携手创作,共同成长!这是我参与「掘金日新计划 · 8 月更文挑战」的第12天,点击查看活动详情
🍁 作者:知识浅谈,CSDN签约讲师,CSDN博客专家,华为云云享专家,阿里云星级博主
📌 擅长领域:全栈工程师、爬虫、ACM算法
💒 公众号:知识浅谈
🔥 联系方式vx:zsqtcc
🤞RabbitMQ高可用架构总结🤞
16 在脚手架中使用axios
16.1安装axios
# 1.安装axios
npm install axios --save-dev
# 2.配置axios(因为上边的知识把axios下载下里并没有配置到项目中)
在main.js中引入axios
import axios from 'axios'
在main.js中修改如下配置
Vue.prototype.$http=axios //修改内部的$http为axios,之后可以使用$http发axios的请求
# 3.使用axios
在需要发送异步请求的位置使用$http代替axios
this.$http.get("url").then((res)=>{})
this.$http.post("url").then((res)=>{})
17. vuecli 的打包部署
# 1.在项目的根目录中执行命令
vue run build
注意:vue打包的项目必须在服务器上运行,不能直接双击运行
# 2.打包之后项目的变化
打包之后出现dist目录,dist目录就是vue脚手架项目的生产目录,或者说是直接部署目录
# 3.项目的运行
可以把dist放到服务器中运行,可以直接放到springboot项目的红static静态目录中。
18. vuex的使用
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
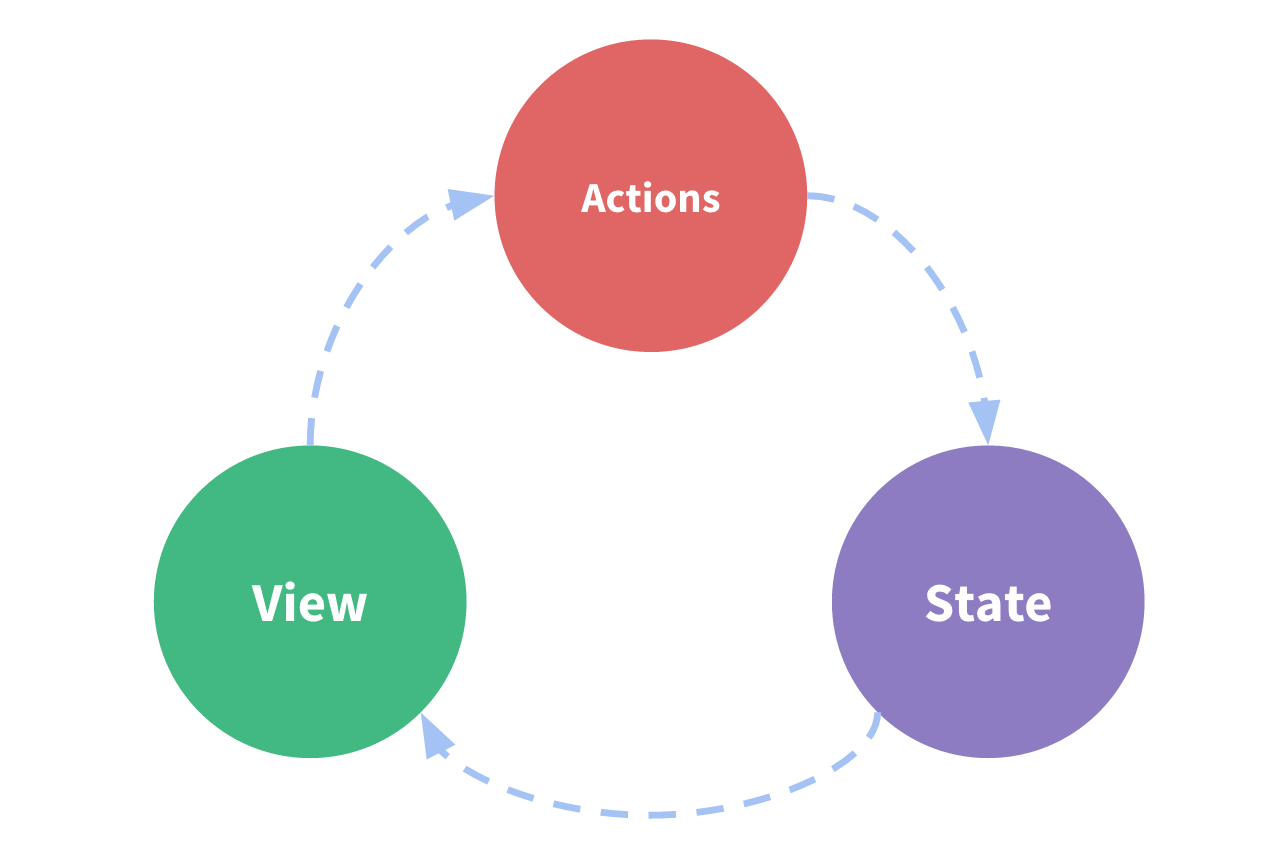
状态子管理包含三个部分:
- state,驱动应用的数据源;
- view,以声明方式将 state 映射到视图;
- actions,响应在 view 上的用户输入导致的状态变化。
以下是一个表示“单向数据流”理念的简单示意
但是,当我们的应用遇到多个组件共享状态时,单向数据流的简洁性很容易被破坏。
通俗解释:

-
下载vuex.js导入文件
<!--导入vue和vuex--> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script src="js/vuex.js"></script> -
在三个继承的组件中按照非继承的方式使用共享数据
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!--导入vue和vuex--> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script src="js/vuex.js"></script> </head> <body> asdada <div id="app"> <grandfather></grandfather> </div> asdda <template id="grandfather"> <div > <!--在使用Vuex中保存的共享数据的是偶--> <p> {{ this.$store.state.msg }}</p> <father></father> </div> </template> <template id="father"> <div> <p></p> <p> {{ this.$store.state.msg }}</p> <son></son> </div> </template> <template id="son"> <div> <p></p> <p> {{ this.$store.state.msg }}</p> </div> </template> <script> //创建Vuex对象 const store = new Vuex.Store({ //注意这个Store中的S是大写 这个大括号就相当于给这个方法传递的一个对象 //state这个可以就相当于组件中的data,用来保存共享数据 state:{ msg:"你咋不出来", count:0, }, }); Vue.component("grandfather",{ template:"#grandfather", //3.在祖先中添加store的key保存Vuex对象 //只要祖先中保存了vuex对象,那么祖先组件和所有的后代组件就可以使用Vuex中保存的共享数据了 store:store, components:{ "father":{ template: "#father", //儿子组件 components: { "son":{ template:"#son", } } } } } ); const app = new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ }, methods:{ }, }); </script> </body> </html> -
如何操作保存的共享数据(不要通过直接对共享数据进行操作,不便于排错,通过commit调用store中的方法进行操作)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>test1</title> <script src="js/vuex.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <father></father> </div> <template id="father"> <div > <!--在使用Vuex中保存的共享数据的是偶--> <p> {{ this.$store.state.count }}</p> <son1></son1> <son2></son2> </div> </template> <template id="son1"> <div> <button @click="add">增加</button> <!--不推荐直接修改共享数据,因为如果多个组件都修改了共享的数据那么后期可能会发生错误, 我们如果去调试错误,需要去检查每一个修改共享数据的组件,很不方便--> <button @click="sub">减少</button> <!-- <p> {{ this.$store.state.msg }}</p>--> <input type="text" :value="this.$store.state.count"> </div> </template> <template id="son2"> <div> <p> {{ this.$store.state.count }}</p> </div> </template> <!--引入vue 生产环境版本,优化了尺寸和速度 --> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script> <!--引入路由--> <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script> <!--引入axios--> <script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> const store = new Vuex.Store({ //用于保存共享数据 state:{ count:0, }, //用于保存修改共享数据的方法 mutations:{ //在执行mutation中定义的方法时候,传递一个state方法给这些方法 mAdd(state){ state.count++; }, mSub(state){ state.count--; }, } }); Vue.component("father", { template: "#father", store: store, components: { "son1": { template: "#son1", methods: { add(){ // this.$store.state.count++; this.$store.commit("mAdd"); }, sub(){ // this.$store.state.count--; this.$store.commit("mSub"); }, }, }, "son2": { template: "#son2", } } } ); const app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data: {}, methods: {}, components: {}, }); </script> </body> </html> -
什么是vuex中的getters?
Vuex的getter属性就和组件的计算属性一样,会将数据缓存起来,只有数据发生变化的时候,才会重新计算
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>test1</title> <script src="js/vuex.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <father></father> </div> <template id="father"> <div > {{ this.$store.getters.format }} {{ this.$store.getters.format }} {{ this.$store.getters.format }} <!--虽然调用了三次,但是只会执行一次format,就会被缓存起来--> <!-- {{ this.$store.state.msg }}--> <!-- {{ this.$store.state.msg }}--> <!-- {{ this.$store.state.msg }}--> <!-- {{ format }}--> <!-- {{ format }}--> <!-- {{ format }}--> <!--在使用Vuex中保存的共享数据的是偶--> <!-- <p> {{ this.$store.state.count }}</p>--> <!-- <son1></son1>--> <!-- <son2></son2>--> </div> </template> <!--引入vue 生产环境版本,优化了尺寸和速度 --> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script> <!--引入路由--> <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script> <!--引入axios--> <script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> const store = new Vuex.Store({ //用于保存共享数据 state:{ count:0, }, //用于保存修改共享数据的方法 mutations:{ //在执行mutation中定义的方法时候,传递一个state方法给这些方法 mAdd(state){ state.count++; }, mSub(state){ state.count--; }, }, getters:{ //和组件中的computed一样,会做缓存 format(state){ console.log("getters执行"); return state.count +1; } } }); Vue.component("father", { template: "#father", store:store, // data(){return{ // msg:"cyl", // }}, // computed: { // format(){ // console.log("test"); // return this.msg+"adsasda"; // } // } // store: store, // components: { // "son1": { // template: "#son1", // methods: { // add(){ // // this.$store.state.count++; // this.$store.commit("mAdd"); // }, // sub(){ // // this.$store.state.count--; // this.$store.commit("mSub"); // }, // }, // }, // "son2": { // template: "#son2", // } // } } ); const app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data: {}, methods: {}, components: {}, computed:{}, //专门用于定义计算属性的,只要计算结果不改变就是用缓冲中的数据 }); </script> </body> </html>