什么是装饰器模式
定义
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern) 也称为包装模式(Wrapper Pattern) 是指在不改变原有对象的基础之上,将功能附加到对象上,提供了比继承更有弹性的替代方案(扩展原有对象的功能),属于结构型模式。装饰器模式的核心是功能扩展,使用装饰器模式可以透明且动态地扩展类的功能。
特点
- 最直观地就是我们买房后的装修
- 装饰比继承更加灵活,可以实现装饰者和被装饰者之间松耦合
- 被装饰者可以使用装饰者动态地增加和撤销功能
装饰器模式的角色组成
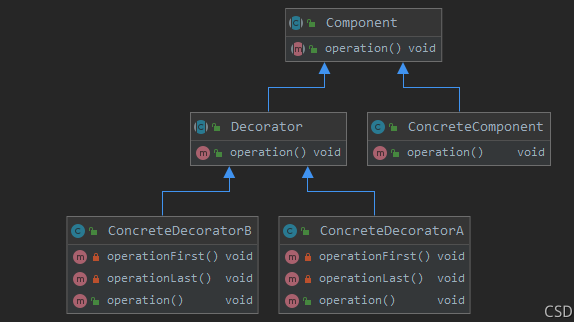
- 抽象组件(Component): 可以是一个接口或者抽象类,其充当被装饰类的原始对象,规定了被装饰对象的行为
- 具体组件(ConcreteComponent): 实现/继承Component的一个具体对象,也即被装饰对象
- 抽象装饰器(Decorator): 通用的装饰ConcreteComponent的装饰器,其内部必然有一个属性指向Component+ 抽象组件;其实现一般是一个抽象类,主要是为了让其子类按照其构造形式传入一个Component抽象组件,这是强制的通用行为(当然,如果系统中逻辑单一,并不需要实现许多装饰器,那么我们可以直接省略该类,而直接实现一个具体装饰器(ComcreteDecorator)即可
- 具体装饰器(ConcreteDecorator): Decorator的具体实现类,理论上,每个ConcreteDecorator都扩展了Component对象的一种功能
案例
类图
代码
abstract class Shape {
abstract draw(): void;
}
class Circle extends Shape {
draw() {
console.log('绘制圆形');
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
draw() {
console.log('绘制矩形');
}
}
abstract class ColorfulShape extends Shape {
public constructor(public shape: Shape) {
super();
}
abstract draw(): void;
}
class RedColorfulShape extends ColorfulShape {
draw() {
this.shape.draw();
console.log('把边框涂成红色');
}
}
class GreenColorfulShape extends ColorfulShape {
draw() {
this.shape.draw();
console.log('把边框涂成绿色');
}
}
let circle = new Circle();
let redColorfulShape = new RedColorfulShape(circle);
redColorfulShape.draw();
let rectangle = new Rectangle();
let greenColorfulShape = new GreenColorfulShape(rectangle);
greenColorfulShape.draw();
应用场景
装饰器
- 装饰器是一种特殊类型的声明,它能够被附加到类声明、方法、属性或参数上,可以修改类的行为
- 常见的装饰器有类装饰器、属性装饰器、方法装饰器和参数装饰器
- 装饰器的写法分为普通装饰器和装饰器工厂
类装饰器
- 类装饰器在类声明之前声明,用来监控、修改或替换类定义
- 参数是类的定义或者说构造函数
- babel-plugin-proposal-decorators
decorator
export { }
namespace decorator {
interface Animal {
swings: string;
fly: any
}
function flyable(target: any) {
console.log(target);
target.prototype.swings = 2;
target.prototype.fly = function () {
console.log('I can fly');
}
}
@flyable
class Animal {
constructor() { }
}
let animal: Animal = new Animal();
console.log(animal.swings);
animal.fly();
}
decorator_factory
namespace decorator_factory {
interface Animal {
swings: string;
fly: any
}
function flyable(swings: number) {
return function flyable(target: any) {
console.log(target);
target.prototype.swings = swings;
target.prototype.fly = function () {
console.log('I can fly');
}
}
}
@flyable(2)
class Animal {
constructor() { }
}
let animal: Animal = new Animal();
console.log(animal.swings);
animal.fly();
}
属性装饰器
- 属性装饰器表达式会在运行时当作函数被调用
- 属性分为实例属性和类属性
- 方法分为实例方法和类方法
namespace property_namespace {
//实例属性target是类的原型对象,key是属性名称
function instancePropertyDecorator(target: any, key: string) {
}
//类属性target是的构造函数
function classPropertyDecorator(target: any, key: string) {
}
//实例方法装饰器target是原型对象,key方法名,descriptor是方法描述符
function instanceMethodDecorator(target: any, key: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
}
//类方法装饰器target是类的构造函数
function classMethodDecorator(target: any, key: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
}
class Person {
@instancePropertyDecorator
instanceProperty: string;
@classPropertyDecorator
public static classProperty: string;
@instanceMethodDecorator
instanceMethod() {
console.log('instanceMethod');
}
@classMethodDecorator
classMethod() {
console.log('classMethod');
}
}
}
core-decorator
core-decorator deprecate-alias-deprecated
let { readonly } = require('core-decorators');
function deprecate(msg: string, options: any) {
return function (target: any, attr: any, descriptor: any) {
//DEPRECATION Calculator#add: This function will be removed in future versions.
let oldVal = descriptor.value;
descriptor.value = function (...args: any[]) {
let message = msg ? msg : `DEPRECATION ${target.constructor.name}#${attr}: This function will be removed in future versions.`;
let see = options && options.url ? `see ${options.url}` : ``;
console.warn(message + '\r\n' + see);
return oldVal(...args);
}
}
}
class Calculator {
@deprecate('stop using this', { url: 'http://www.baidu.com' })
add(a: number, b: number) {
return a + b;
}
}
let calculator = new Calculator();
calculator.add(1, 2);
AOP概念
- 在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为面向切面编程
- 可以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态统一添加功能的一种技术
埋点
- 埋点分析: 是网站分析的一种常用的数据采集方法
- 无痕埋点: 通过技术手段,完成对用户行为数据无差别的统计上传的工作,后期数据分析处理的时候通过技术手段筛选出合适的数据进行统计分析
项目配置
- 创建项目
create-react-app tract-demo
yarn add customize-cra react-app-rewired --dev
- config-overrides.js
const {
override,
addDecoratorsLegacy,
} = require("customize-cra");
module.exports = override(
addDecoratorsLegacy(),
);
- jsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"experimentalDecorators": true
}
}
ndex.js
import React from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { before, after } from './track';
class App extends React.Component {
@before(() => console.log('点击方法执行前'))
onClickBeforeButton() {
console.log('beforeClick');
}
@after(() => console.log('点击方法执行后'))
onClickAfterButton() {
console.log('afterClick');
}
@after(() => fetch('/api/report'))
onClickAjaxButton() {
console.log('ajaxClick');
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.onClickBeforeButton}>beforeClick</button>
<button onClick={this.onClickAfterButton}>afterClick</button>
<button onClick={this.onClickAjaxButton}>ajaxClick</button>
</div>
)
}
}
render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
track.js
export const before = function (beforeFn) {
return function (target, methodName, descriptor) {
let oldMethod = descriptor.value;
descriptor.value = function () {
beforeFn.apply(this, arguments);
return oldMethod.apply(this, arguments);
}
}
}
export const after = function (afterFn) {
return function (target, methodName, descriptor) {
let oldMethod = descriptor.value;
descriptor.value = function () {
oldMethod.apply(this, arguments);
afterFn.apply(this, arguments);
}
}
}
表单校验
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>用户注册</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
用户名<input type="text" name="username" id="username">
密码<input type="text" name="password" id="password">
<button id="submit-btn">注册</button>
</form>
<script>
Function.prototype.before = function (beforeFn) {
let _this = this;
return function () {
let ret = beforeFn.apply(this, arguments);
if (ret)
_this.apply(this, arguments);
}
}
function submit() {
alert('提交表单');
}
submit = submit.before(function () {
let username = document.getElementById('username').value;
if (username.length < 6) {
return alert('用户名不能少于6位');
}
return true;
});
submit = submit.before(function () {
let username = document.getElementById('username').value;
if (!username) {
return alert('用户名不能为空');
}
return true;
});
document.getElementById('submit-btn').addEventListener('click', submit);
</script>
</body>
</html>
装饰器模式优缺点
优点
- 装饰器是继承的有力补充,比继承灵活,不改变原有对象的情况下动态地给一个对象扩展功能,即插即用
- 通过使用不同装饰类以及这些装饰类的排列组合,可以实现不同效果
- 装饰器完全遵守开闭原则
缺点
- 从代码层面来看,使用装饰器模式会出现更多的代码,更多的类,增加程序复杂性
- 动态装饰时,多层装饰时会更复杂