g'y## 知识 是否可以通过遍历二叉树得到答案,单独拿出一个节点,他需要做什么?
- 前后序遍历
- 层序遍历
遍历框架
traverse (TreeNode root) {
if root == nil {
return;
}
// 1. 2.
traverse(root.Left)
// 3.
traverse(root.Right)
}
打印出每个节点的左右子树各有多少节点
// 定义:输入一棵二叉树,返回这棵二叉树的节点总数
int count(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftCount = count(root.left);
int rightCount = count(root.right);
// 后序位置
// 访问的变量是该层的含义
printf("节点 %s 的左子树有 %d 个节点,右子树有 %d 个节点",
root, leftCount, rightCount);
// 对于每个节点返回 左右子树的节点数量和当前节点的数量
res :=leftCunt + rightCount + 1
return res
}
打印每个节点左右子树的高度
// 定义:输入一棵二叉树,返回这棵二叉树的节点总数
int traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int lHeight = traverse(root.left);
int rHeight = traverse(root.right);
// 后序位置
// 访问的变量是该层的含义
printf("节点 %s 的左子树有 %d 个节点,右子树有 %d 个节点",
root, leftCount, rightCount);
// 对于每个节点返回 左右子树的节点数量和当前节点的数量
res :=max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1
return res
}
## [104. 二叉树的深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
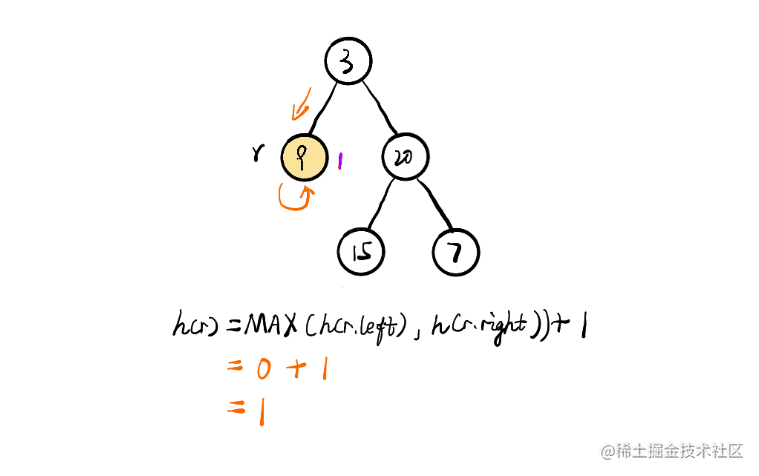
```go
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 在变量的作用域方面,任然是直观所示
// 3. 上一层接收来自下面的返回值
// 因为要接收返回值,所有递归赋值
lHeight := maxDepth(root.Left)
rHeight := maxDepth(root.Right)
// 1. 后序退出的时候,进行左右子树的max +1计算
// 2. 后续的结果又可以返回上一层
res := max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1
return res
}
func max(l,r int) int{
if(l>r){
return l
}
return r
}
var depth int
var res int
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
depth = 0
res = 0
traverse(root)
return res
}
func traverse(root *TreeNode){
if root == nil {
return
}
depth ++
if depth > res {
res = depth
}
traverse (root.Left)
traverse (root.Right)
depth --
}
画解算法:104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
110. 平衡二叉树
高度随便加两行代码就又是一道题
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
if maxDepth(root) < 0 {
return false
}
return true
}
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
lHeight := maxDepth(root.Left)
rHeight := maxDepth(root.Right)
// lHeight < 0 是接受来自之前的返回值
if abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1 || lHeight < 0 || rHeight < 0 {
return -1
}
res := max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1
return res
}
func max(l,r int) int{
if(l>r){
return l
}
return r
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -1 * x
}
return x
}
543. 二叉树的直径
转化为去求每个节点的左右子树的高度和
func diameterOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
var traverse func(root *TreeNode) int
var res int
traverse =func (root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil{
return 0
}
lHeight := traverse(root.Left)
rHeight := traverse(root.Right)
// 当前层自己用的,看看自己的左右和是多少
if lHeiht+rHeight > res {
res = lHeiht + rHeight
}
// 返回给上一层的
height := max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1
return height
}
traverse(root)
return res
}
101. 对称二叉树
其实我们要比较的是两个树(这两个树是根节点的左右子树。核心比较的是两个子树的里侧和外侧的元素是否相等
本题遍历只能是“后序遍历”,因为我们要通过递归函数的返回值来判断两个子树的内侧节点和外侧节点是否相等。
本题加强了对树遍历的理解
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
// 这一部分不想参与到递归里面去,所以分成两个函数去写
if (root == nil ){
return true
}
return compare(root.Left, root.Right)
}
func compare(left, right *TreeNode) bool{
// 返回条件
// 到底部了,或者出错了返回false
if (left == nil && right == nil) {
return true
}
if (left != nil && right == nil) {
return false
}
if (left == nil && right != nil) {
return false
}
if (left.Val != right.Val) {
return false
}
// 注意:以上条件并没有覆盖 left.Val == right.Val的情况, 这种情况下需要继续遍历,去验证对称性
// 对两边同时进行遍历
oneSide := compare(left.Left, right.Right)
anotherSide := compare(left.Right, right.Left)
return oneSide && anotherSide
}
257. 二叉树的所有路径
// 局部变量每一层有自己的path, 用完就销毁了,所以没有退栈的操作
// strconv.Itoa() 字符串的+ 操作,
// s := ""
func binaryTreePaths(root *TreeNode) []string {
res := []string{}
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, path string)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, path string) {
if root == nil {
return
}
path += strconv.Itoa(root.Val)
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
res = append(res, path)
}
dfs(root.Left, path + "->")
dfs(root.Right, path + "->")
}
dfs(root,"")
return res
}
404. 左叶子之和
遍历每个节点,然后看他的左子树是不是叶子节点
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
res := 0
var dfs func(root *TreeNode)
dfs = func (root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
// 就简单的全遍历一下,判断是否是左叶子
if (root.Left != nil && root.Left.Left == nil && root.Left.Right == nil) {
res += root.Left.Val
}
dfs (root.Left)
dfs (root.Right)
}
dfs(root)
return res
}
513. 找树左下角的值
找最后一层的第一个节点
// 最后一层- maxDepth
// 最左边- 其实想说的是最后一层的第一个..倒不一定非得是左子树
func findBottomLeftValue(root *TreeNode) int {
res := 0
if root != nil{
res = root.Val
}
maxDepth := 0
var dfs func (root *TreeNode, depth int)
dfs = func (root *TreeNode, depth int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if depth > maxDepth {
maxDepth = depth
res = root.Val
}
dfs(root.Left, depth + 1)
dfs(root.Right, depth + 1)
}
dfs(root, 0)
return res
}
112. 路径总和
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, pathSum int) bool
dfs = func (root* TreeNode, pathSum int) bool {
if root == nil {
return false
}
// 1. 前序遍历做一些事情
pathSum += root.Val
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
if pathSum == targetSum {
return true
}
}
// 2. 因为需要返回值
getLeft := dfs(root.Left,pathSum)
getRight := dfs(root.Right,pathSum)
// 3. 遍历过程中有一个true即可
return getLeft || getRight
}
return dfs(root,0)
}
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
递归图解,理解不了算我输 Golang/C++ - 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
* 1. 从题目可知是一道二叉树相关问题,首先想到递归或栈结构
* 2. 构建二叉树,二叉树具有递归结构性,自然想到使用递归来构建二叉树
* 3. 如何构建递归子问题? 根据前序遍历可以快速底定位根的位置,中序遍历可以划分出左子树与右子树的元素集合
* 4. 递归基是什么? 中序数组被划分为空,说明已经到达叶子节点返回nil即可
* 5. 递归体如何实现? 搜索划分点 + 构建二叉树
*/
func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(inorder) == 0{
return nil
}
idx := -1
for i,v:=range inorder{
if v == preorder[0]{
idx = i
}
}
root := &TreeNode{Val:preorder[0]}
root.Left = buildTree(preorder[1:idx+1],inorder[:idx])
root.Right = buildTree(preorder[idx+1:],inorder[idx+1:])
return root
}
作者:jueyoq
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/solution/golang-biao-zhun-ban-by-jueyoq/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
构建二叉树 - 找规律递归分治
模板
root := &TreeNode{Val:nums[maxId]}
root.Left = dfs(nums[:maxId])
root.Right = dfs(nums[maxId + 1:])
654. 最大二叉树
每一层构建左右子树都是规律 - 递归分治
func constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums []int) *TreeNode {
return dfs(nums)
}
func dfs(nums []int) *TreeNode {
if len(nums) <= 0 {
return nil
}
maxId := getMaxId(nums)
root := &TreeNode{Val:nums[maxId]}
root.Left = dfs(nums[:maxId])
root.Right = dfs(nums[maxId + 1:])
return root
}
func getMaxId(nums []int) int {
maxId := -1
maxVal := 0
for i,v := range nums {
if v >= maxVal {
maxVal = v
maxId = i
}
}
return maxId
}
func buildTree(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(inorder) == 0 || len(postorder) == 0 {
return nil
}
id := getIndex(inorder, postorder[len(postorder)-1])
root := &TreeNode{Val: postorder[len(postorder)-1]}
// 在一个例子里找一下规律就行了
root.Left = buildTree(inorder[:id], postorder[:id])
root.Right = buildTree(inorder[id+1:], postorder[id : len(postorder) - 1])
return root
}
func getIndex(inorder []int, target int) int {
for i := 0; i < len(inorder); i ++ {
if inorder[i] == target {
return i
}
}
return -1
}
617. 合并二叉树
func mergeTrees(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
// 1. 递归的终止条件,让另一边 做节点就行了
if root1 == nil {
return root2
}
if root2 == nil {
return root1
}
// -- 刚进来让节点干啥
// 2. 节点的生成规律-逻辑在这儿
root := &TreeNode{Val:(root1.Val+root2.Val)}
root.Left = mergeTrees(root1.Left, root2.Left)
root.Right = mergeTrees(root1.Right, root2.Right)
return root
}
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
学到了递归的一些其他写法
func searchBST(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
// 其实也只有一个返回值
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root.Val == val {
return root
}
// 这两个分支一次只走一个
if val > root.Val {
return searchBST (root.Right, val)
}
return searchBST (root.Left, val)
}
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
二叉搜索树的玩法-有序数组
func getMinimumDifference(root *TreeNode) int {
var pre *TreeNode
res := math.MaxInt64
var getDiff func(root *TreeNode)
getDiff = func (root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
getDiff(root.Left)
// 中序遍历生成的有序数组,记录,做差值
if pre != nil {
res = min(res, abs(pre.Val, root.Val))
}
pre = root
getDiff(root.Right)
}
getDiff(root)
return res
}
func abs(num1 int, num2 int) int{
if num1 > num2 {
return (num1 - num2)
}
return (num2 - num1)
}
func min(num1 int, num2 int) int{
if num1 > num2 {
return num2
}
return num1
}
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
func findMode(root *TreeNode) []int {
var maxCount int
var pre *TreeNode
var count int
var traverse func(*TreeNode)
var res []int
traverse = func (root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
traverse(root.Left)
// 二叉搜索树的中序遍历,当成有序数组来做
// 在这个有序数组中,pre 是 root的前一个指针
if pre != nil {
if pre.Val == root.Val {
count ++
} else {
count = 0
}
}
// 重新指向和依附
if count > maxCount {
maxCount = count
// 重新指向!非常妙
res = []int{root.Val}
} else if maxCount == count {
res = append(res, root.Val)
}
pre = root
traverse(root.Right)
}
traverse(root)
return res
}
889. 根据前序和后序遍历构造二叉树
// 取前序遍历的第一个节点为根
// 以此为根去后序遍历划分左右子树
// 在去前序遍历中找对应的位置
func constructFromPrePost(preorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(preorder) == 0 {
return nil
}
root := &TreeNode{Val: preorder[0]}
// 这样pos+2就不会溢出了
if len(preorder) == 1 {
return root
}
// 在postorder中找到左子树根节点的位置pos
pos := FindPosInArray(postorder, preorder[1])
// 根据pos确定左子树的范围
root.Left = constructFromPrePost(preorder[1:pos+2], postorder[:pos+1])
// 根据pos确定右子树的范围
root.Right = constructFromPrePost(preorder[pos+2:], postorder[pos+1:len(postorder)-1])
return root
}
func FindPosInArray(s []int, target int) int {
for index, value := range s {
if value == target {
return index
}
}
return -1
}
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
leetcode.cn/problems/po…
核心:去寻找每个节点应该做的事情,之后就是简单遍历二叉树了
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return root
}
modify(root)
return root
}
func modify(root *Node) {
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return
}
// 核心 + 前序遍历
root.Left.Next = root.Right
if root.Next != nil {
root.Right.Next = root.Next.Left
}
modify(root.Left)
modify(root.Right)
}
114. 二叉树展开为链表
还是去找每个节点应该做的事情
func flatten(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
flatten(root.Left)
flatten(root.Right)
r :=root.Right
root.Right,root.Left =root.Left,nil
for root.Right != nil{
root =root.Right
}
root.Right =r
}