我正在参加「掘金·启航计划」
2020年北京大学张志华教授:机器学习基础讲座笔记从以下三方面讲解
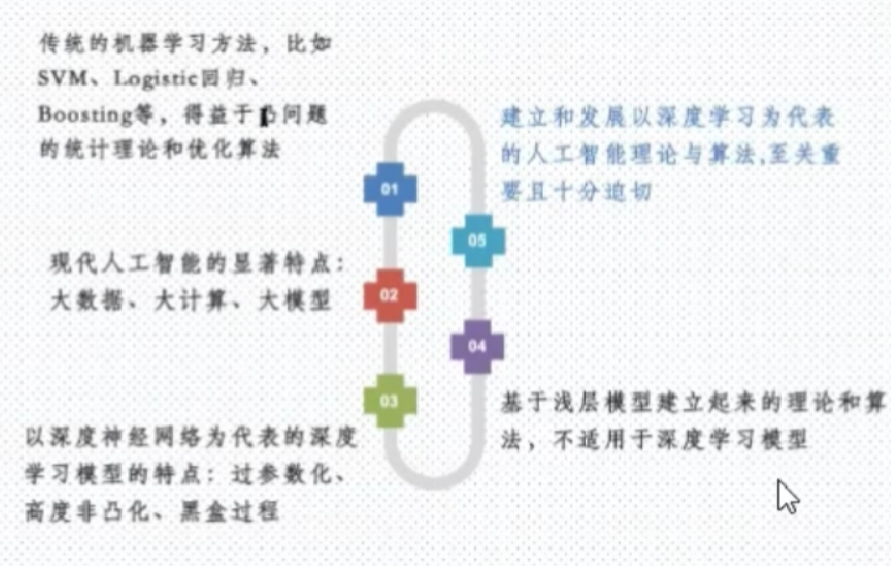
机器学习的发展现状
- Unlike artificial intelligence,machine learning aims to not mimic human thoughts and behaviors but to improve experience and interaction.
- Machine learning explores the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data.
发展脉络如下:
-
专家系统
-
句法模式识别
-
硬推理转为软推理
-
精确推理代为近似推理
-
特征工程:从数据到表示牵涉到深入的领域知识。
-
基于规则的模型对于浅层推理有效,但没法用来进行深层次的推理。
-
大规模规则空间搜索往往导致“维数灾难“问题。
David Marr treated vision as an information processing system,and put forth the idea that one must understand information processing systems at three distinct levels.This is known as Marr's Tri-Level Hypothesis:
- Implementational/physical level:how is the system physically realized(in the case of biological vision, what neural structures and neuronal activities implement the visual system)
- Algorithmic/representational level:how does the system do,specifically,what representations does it use and what processes does it employ to build and manipulate the representations
- Computational level:what does the system do,and why does it do these things
三十年之后,Tomaso Poggio 在计算层之上加了一更高层,即"Learning"。
-
"I am not sure that Marr would agree,but I am tempted to add learning as the very top level of understanding,above the computational level.Only then may we be able to build intelligent machines that could learn to see-and think-without the need to be programmed to do it.
1995 -- 2006的发展
统计学习:统计建模+算法计算
- SVM,Boosting,Sparse learning,Kernel machine,Nonparametric Bayes,etc.
- 统计模式识别、统计计算机视觉、统计自然语言处理模型、统计语音识别(隐马尔可夫模型;贝叶斯决策理论)
- 神经网纬(MLP):非线性的预测或者决策模型
一个自然的思路: 通过机器学习的途径来求解表示问题,从而弱化研究者对于领域背景高度掌握的要求。
- 大模型+大数据+大计算,使得这种思路变得可行。
- 深度模型
- 计算机视觉:ImageNet
- GPU实现

深度学习的关键技术
网络结构:
- Deep Architecture for Representation (Hinton et al.2006)
- Convolutional Structure (LeCun,1989)and Pooling (Zhou and Chellappa,1988)
- Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)(2009,2010)
- ResNet (He et al.2015)
网络训练:
- Back-Propagation for Gradient Computation (Rumelhart et al.,1986)
- Stochastic Gradient Descent (Robbins and Monro,1951).
- Stochastic Gradient Descent with Momentum (Polyak,1964) and Adam (Kingma and Ba,2014)
应用:给计算机视觉、语言识别、自然语言处理、自动驾驶、游戏类等领域带来了颠覆性的突破、给自然科学领域带来了新的研究手段。促进了人工智能产生了根本性的发展,成为各国科技竞争着力点。
进展:
- 生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks,GAN)
- 元学习(Meta Learning)
- 联邦学习(Federated Learning)
- 自动机器学习(AutoML)
- 深度蛋化学习(Deep Reinforcement Learning)
- 深度无监督学习(Deep Unsupervised Learning)
- 因果学习(Causal Learning)

机器学习:
"It is one of today's rapidly growing technical fields, lying at the intersection of computer science and statistics,and at the core of artificial intelligence and data science."
 "When you are raising money,it's Al.When you are hiring,it's machine learning.When you are actually doing it,it's statistics."
"When you are raising money,it's Al.When you are hiring,it's machine learning.When you are actually doing it,it's statistics."
机器学习的研究内容
- 机器学习与统计学
- Three major machine learning scenarios:supervised learning.unsupervised learning,and reinforcement learning.
- Machine learning mainly cares about classification (clustering and dimension reduction),while statistics more about regression(density estimation)
- The Data Modeling Culture:The analysis in this culture starts with assuming a stochastic data model for the inside of the black box.
- The Algorithmic Modeling Culture:The analysis in this culture considers the inside of the box complex and unknown.Their approach is to find a function f(x)-an algorithm that operates on x to predict the responses y.
(Leo Breiman.Statistical Modeling:The Two Cultures.Statistical Science,16(3):199-231.2001.)
- Prediction:Random forests,gradient boosting,support vector machines,deep neural networks."If media attention is the appropriate metric,then the pure prediction algorithms are our era's statistical stars."
- Estimation:statistical estimation theory is intended as an instrument for peering through the noisy data and discerning a smooth underlying truth.
- Attribution:the assignment of significance of individual predictors.
(Bradley Efron.Prediction,Estimation,and Attribution (with discussion).JASA.119(530):636-655.2020.)
机器学习与优化
-
A machine learning model is typically formulated as an optimization problem.
-
In Machine leaming scenarios,one not only cares about fitting performance but also performance measure w.r.t.the test set(Generalization).
-
For pure optimization,minimizing the objective function is a goal in and of itself.
机器学习=优化+泛化
Convex and Nonconvex Optimzation
- A conventional statistical learning model is defined as convex optimization.For example,the hinge loss for SVM,logit loss for logistic regression,and the exponential loss for AdaBoost.
- In deep learning scenarios,the resulting problem becomes nonconvex.
- Acceleration and Generalization
机器学习:数据设置
- Training data. These data are used to fit each of the models indexed by the tuning parameter.
- Validation data. These data are used to evaluate the performance of each of the models fit in the previous step;that is,to evaluate the prediction performance. One then chooses a final model from the list.
- Test data. A final data set is often reserved to evaluate the chosen model,because the previous step can be viewed as "fitting"the validation data.
机器学习:算法分类
-
Frequentist view
- The frequentist views the model parameters as unknown constants and estimates them by matching the model to the available training data using an appropriate metric.
- Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE)is a general approach when the model is specified via a(conditional)probability distribution.
-
Bayesian approach
- The model specifies a family of(conditional) probability distributions, indexed by parameters.These parameters are considered random as well,so a prior distribution needs to be specified for them.
- Frequentist methods often take the form of optimization procedures, and Bayesian methods often take posterior sampling the form integration procedure.
-
Parametrics vs. Nonparametrics
- The difference in that in a parametric model,the number of parameters is fixed once and for all,irrespective of the number of data samples.
- A nonparametric model is "not parametric,"in that the number of parameters is not fixed,but rather grows as a function of the number of the data samples.
- Overparametric model (p >> n)
-
Discriminant Models vs.Generative Models
- In a discriminant model,one care the conditional likelihood function p(y | x;theta)which is used to estimate the parameters theta from training data.
- A generative model considers p(y,x)=p(y)p(xly).
机器学习三个层面
- Applications :为领域学科提供解决问题 方法与途径
- Methodology:算法构造与计算
- Mathematics:算法的理论分析
表示学习:
-
机器学习的关键在于表示学习
- 表示需要适看预测
- 表示需要适合计算
-
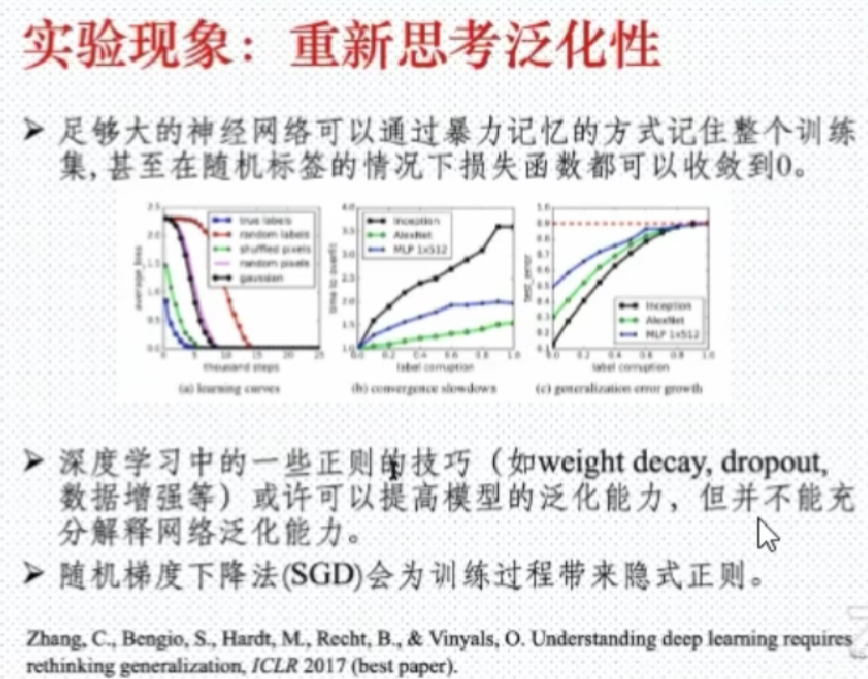
深度表示的挑战
- 过参数化
- 非凸化
- 运行黑盒化
机器学习的关键技术思路
- 深度表示/隐含
- 正则化/规范技术/先验 处理过拟合、过饱和、病态、非稳定性
- 集成Ensemble/平均化技术/贝叶斯
- Boosting,Bagging方差减少,加速
- 自适应技术
- 随机
机器学习:统计思维和计算思维统一
-
统计为求解问题提供了数据驱动的建模途径
-
无论从统计角度还是从数学角度来研究AI,其实际性能最后都要通过计算呈现出来。
- 数值分析,即求解连续数学问题的算法
- 离散算法,即求解离散结构问题的算法
- 大规模计算架构
机器学习:数学工程是趋向AI的重要途径
- 概率论、随机分析、微分方程、微分流形等工具可以引入来研究AI的数学机理。
- 数学帮助我们化繁为简。
- 工程是技术也是艺术,它是算法的必要补充,是新算法提出的源泉。计算图和自动微分
- 深度学习是数学和工程的一个完美结合的杰作。
- 如果强化学习能得以获得巨大成功,肯定是数学和工程合作的又一个巅峰。
应用数学的魅力在于通过严格的数学推理来寻找解决问题的算法或化繁为筒。一些构造性数学证明过程其实就蕴含了精妙的算法,而存在性证明则能给出一个模型解决问题的有效性边界。
机器学习基础问题
-
机器学习是指利用统计和计算的手段探索算法的构造和机理,以期从数据和经验中学习,来改善学习系统在各类任务中的性能。
-
设计和分析机器学习方法牵涉到一些基础问题:性能上可预测性或泛化性、计算上复杂性和稳定性、运行机理上可解释性等。
"Using fancy tools like neural nets,boosting,and support velcor machines without understanding basic statistics is like doing brain surgery before knowing how to use a band-aid." ------ Larry Wasserman,2003
机器学习的基础原则
- 可预测性Predictability)/泛化性(Generalization)模型泛化性、算法泛化性
- 可计算性(Computability)/易处理性(Tractability)
- 稳定性(Stability): 模型稳健性、对抗性,算法适定性,数据隐私性
- 可解释性Interpretability)
- 可扩展性(Scalability)

研究现状:代表性学者
斯坦福:Emmanuel Candes,David Donoho,Trevor Hastie,Andrea Montanari,etc.
伯克利:Peter Bartlett,Mike Jordan,.Bin Yu,,etc.
普林斯顿:Sanjeev Arora,Weinan E,ctc.
纽约大学:Yann LeCun,etc.
机器学习的知识体系
-
机器学习可以分为三个层面:应用、方法和理论(Applications,Methods,and Theory)。因此,对应应该有三个层次课程体系,服务于不同人的不同需求。
-
层面一和层面二之间类比于“高等数学”;层面二和层面三之间类比于“数学分析
-
第一层次学会如何实现或应用机器学习方法和模型。比如:
- 对于降维方法,我们要会用PCA、MDS;对于聚类方法,我们会用K均值、高斯混合体、谱聚类等;
- 对于分类方法,我们需要会用朴素贝叶斯、Losc回归、SVM、boosting等
- 还需要会用一些复杂模型,Kernel方法、深度神经网络以及深度强化学习一些具体算法
-
这里说会用是我们掌握这些方法实现程序,而且对模型中一些超参数也知道如何设定,比如Kernel SVM中核函数中参数以及正则化因子的选取,深度神经网络中训练算法的学习率的确定等。进一步,还期许能了解这些方法工作的基本原理。
-
这个层次适用于从事非统计学和机器学习领域的实践者。
-
第二个层次学会机器学习方法运行的数学机理,从这个层面我们可以把机器学习看成应用数学或统计学。
- 举SVM为例,我们需要知道它是如何导出,它的数学模型是如何定义,它的模型又是如何求解的。
- 对于深度学习候型,我们同样需要去了解这些问题,
-
需要掌握其中的数学背景知识:
- 数值线性代数、数值优化、姬患统计学签。 我之前5、6年时间的课程就是致力这个层面: 《机器学习导论》、《统计机器学习》、《应用数学基础》这几门课
-
这个层面适用于从事机器学习相关领域研发的学者或者工程师
- 第三个层次是掌握分析和设计机器学习的数学理论。
- 面对具体的机器学习问题,到底有没有办法可以找出有效的算法;
- 面对一个具体的机器学习算法,我们需要考虑算法可以达到的精确性、稳健性、复杂性。
- 总之,设计和分析机器学习算法将牵涉到可学习性、可解释性、泛化性、稳定性、计算复杂性等基础问题。
- 该层次适用于从事机器学或者统计学理论研究的学者
机器学习课程 --- “高等数学”
《An Introduction to Probabilistic Graphical Models》 M I Jordan 《Information Theory,Inference,and Learning Algorithms》 D J Mackay 《Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning》
C Bishop 《Multivariate Analysis》
V Mardia,J T Kent and J M Bibby
机器学习课程 --- “数学分析”
《Foundations of Machine Learning,Second Edition》 M Mohri,A Rostamizadeh,and A Talwalkar 《Understanding Machine Learning:From Theory to Algorithms 》 S Shalev-Shwartz and S Ben-David 《Computer Age Statistical Inference:Algorithms, Evidence and Data Science》 B Efron and T Hastie 《Machine Learning:A Probabilistic Perspective》(深度不够) K P Murphy
设置三门课程
统计学基础(Larry Wasserman,.All of Statistics) 计算与优化(Daniel A.Spielman,S&DS631) 并行编程(CUDA编程)
参考书目:概率统计
-
概率统计基础
- 《Probability and Statistics》M HDeGroot and M J Schervish 《An Introduction to Probability:Theory and its Applications》Vol.1&2,William Feller 《All of Statistics》Larry Wasserman 《Statistical Inference》 G Casella and R L Berger
-
多元统计
- 《Multivariate Analysis》V Mardia.J T Kent and J M Bibby 《An Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis》 T W Anderson 《Aspects of Multivariate Statistical Theory》 R J Muirhead 《Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis 》R A Johnson and D Wchern
-
理论机器学习
- 《理论机器学习》是想在第三层面做探索。
- 《高等统计学》或《经验过程》适用这个层面
- 但《高等统计学》或《经验过程》纯粹从统计学出发,缺少一些机器学习或理论计算机科学的元素。
- 更重要的,已有的理论也不能解决深度学习所带来新的基础问题。
《Asymptotic Stptistics》A W van der Vaart 《High-Dimensional Statistics:A Non-Asymptotic Viewpoint》Martin J Wainwright 《Foundations of Data Science》Avrim E Blum,John Hopcroft,and Ravi Kannan
做科研的心得:
有造境,有写境,此理想与写实二派之所由分。然二者颇难分别。因大诗人所造之境,必合乎自然,所写之境 亦必邻于理想故也。 ------王国维《人间词话》