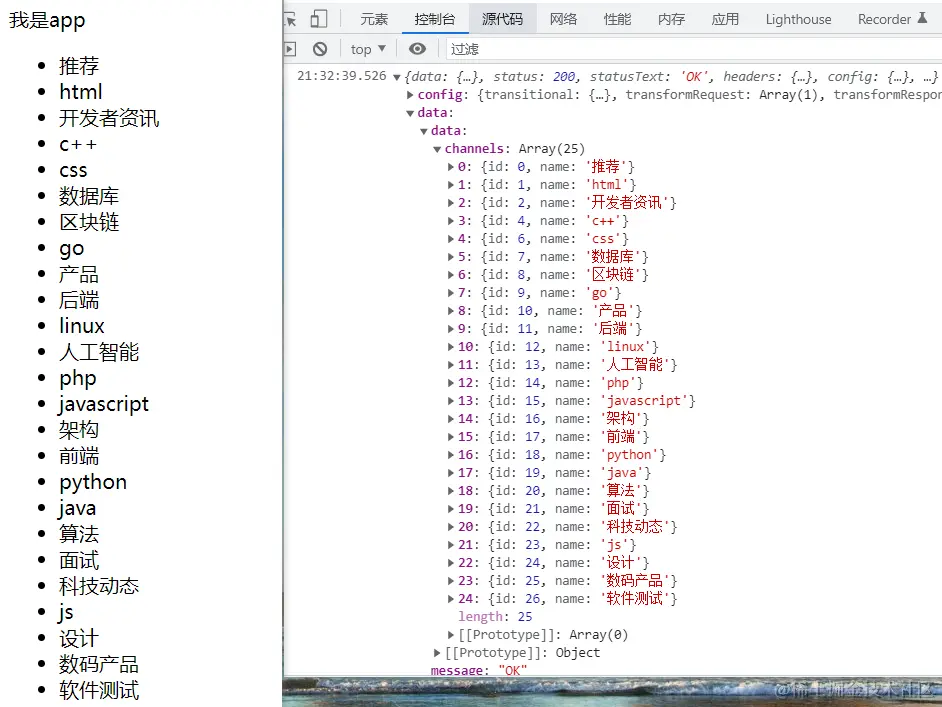
1.泛型约束
默认情况下,泛型函数的类型变量 Type 可以代表多个类型,这导致无法访问任何属性
比如,id('a') 调用函数时获取参数的长度:
function id<Type>(value: Type): Type {
console.log(value.length)
return value
}
id('a')
解释:Type 可以代表任意类型,无法保证一定存在 length 属性,
比如 number 类型就没有 length 此时,就需要为泛型添加约束来收缩类型(缩窄类型取值范围)
添加泛型约束收缩类型,主要有以下两种方式:1 指定更加具体的类型 2 添加约束
1.指定更加具体的类型
比如,将类型修改为 Type[](Type 类型的数组),因为只要是数组就一定存在 length 属性,因此就可以访问了
function id<Type>(value: Type[]): Type[] {
console.log(value.length)
return value
}
2.添加约束
interface ILength { length: number }
function id<Type extends ILength>(value: Type): Type {
console.log(value.length)
return value
}
解释:
1. 创建描述约束的接口 ILength,该接口要求提供 length 属性
2. 通过 extends 关键字使用该接口,为泛型(类型变量)添加约束
3. 该约束表示:传入的类型必须具有 length 属性
- 注意:传入的实参(比如,数组)只要有 length 属性即可(类型兼容性)
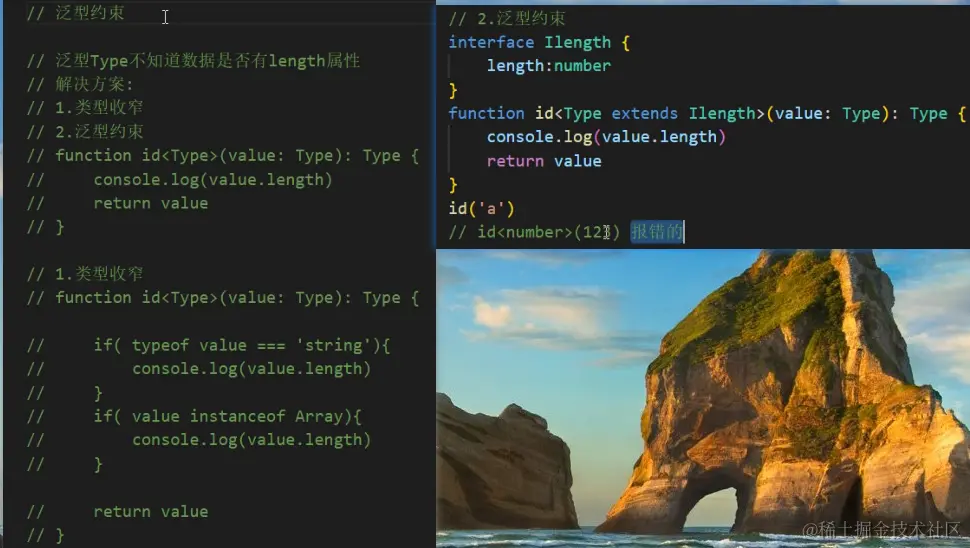
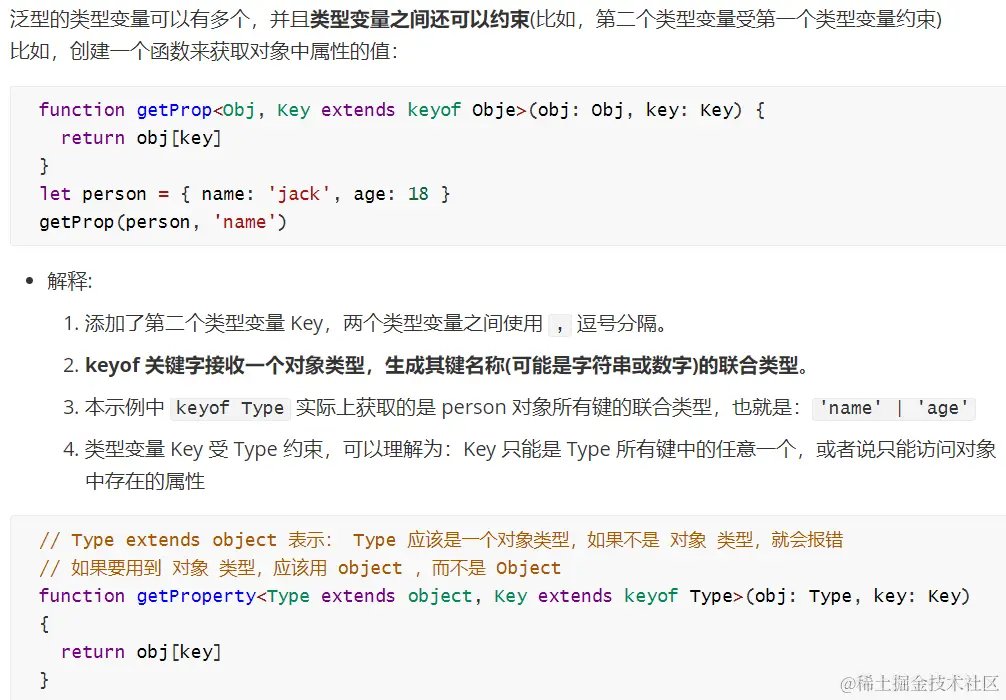
2.多个类型变量
3.泛型接口
泛型接口:接口也可以配合泛型来使用,以增加其灵活性,增强其复用性
interface Person<T> {
name:T
tell():void
say(username:T):string
}
let obj1 : Person<string> = {
name:"小明",
tell(){
console.log("我是"+this.name);
},
say(username){
return "你好"+username
}
}
let obj2 : Person<number> = {
name: 101,
tell(){
console.log("我是"+this.name);
},
say(username){
return "你好"+username
}
}
let arr1: number[] = [1,2,3]
let arr2: Array<number> = [1,2,3]
解释:
1. 在接口名称的后面添加 `<类型变量>`,那么,这个接口就变成了泛型接口。
2. 接口的类型变量,对接口中所有其他成员可见,也就是接口中所有成员都可以使用类型变量
3. 使用泛型接口时,需要显式指定具体的类型(比如,此处的 Person<nunber>)。
4.TypeScript与Vue
下载插件:
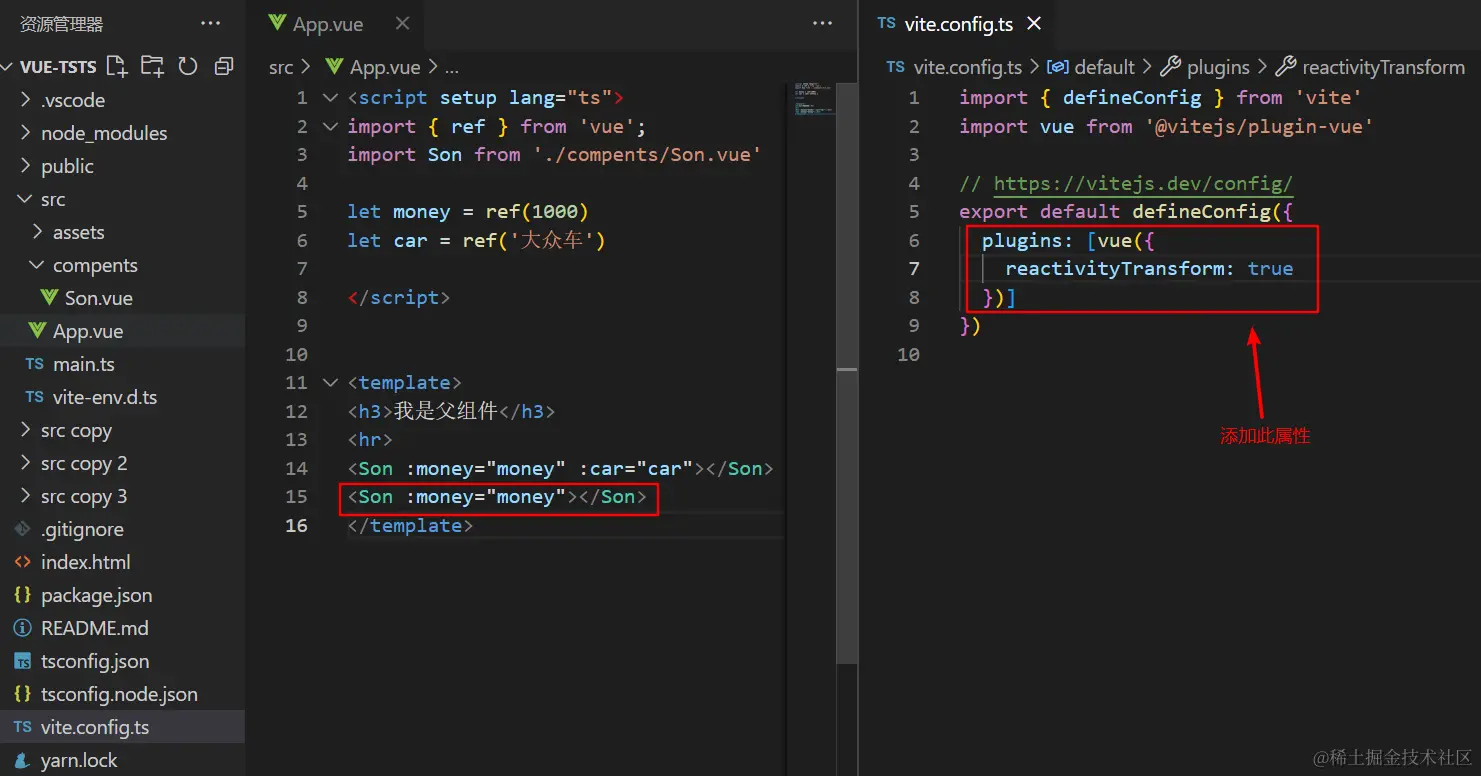
父向子传值:


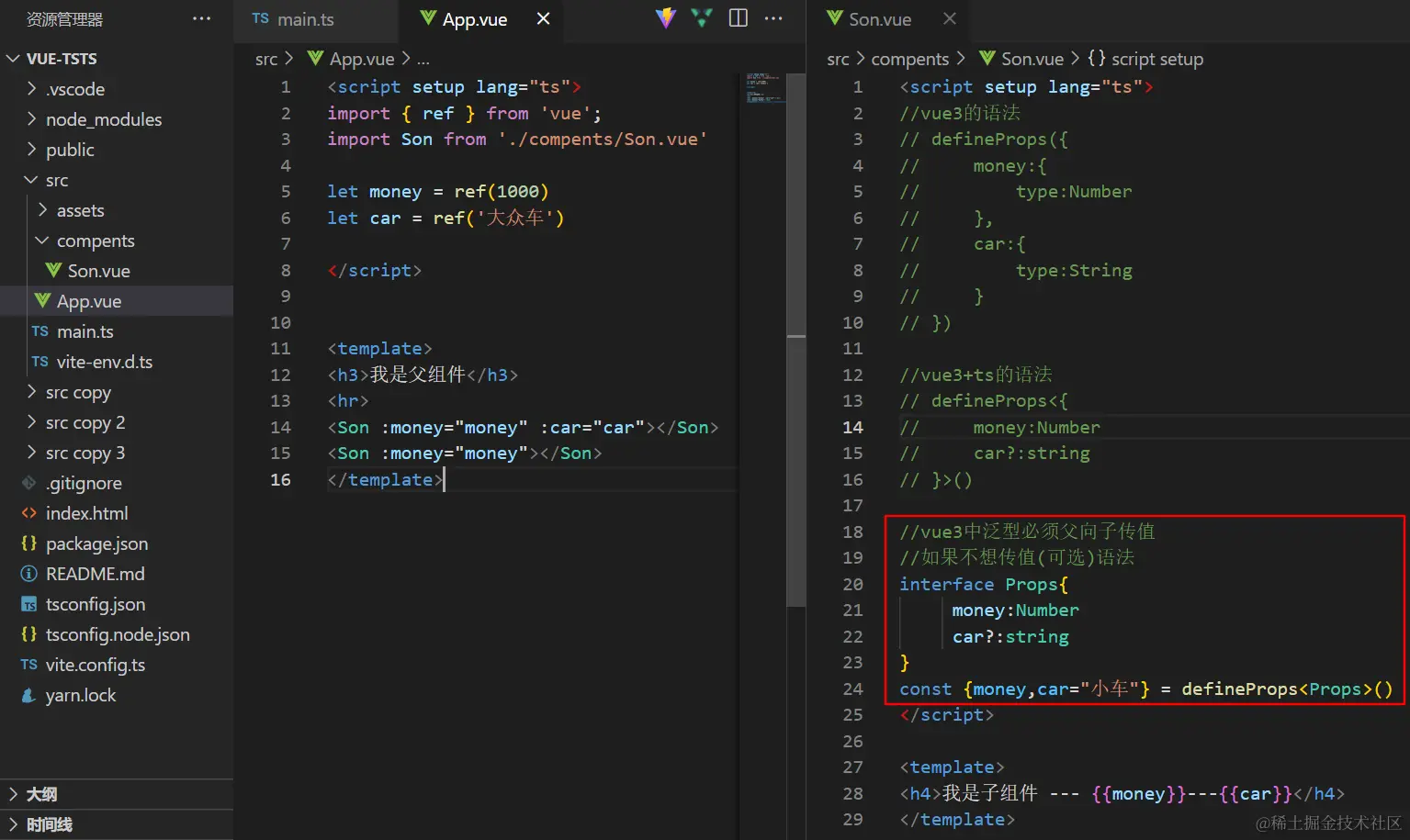
5.vue+ts父向子传值的可选属性及默认值设置

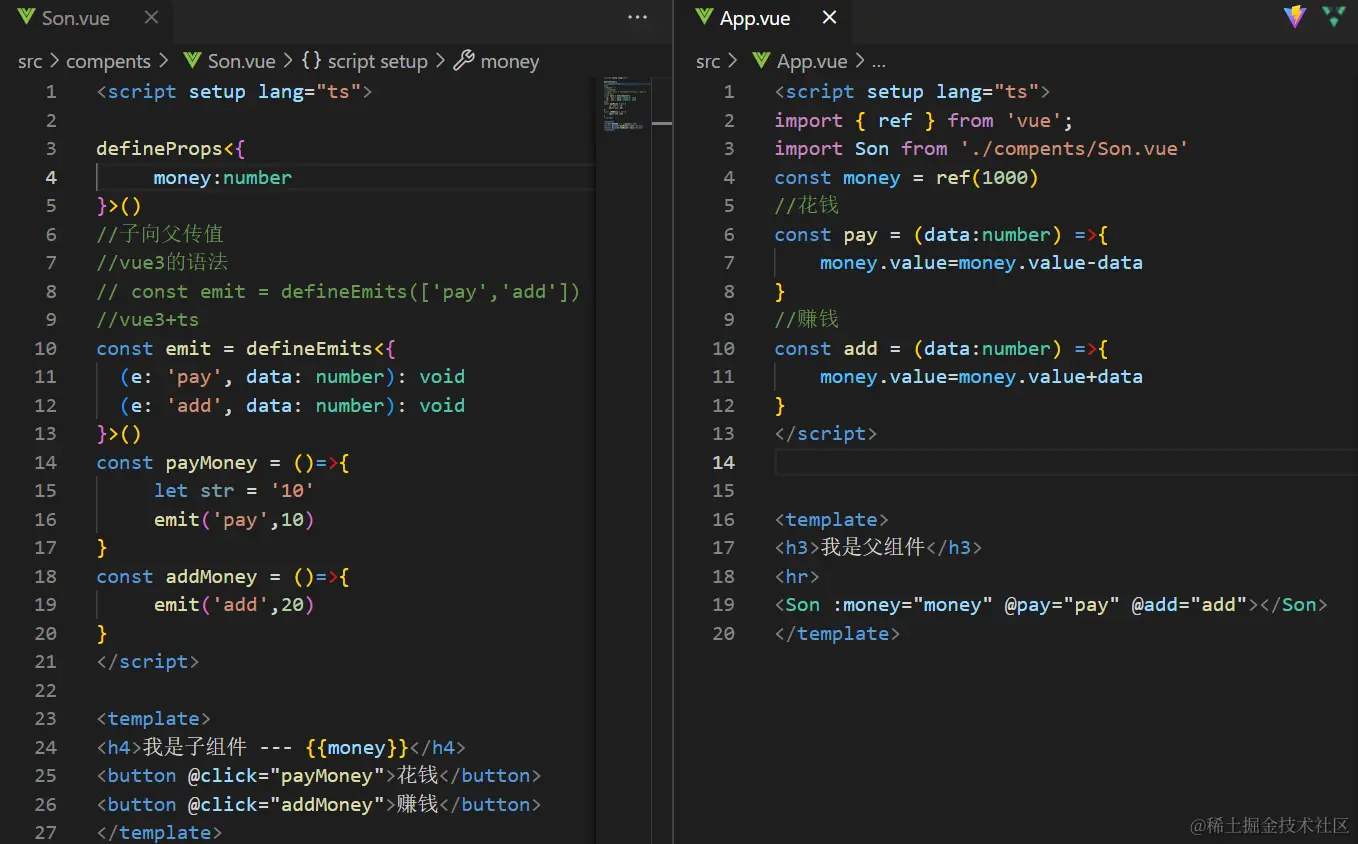
6.vue+ts子向父传值

7.ref与Typescript
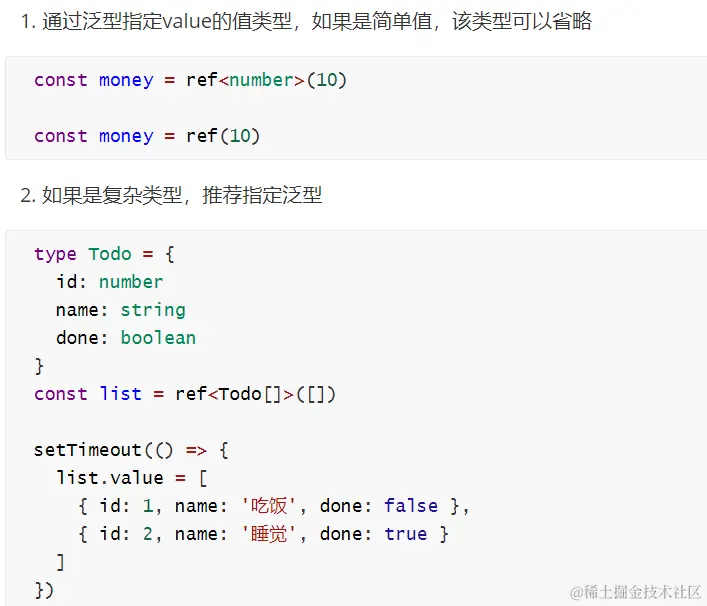
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue';
type TodoList = {
id:number
name:string
done:boolean
}[]
const list = ref<TodoList>([])
setTimeout(()=>{
list.value = [
{id:1,name:'jack',done:true},
{id:1,name:'jack',done:true}
]
},1000)
</script>
<template>
<h3>我是父组件</h3>
</template>
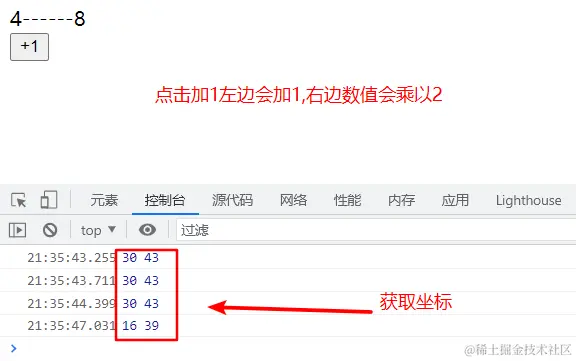
8.computed与Typescript

<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed, ref } from 'vue';
const num = ref(0)
const double = computed<number>(()=>{
return num.value*2
})
const add = (e:MouseEvent) =>{
num.value++
console.log(e.pageX,e.pageY);
}
</script>
<template>
<div>{{num}}------{{double}}</div>
<button @click="add">+1</button>
</template>
9.ref给dom元素指定类型
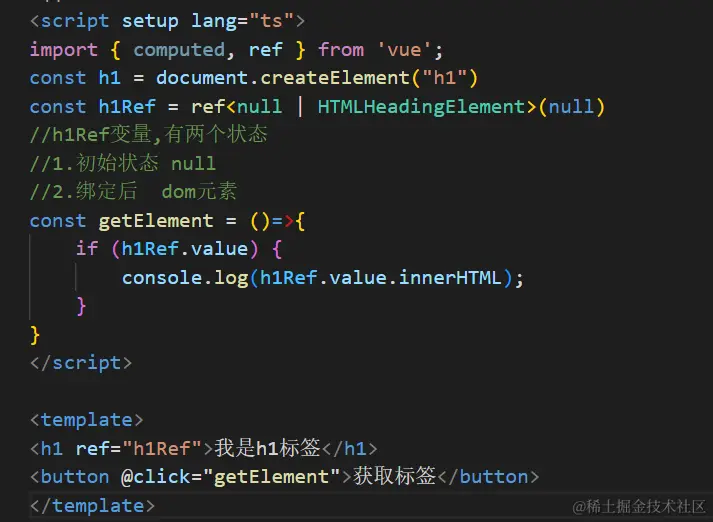
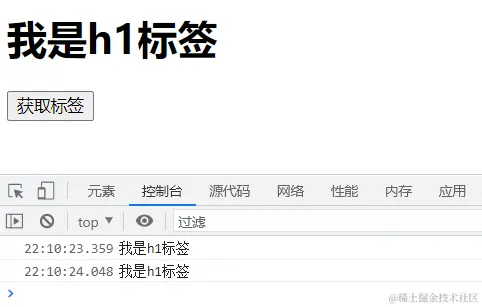
10.可选链操作符
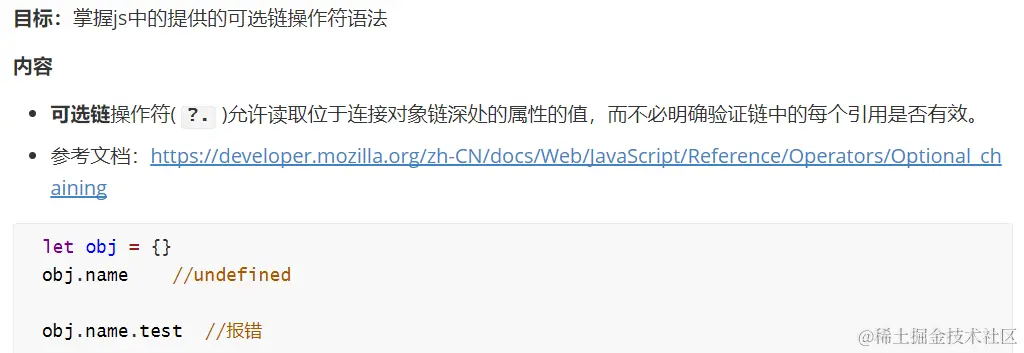
11.非空断言

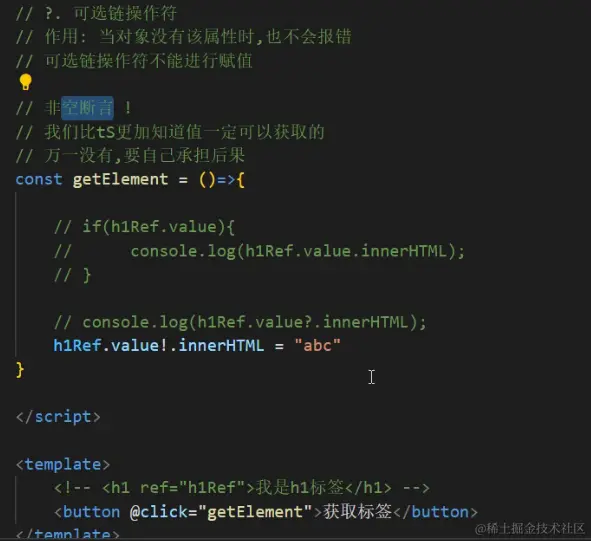
12.类型声明文件
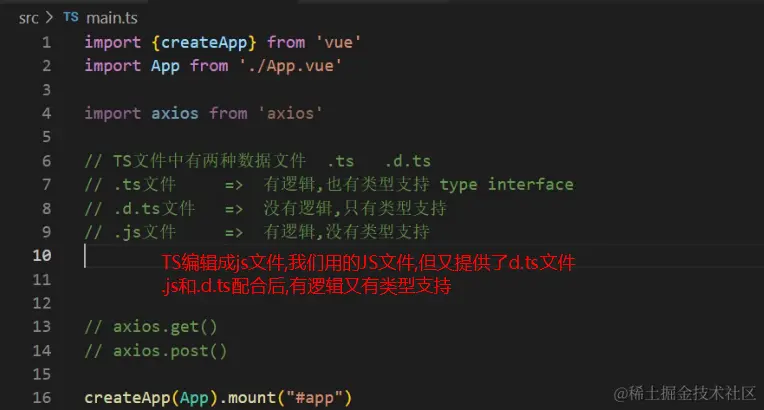
类型声明文件:用来为已存在的 JS 库提供类型信息
TS 中有两种文件类型:1 .ts 文件 2 .d.ts文件
.ts 文件:
1. 既包含类型信息又可执行代码
2. 可以被编译为 .js 文件,然后,执行代码
3. 用途:编写程序代码的地方
.d.ts 文件:
1. 只包含类型信息的类型声明文件
2. 不会生成 .js 文件,仅用于提供类型信息,在.d.ts文件中不允许出现可执行的代码,只用于提供类型
3. 用途:为 JS 提供类型信息
总结:.ts 是 `implementation`(代码实现文件); .d.ts 是 declaration(类型声明文件)
如果要为 JS 库提供类型信息,要使用 .d.ts 文件
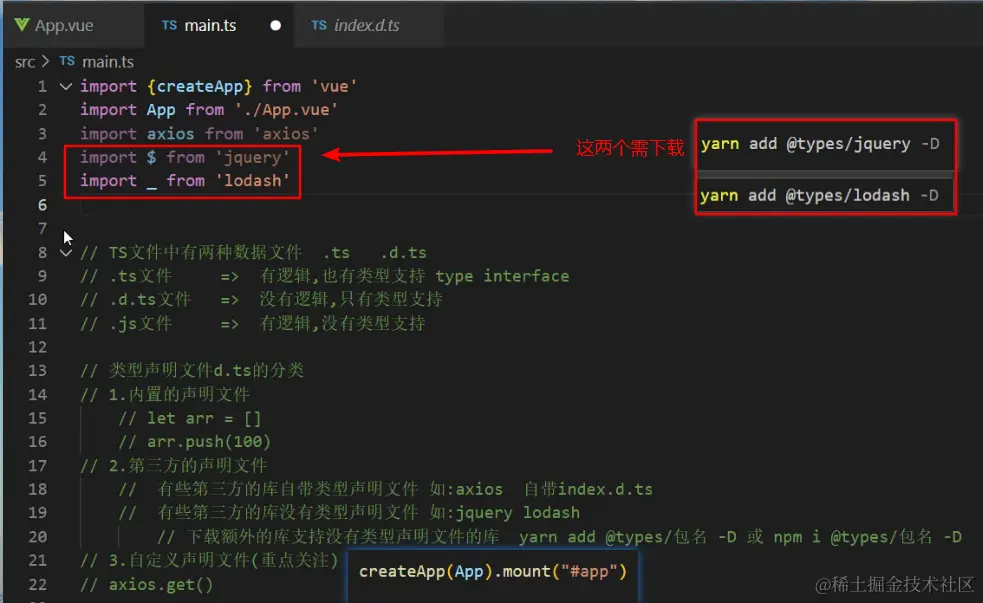
13.第三方库类型声明文件
第三方库的类型声明文件有两种存在形式:1 库自带类型声明文件 2 由 DefinitelyTyped 提供。
1.库自带类型声明文件:比如,axios 查看 node_modules/axios 目录
2. 由 DefinitelyTyped 提供
DefinitelyTyped 是一个 github 仓库,用来提供高质量 TypeScript 类型声明
[DefinitelyTyped 链接](https:
可以通过 npm/yarn 来下载该仓库提供的 TS 类型声明包,这些包的名称格式为:@types
14.自定义类型声明文件
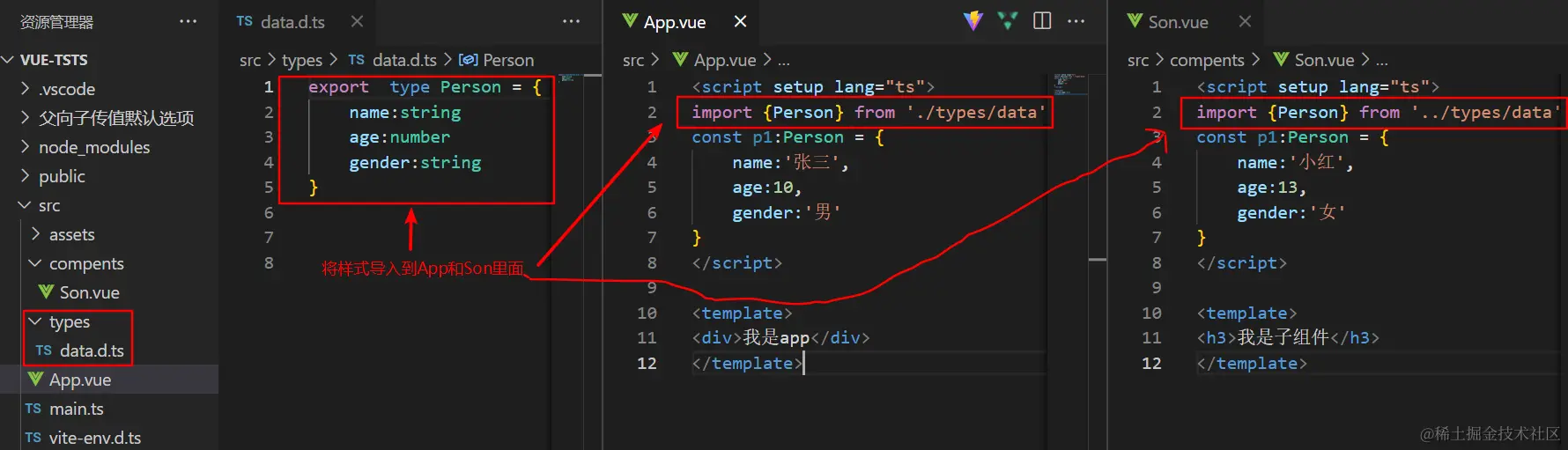
15.axios与ts的配合使用
<script setup lang="ts">
import axios from 'axios';
type ChannelRes = {
data: {channels: {id: number, name: string} []},
message: string
}
async function getChannel(){
const res = await axios.get<ChannelRes>('http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels')
console.log(res.data.data.channels)
}
getChannel()
</script>
<template>
<div>我是app</div>
</template>
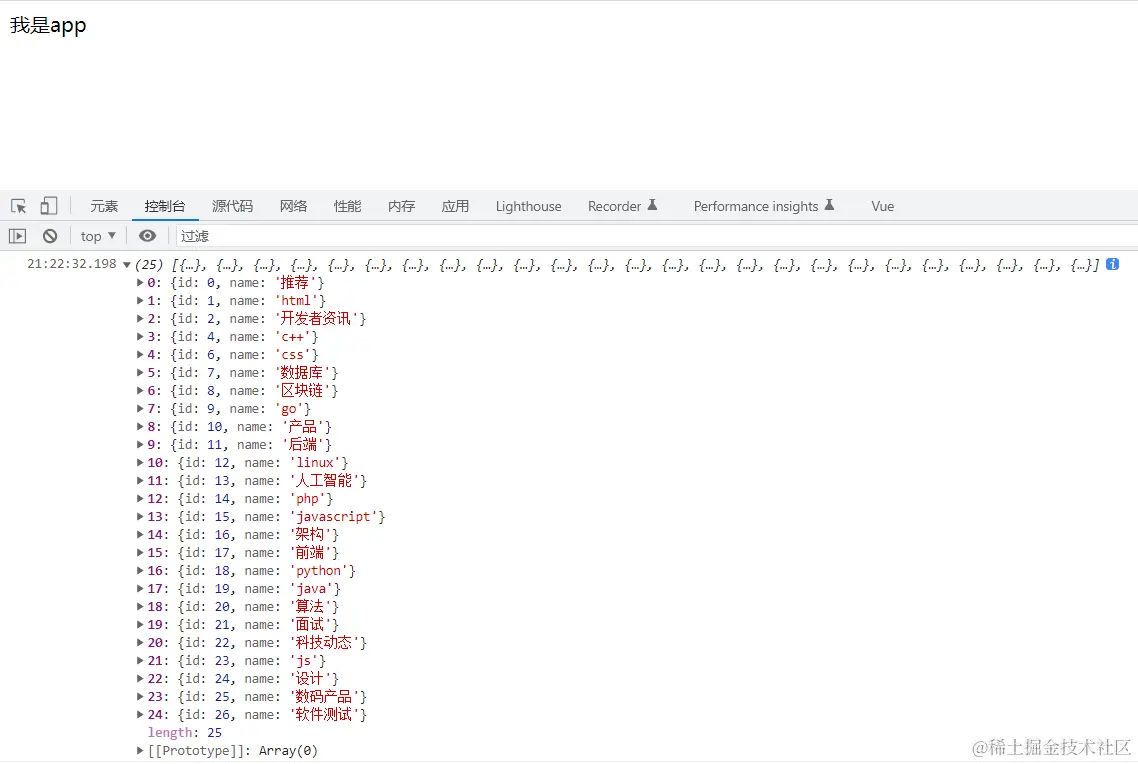
16.渲染axios返回数据
<script setup lang="ts">
import axios from 'axios';
import { ref } from 'vue';
type ChannelList = {
id: number, name: string
}[]
type ChannelRes = {
data: {channels:ChannelList},
message: string
}
const list = ref<ChannelList>([])
async function getChannel(){
const res = await axios.get<ChannelRes>('http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels')
console.log(res)
list.value = res.data.data.channels
}
getChannel()
</script>
<template>
<div>我是app</div>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in list" :key="item.id">{{item.name}}</li>
</ul>
</template>