
C++中的运算符重载简介
操作符重载是用来重新定义操作符,以便对用户定义的数据类型进行操作。操作符重载是一种编译时的多态性。操作符重载是一种静态的多态性,操作符被重载以对用户定义的数据类型执行某种意义。在C++中,几乎所有的操作符都可以被重载,除了范围操作符(::)、成员选择器( . )、sizeof、三元操作符( ? :)和成员指针选择器( * )。
操作符重载的语法
return_type class_name : : operator op (Parameter_list)
{
// statements to be execute.
}
操作符op是一个操作符函数,其中操作符是一个关键字,所有操作符的重载都会出现,op是被重载的操作符。
- 一元运算符的重载
- 二元运算符重载
- 关系运算符的重载
- 赋值运算符重载
- ++和-运算符的重载
- 输入/输出操作符重载
- 下标[]操作符重载
- 类成员访问操作符 -> 重载
C++中操作符重载的例子
下面是下面提到的例子。
例子 #1 - 单元运算符重载
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class number
{
public:
int no;
number(int num)
{
no = num;
}
void print( )
{
cout<<no<<endl;
}
// - unary operators overloading
void operator - ( )
{
no = -no;
}
};
int main()
{
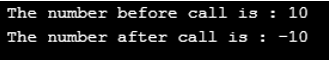
number n1(10);
cout<<" The number before call is : ";
n1.print( );
-n1;
cout<<" The number after call is : ";
n1.print( );
return 0;
}
输出
例子 #2 - 二元运算符重载
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
public:
int salary;
Employee( int sal )
{
salary = sal;
}
void print( )
{
cout<< salary <<endl;
}
// Binary Operators Overloading
Employee operator + ( Employee n )
{
return salary + n.salary;
}
};
int main()
{
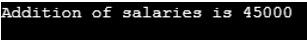
Employee e1(20000);
Employee e2(25000);
Employee e3 = e1 + e2;
cout<<"Addition of salaries is "<< e3.salary;
return 0;
}
输出
例子 #3 - 关系运算符重载
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
public:
int salary;
Employee( int sal )
{
salary = sal;
}
void print( )
{
cout<<salary<<endl;
}
bool operator > ( Employee n )
{
if(salary > n.salary)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
};
int main()
{
Employee e1(20000);
Employee e2(25000);
if(e1 > e2)
cout<<"Employee e1 slary is greater than employee e2. ";
else
cout<<"Employee e1 slary is lesser than employee e2. ";
return 0;
}
输出

例子 #4 - 赋值运算符重载
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
public:
int salary;
Employee( int sal )
{
salary = sal;
}
// Assignment Operators Overloading
Employee operator = ( Employee n )
{
Employee temp = n.salary;
return temp;
}
};
int main()
{
Employee e1(20000);
Employee e2(25000);
Employee e3 = e1;
cout<< e3.salary;
return 0;
}
输出

例子 #5 - ++ 或 - 运算符重载
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
public:
int salary;
Employee(int sal)
{
salary = sal;
}
//post increment operator overloading
Employee operator ++ ( int )
{
Employee temp = salary;
salary++;
return temp;
}
//pre increment operator overloading
Employee operator ++( )
{
salary=salary+1;
Employee temp=salary;
return temp;
}
};
int main()
{
Employee e1(20000);
Employee e2 = ++e1;
cout<<"Pre increment salary: "<< e2.salary<<endl;
Employee e3(20000);
Employee e4=e3++;
cout<<"Post increment salary: "<<e4.salary<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出

例子 #6 - 输入/输出运算符重载
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
public:
int salary;
Employee(int sal)
{
salary = sal;
}
// Output Operator Overloading
friend ostream &operator << ( ostream &output, const Employee &e ) {
output << "This object is of employee class. ";
return output;
}
};
int main()
{
Employee e1(20000);
cout<<e1;
return 0;
}
输出

例子 #7 - 下标操作符重载
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
public:
int allsalaries[50];
Employee(int sal)
{
static int count = 0;
allsalaries[count] = sal;
count++;
}
//Subscripting [] Operator Overloading
//return first employee salary
int &operator [] ( int i ) {
if( i > 10 ) {
cout << "Out of bound index. " <<endl;
return allsalaries[0];
}
}
};
int main()
{
Employee e1(20000);
Employee e2(21000);
int res = e1[1];
cout<< res;
return 0;
}
输出

例子 #8 - 类成员访问操作符 -> 重载
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee{
int salary;
public:
Employee( int sal ){
salary = sal;
}
void print( )
{
cout << "Salary is "<< salary << endl;
}
//Class Member Access Operator -> Overloading
Employee *operator -> ( )
{
return this;
}
};
int main()
{
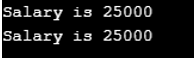
Employee e1( 25000);
e1.print();
e1 -> print();
return 0;
}
输出
结论
操作符重载是一种静态的多态性,操作符被重载,在用户定义的数据类型上执行与内置数据类型相同的操作(根据需要)。在C++中,几乎所有的操作符都可以被重载,正如我们在上面的例子中看到的那样。