray* myQueue = queue;
return myQueue->pAddr[0];
}
void* backSeqQueue(seqQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct dynamicArray* myQueue = queue;
return myQueue->pAddr[myQueue->mSize-1];
}
void destroySeqQueue(seqQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return;
}
destroyDynamicArray(queue);
}
队列的链式存储
利用链表模拟出 先进先出数据结构
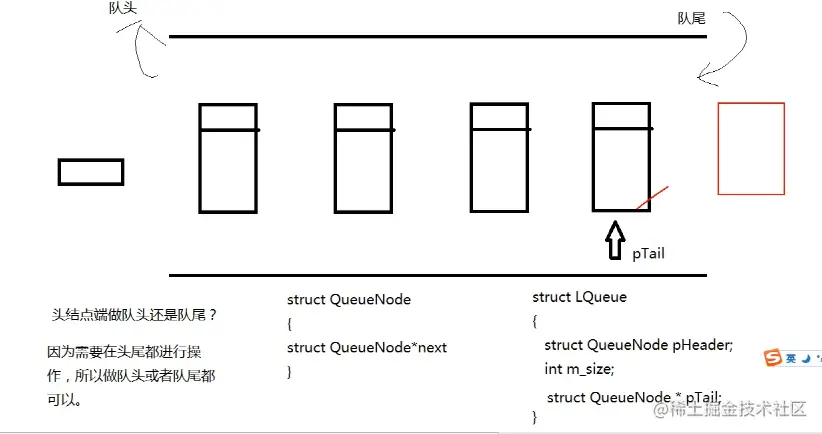
设计:
节点 只维护指针域
队列结构体:
struct QueueNode pHeader; 头节点
int m_Size; 队列大小
struct QueueNode * pTail; 尾节点指针
接口:
初始化队列 init
入队 push
出队 pop
返回队列大小 size
判断是否为空 isEmpty
队头元素 front
队尾元素 back
销毁队列 destroy
示例
//初始化队列
LinkQueue initLinkQueue()
{
struct LQueue* myQueue = malloc(sizeof(struct LQueue))
if (myQueue == NULL)
{
return NULL
}
myQueue->pHeader.next = NULL
myQueue->mSize = 0
myQueue->pTail = &myQueue->pHeader
return myQueue
}
// 入队
void pushLinkQueue(LinkQueue queue, void* data)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return
}
if (data == NULL)
{
return
}
//本质 尾插
struct LQueue* myQueue = queue
struct QueueNode* myNode = data
//更改指针的指向
myQueue->pTail->next = myNode
myNode->next = NULL
//更新新的尾节点
myQueue->pTail = myNode
myQueue->mSize++
}
// 出队
void popLinkQueue(LinkQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return
}
//本质 头删
struct LQueue* myQueue = queue
if (myQueue->mSize == 0)
{
return
}
if (myQueue->mSize == 1)
{
myQueue->pHeader.next = NULL
myQueue->pTail = &myQueue->pHeader
myQueue->mSize--
return
}
//记录第一个有数据的节点
struct QueueNode* pFirst = myQueue->pHeader.next
//更改指针指向
myQueue->pHeader.next = pFirst->next
//更改链表长度
myQueue->mSize--
}
// 返回队列大小
int sizeLinkQueue(LinkQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return -1
}
struct LQueue* myQueue = queue
return myQueue->mSize
}
// 判断是否为空
int isEmptyLinkQueue(LinkQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return -1
}
struct LQueue* myQueue = queue
if (myQueue->mSize == 0)
{
return 1
}
return 0
}
// 返回队头
void* frontLinkQueue(LinkQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return NULL
}
struct LQueue* myQueue = queue
return myQueue->pHeader.next
}
// 返回队尾
void* backLinkQueue(LinkQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return NULL
}
struct LQueue* myQueue = queue
return myQueue->pTail
}
// 销毁队列
void destroyLinkQueue(LinkQueue queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
return
}
free(queue)
queue = NULL
}
树的基本概念
由一个或多个(n≥0)结点组成的有限集合T
有且仅有一个结点称为根(root),当n>1时,其余的结点分为**m(m≥0)个互不相交的有限集合**T1,T2,…,Tm。
每个集合本身又是棵树,被称作这个根的子树 。
特点:
非线性结构,有一个直接前驱,但可能有多个直接后继
定义具有递归性,树中还有树
树可以为空,即结点个数为0
术语
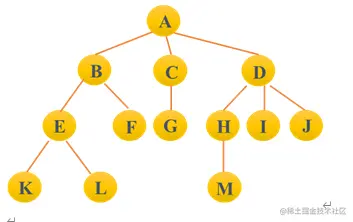
*根
即根结点,没有前驱
*叶子
终端结点,没有后继
森林
m棵不相交的树的集合
有序树
结点各子树从左至右有序,不能互换(左为第一)
无序树
结点各子树可互换位置
*双亲
即上层的那个结点(直接前驱) parent
*孩子
即下层结点的子树 (直接后继) child
兄弟
同一双亲下的同层结点(孩子之间互称兄弟)sibling
堂兄弟
即双亲位于同一层的结点(但并非同一双亲)cousin
祖先
即从根到该结点所经分支的所有结点
子孙
即该结点下层子树中的任一结点
结点
即树的数据元素
* 结点的度
直接后继的数量
结点的层次
从根到该结点的层数(根结点算第一层)
终端结点
即度为0的结点,即叶子
分支结点
除树根以外的结点(也称为内部结点)
*树的度
所有结点度中的最大值(Max{各结点的度})
*树的深度(或高度)
指所有结点中最大的层数(Max{各结点的层次})
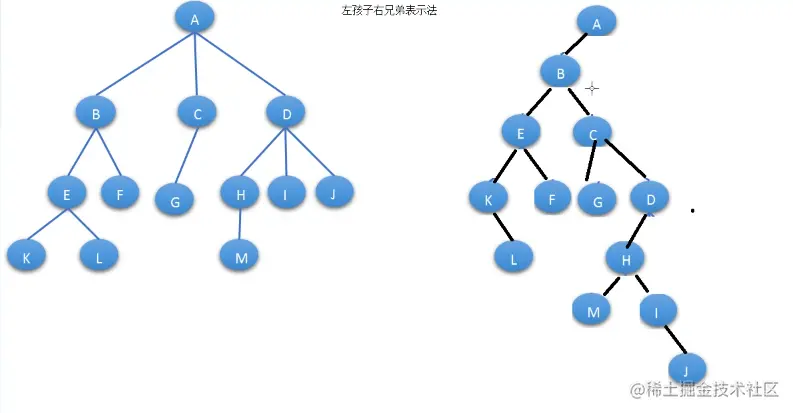
表示法:
图形、广义 、左孩子右兄弟(将多叉树转为二叉树)
左孩子右兄弟表示法 示意图
二叉树的基本性质
性质1: 在二叉树的第i层上至多有2^(i-1)个结点(i>0)
性质2: 深度为k的二叉树至多有2^k - 1个结点(k>0)
性质3: 对于任何一棵二叉树,若度为2的结点数有n2个,则叶子数(n0)必定为n2+1 (即n0=n2+1) 度为2 数 + 1 = 叶子数
满二叉树 深度为k的数 并且节点数量为 2^k - 1
完全二叉树 除了最后一层,上面是一颗满二叉树,在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干结点
性质4: 具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度必为log2n+1
(如 log2 (15) 点击 15 log / 2 log =)
性质5: 对完全二叉树,若从上至下、从左至右编号,则编号为i 的结点,其左孩子编号必为2i,其右孩子编号必为2i+1;其双亲的编号必为i/2(i=1 时为根,除外)
二叉树的递归遍历
先序遍历 : 先根 再左 再右
中序遍历 : 先左 再根 再右
后序遍历 : 先左 再右 再根

示例
struct BinaryNode
{
//数据域
char ch
//指针域
struct BinaryNode* lChild
struct BinaryNode* rChild
}
void recursion(struct BinaryNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return
}
//先序遍历
printf("%c ", root->ch)
recursion(root->lChild)
recursion(root->rChild)
//中序遍历
recursion(root->lChild)
printf("%c ", root->ch)
recursion(root->rChild)
//后序遍历
recursion(root->lChild)
recursion(root->rChild)
printf("%c ", root->ch)
}
void test01()
{
struct BinaryNode nodeA = { 'A',NULL,NULL}
struct BinaryNode nodeB = { 'B',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeC = { 'C',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeD = { 'D',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeE = { 'E',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeF = { 'F',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeG = { 'G',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeH = { 'H',NULL,NULL }
//建立关系
nodeA.lChild = &nodeB
nodeA.rChild = &nodeF
nodeB.rChild = &nodeC
nodeC.lChild = &nodeD
nodeC.rChild = &nodeE
nodeF.rChild = &nodeG
nodeG.lChild = &nodeH
//递归遍历
recursion(&nodeA)
}
int main(void)
{
test01()
system("pause")
return EXIT_SUCCESS
}
二叉树编程
求二叉树叶子数量
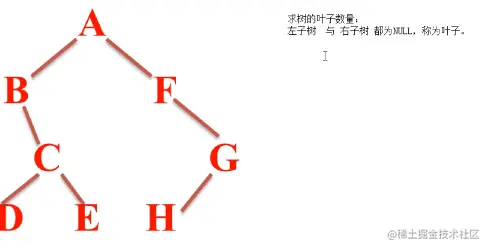
左子树与右子树都同时为NULL,称为叶子
求二叉树高度
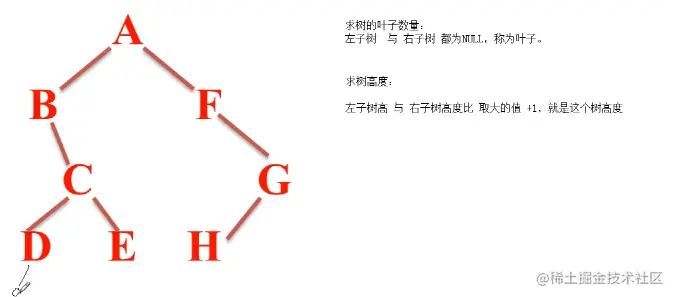
左子树高度 与 右子树高度比 ,取大的值 +1 就是这个树的高度
拷贝二叉树
先拷贝左子树
再拷贝右子树
再创建根节点 挂载拷贝出的左右子树,返回给用户
释放二叉树
利用递归特性释放二叉树
示例
struct BinaryNode
{
//数据域
char ch
//指针域
struct BinaryNode* lChild
struct BinaryNode* rChild
}
//获取叶子数量
void calLeafNum(struct BinaryNode* root, int* p)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return
}
//如果节点 左子树与右子树同时为空,称为叶子
if (root->lChild == NULL && root->rChild == NULL)
{
(* p)++
}
calLeafNum(root->lChild, p)
calLeafNum(root->rChild, p)
}
//获取树的高度
int getTreeHeight(struct BinaryNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0
}
//获取左子树高度
int lHeight = getTreeHeight(root->lChild)
//获取右子树高度
int rHeight = getTreeHeight(root->rChild)
//从左子树和右子树高度选择大的然后+1
int height = lHeight > rHeight ? lHeight + 1 : rHeight + 1
return height
}
struct BinaryNode* copyTree(struct BinaryNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL
}
//先拷贝左子树
struct BinaryNode* lChild = copyTree(root->lChild)
//再拷贝右子树
struct BinaryNode* rChild = copyTree(root->rChild)
//创建新的根节点
struct BinaryNode* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode))
newNode->ch = root->ch
newNode->lChild = lChild
newNode->rChild = rChild
return newNode
}
void recursion(struct BinaryNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return
}
printf("%c ", root->ch)
recursion(root->lChild)
recursion(root->rChild)
}
void freeTree(struct BinaryNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return
}
//先释放左子树,再释放右子树
freeTree(root->lChild)
freeTree(root->rChild)
//释放根节点
free(root)
root = NULL
}
void test01()
{
struct BinaryNode nodeA = { 'A',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeB = { 'B',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeC = { 'C',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeD = { 'D',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeE = { 'E',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeF = { 'F',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeG = { 'G',NULL,NULL }
struct BinaryNode nodeH = { 'H',NULL,NULL }
//建立关系
nodeA.lChild = &nodeB
nodeA.rChild = &nodeF
nodeB.rChild = &nodeC
nodeC.lChild = &nodeD
nodeC.rChild = &nodeE
nodeF.rChild = &nodeG
nodeG.lChild = &nodeH
//1. 求二叉树 叶子数量
int num = 0
calLeafNum(&nodeA, &num)
printf("树的叶子的数量为:%d\n", num)
//2. 求树的高度 或者说 深度
int height = getTreeHeight(&nodeA)
printf("树的高度为:%d\n", height)
//3. 拷贝二叉树
struct BinaryNode* newTree = copyTree(&nodeA)
//递归遍历
recursion(newTree)
//4. 释放二叉树
freeTree(&newTree)
}
int main(void)
{
test01()
system("pause")
return EXIT_SUCCESS
}
二叉树非递归遍历
1. 将根节点入栈
2. 只要栈中元素个数大于0,执行循环
2.1 弹出栈顶元素
2.2 如果这个栈顶元素标志为真,输出这个元素并且执行下一次循环
2.3 如果栈顶元素标志为假,将节点的标志设为真
2.4 将该节点的右子树,左子树,根 压入到栈中
2.5 执行下一次循环
执行上述流程,可以得到先序遍历的结果,如果想得到其他二叉树遍历结果,修改2.4步骤即可。
示例
struct BinaryNode
{
//数据域
char ch
//指针域
struct BinaryNode* lChild
struct BinaryNode* rChild
//标志
int flag
}
/*
1. 将根节点入栈
2. 只要栈中元素个数大于0,执行循环
2.1 弹出栈顶元素
2.2 如果这个栈顶元素标志为真,输出这个元素并且执行下一次循环
2.3 如果栈顶元素标志为假,将节点的标志设为真
2.4 将该节点的右子树,左子树,根 压入到栈中
2.5 执行下一次循环
执行上述流程,可以得到先序遍历的结果,如果想得到其他二叉树遍历结果,修改2.4步骤即可。
*/
void nonRecursion(struct BinaryNode* root)
{
//初始化栈
SeqStack myStack = initSeqStack()
//将根节点入栈
pushSeqStack(myStack, root)
//只要栈中元素个数大于0,执行循环
while (sizeSeqStack(myStack) > 0)
{
//弹出栈顶元素
struct BinaryNode* pTop = topSeqStack(myStack)
//出栈
popSeqStack(myStack)
//如果标志为真,直接输出,并且执行下一步循环
if (pTop->flag == 1)
{
printf("%c ", pTop->ch)
continue
}
//如果为假,将标志改为真
pTop->flag = 1
//将右子树,左子树,根入栈
if (pTop->rChild != NULL)
{
pushSeqStack(myStack, pTop->rChild)
}
if (pTop->lChild != NULL)
{
pushSeqStack(myStack, pTop->lChild)
}
pushSeqStack(myStack, pTop)
}
//销毁栈
destroySeqStack(myStack)
}
void test01()
{
struct BinaryNode nodeA = { 'A',NULL,NULL,0 }
struct BinaryNode nodeB = { 'B',NULL,NULL,0 }
struct BinaryNode nodeC = { 'C',NULL,NULL,0 }
struct BinaryNode nodeD = { 'D',NULL,NULL,0 }
struct BinaryNode nodeE = { 'E',NULL,NULL,0 }
struct BinaryNode nodeF = { 'F',NULL,NULL,0 }
struct BinaryNode nodeG = { 'G',NULL,NULL,0 }
struct BinaryNode nodeH = { 'H',NULL,NULL,0 }
//建立关系
nodeA.lChild = &nodeB
nodeA.rChild = &nodeF
nodeB.rChild = &nodeC
nodeC.lChild = &nodeD
nodeC.rChild = &nodeE
nodeF.rChild = &nodeG
nodeG.lChild = &nodeH
//非递归遍历
nonRecursion(&nodeA)
}
int main(void)
{
test01()
system("pause")
return EXIT_SUCCESS
}
插入排序
从I = 1位置开始 做外层循环
判断 如果 I -1 > I 将i指向的数据缓存
j开始做内侧循环,找到要插入的位置 将缓存数据插入到 j +1位置上
i++
示例
void insertSort(int arr[], int len)
{
for (size_t i = 0
{
if (arr[i - 1] > arr[i])
{
int temp = arr[i]
int j = i - 1
for (
{
//数据后移
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
}
arr[j + 1] = temp
}
}
}
void printArray(int arr[], int len)
{
for (size_t i = 0
{
printf("%d\n", arr[i])
}
}
void test01()
{
int arr[] = { 4,1,2,3,5,7,6 }
//插入排序
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int)
insertSort(arr, len)
//打印数据
printArray(arr, len)
}
int main(void)
{
test01()
system("pause")
return EXIT_SUCCESS
}