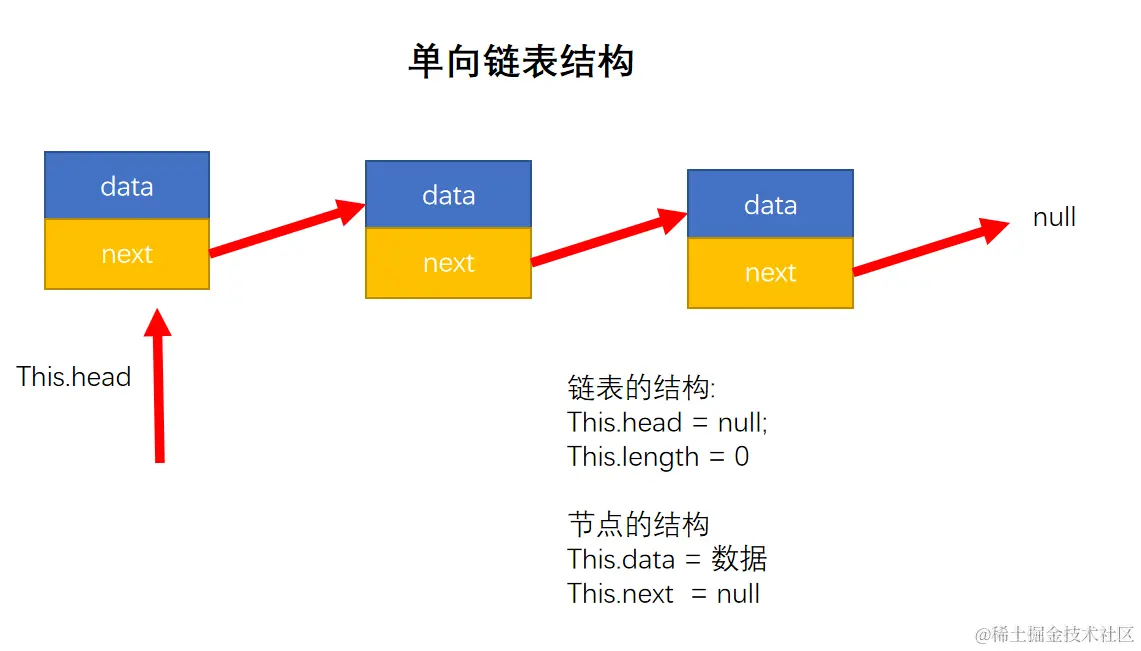
- 单向链表
- 要存储多个元素, 另外一个选择就是使用链表.
- 但不同于数组, 链表中的元素在内存中不必是连续的空间.
- 链表的每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(有些语言称为指针或者链接)组成.
- 相对于数组, 链表有一些优点:
- 内存空间是连续的. 可以充分利用计算机的内存. 实现灵活的内存动态管理.
- 链表不必在创建时就确定大小, 并且大小可以无限的延伸下去.
- 链表在插入和删除数据时, 时间复杂度可以达到O(1). 相对数组效率高很多.
- 相对于数组, 链表有一些缺点:
- 链表访问任何一个位置的元素时, 都需要从头开始访问.(无法跳过第一个元素访问任何一个元素).
- 无法通过下标直接访问元素, 需要从头一个个访问, 直到找到对应的位置.
class Lnode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null
}
}
class LinkList {
constructor() {
this.head = null
this.length = 0
}
append(el) {
let newnode = new Lnode(el)
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newnode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next
};
current.next = newnode;
}
this.length++
}
insert(position, el) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length || !Number.isInteger(position)) {
return false
}
let newnode = new Lnode(el)
if (position == 0) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newnode
} else {
newnode.next = this.head
this.head = newnode
}
this.length++
} else if (
position == this.length) {
this.append()
} else {
let current = this.head
let index = 0
while (index < position - 1) {
current = current.next
index++
}
newnode = current.next
current.next = newnode
}
this.length++
}
removeAt(position) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length || !Number.isInteger(position)) {
return false
}
if (this.head == null) {
return
} else {
if (position == 0) {
this.head = this.head.next
} else {
let current = this.head
var index = 0
while (index < position - 1) {
current = current.next
index++
}
current.next = current.next.next
}
this.length--
}
}
indexOf(el) {
let current = this.head
var index = 0
while (index < this.length) {
if (current.data == el) {
return index
} else {
current = current.next
index++;
}
}
return -1
}
remove(el) {
let index = this.indexOf(el)
console.log(index);
this.removeAt(index)
}
isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
sise() {
return this.length
}
}