前缀树
- 单个字符串中,字符从前到后的加到一棵多叉树上。
- 字符放在路上,节点上有专属的数据项(常见的是pass和end值)。
- 所有样本都这样添加,如果没有路就新建,如有路就复用。沿途节点的pass值增加1,每个字符串结束时来到的节点end值增加1。
- 可以完成前缀相关的查询。
public static class Node2 {
public int pass;
public int end;
public HashMap<Integer, Node2> nexts;
public Node2() {
pass = 0;
end = 0;
nexts = new HashMap<>();
}
}
public static class Trie2 {
private Node2 root;
public Trie2() {
root = new Node2();
}
public void insert(String word) {
if (word == null) {
return;
}
char[] chs = word.toCharArray();
Node2 node = root;
node.pass++;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
index = (int) chs[i];
if (!node.nexts.containsKey(index)) {
node.nexts.put(index, new Node2());
}
node = node.nexts.get(index);
node.pass++;
}
node.end++;
}
public void delete(String word) {
if (search(word) != 0) {
char[] chs = word.toCharArray();
Node2 node = root;
node.pass--;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
index = (int) chs[i];
if (--node.nexts.get(index).pass == 0) {
node.nexts.remove(index);
return;
}
node = node.nexts.get(index);
}
node.end--;
}
}
public int search(String word) {
if (word == null) {
return 0;
}
char[] chs = word.toCharArray();
Node2 node = root;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
index = (int) chs[i];
if (!node.nexts.containsKey(index)) {
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts.get(index);
}
return node.end;
}
public int prefixNumber(String pre) {
if (pre == null) {
return 0;
}
char[] chs = pre.toCharArray();
Node2 node = root;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
index = (int) chs[i];
if (!node.nexts.containsKey(index)) {
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts.get(index);
}
return node.pass;
}
}
计数(桶)排序
public static void countSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
int[] bucket = new int[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
bucket[arr[i]]++;
}
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < bucket.length; j++) {
while (bucket[j]-- > 0) {
arr[i++] = j;
}
}
}
基数排序
public static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
radixSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, maxbits(arr));
}
public static int maxbits(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
int res = 0;
while (max != 0) {
res++;
max /= 10;
}
return res;
}
public static void radixSort(int[] arr, int L, int R, int digit) {
final int radix = 10;
int i = 0, j = 0;
int[] help = new int[R - L + 1];
for (int d = 1; d <= digit; d++) {
int[] count = new int[radix];
for (i = L; i <= R; i++) {
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
count[j]++;
}
for (i = 1; i < radix; i++) {
count[i] = count[i] + count[i - 1];
}
for (i = R; i >= L; i--) {
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
help[count[j] - 1] = arr[i];
count[j]--;
}
for (i = L, j = 0; i <= R; i++, j++) {
arr[i] = help[j];
}
}
}
public static int getDigit(int x, int d) {
return ((x / ((int) Math.pow(10, d - 1))) % 10);
}
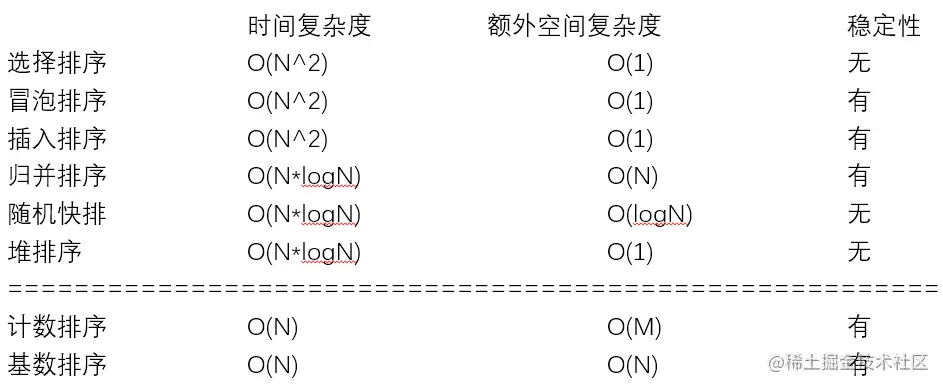
排序总结
- 不基于比较的排序,对样本数据有严格要求,不易改写
- 基于比较的排序,只要规定好两个样本怎么比大小就可以直接复用
- 基于比较的排序,时间复杂度的极限是O(N*logN)
- 时间复杂度O(N*logN)、额外空间复杂度低于O(N)、且稳定的基于比较的排序是不存在的。
- 为了绝对的速度选快排(常数时间最短)、为了省空间选堆排、为了稳定性选归并