本文已参与「新人创作礼」活动,一起开启掘金创作之路。

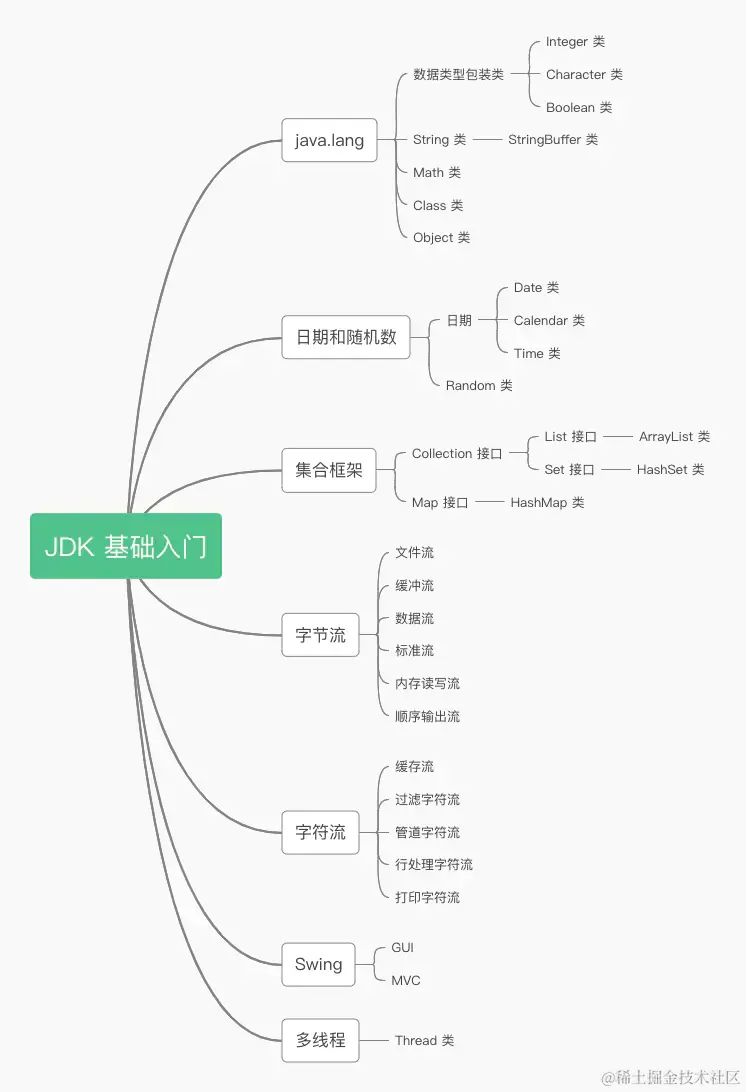
Integer类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| byteValue() | byte | 以 byte 类型返回该 Integer 的值 |
| compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) | int | 在数字上比较 Integer 对象。如果这两个值相等,则返回 0;如果调用对象的数值小于 anotherInteger 的数值,则返回负值;如果调用对象的数值大于 anotherInteger 的数值,则返回正值 |
| equals(Object IntegerObj) | boolean | 比较此对象与指定对象是否相等 |
| intValue() | int | 以 int 型返回此 Integer 对象 |
| shortValue() | short | 以 short 型返回此 Integer 对象 |
| longValue() | long | 以 long 型返回此 Integer 对象 |
| floatValue() | float | 以 float 型返回此 Integer 对象 |
| doubleValue() | double | 以 double 型返回此 Integer 对象 |
| toString() | String | 返回一个表示该 Integer 值的 String 对象 |
| valueOf(String str) | Integer | 返回保存指定的 String 值的 Integer 对象 |
| parseInt(String str) | int | 将字符串参数作为有符号的十进制整数进行解析 |
public class IntegerTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer a = new Integer("02");
Integer b = new Integer(21);
System.out.println(a.byteValue());
System.out.println(a.compareTo(b));
System.out.println(a.equals(b));
System.out.println(a.intValue());
System.out.println(b.longValue());
System.out.println(b.floatValue());
System.out.println(b.doubleValue());
System.out.println(b.toString());
System.out.println(Integer.valueOf("69"));
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("10010",2));
}
}
Character类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| isDigit(char ch) | boolean | 确定字符是否为数字 |
| isLetter(char ch) | boolean | 确定字符是否为字母 |
| isLowerCase(char ch) | boolean | 确定字符是否为小写字母 |
| isUpperCase(char ch) | boolean | 确定字符是否为大写字母 |
| isWhitespace(char ch) | boolean | 确定字符是否为空白字符 |
| isUnicodeIdentifierStart(char ch) | boolean | 确定是否允许将指定字符作为 Unicode 标识符中的首字符 |
public class CharacterTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(Character.isDigit(21));
System.out.println(Character.isLetter('H'));
System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase('a'));
System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase('I'));
System.out.println(Character.isWhitespace(' '));
System.out.println(Character.isUnicodeIdentifierStart('f'));
}
}
Boolean 类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| booleanValue() | boolean | 将 Boolean 对象的值以对应的 boolean 值返回 |
| equals(Object obj) | boolean | 判断调用该方法的对象与 obj 是否相等。当且仅当参数不是 null,而且与调用该方法的对象一样都表示同一个 boolean 值的 Boolean 对象时,才返回 true |
| parseBoolean(String s) | boolean | 将字符串参数解析为 boolean 值 |
| toString() | String | 返回表示该 boolean 值的 String 对象 |
| valueOf(String s) | Boolean | 返回一个用指定得字符串表示值的 boolean 值 |
public class BooleanTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boolean a = new Boolean(true);
Boolean b = new Boolean("true");
String d = new String("OK");
System.out.println(a.booleanValue());
System.out.println(a.equals(b));
System.out.println(Boolean.parseBoolean(d));
System.out.println(b.toString());
System.out.println(Boolean.valueOf(d));
}
}
String类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| indexOf(int ch) | int | 搜索字符 ch 第一次出现的索引 |
| indexOf(String value) | int | 搜索字符串 value 第一次出现的索引 |
| lastIndexOf(int ch) | int | 搜索字符 ch 最后一次出现的索引 |
| lastIndexOf(String value) | int | 搜索字符串 value 最后一次出现的索引 |
| substring(int index) | String | 提取从位置索引开始到结束的字符串 |
| substring(int beginindex, int endindex) | String | 提取 beginindex 和 endindex 之间的字符串部分 |
| trim() | String | 返回一个前后不含任何空格的调用字符串的副本 |
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "12577 731667 3386784809";
System.out.println(s.indexOf('6'));
System.out.println(s.indexOf("77"));
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('8'));
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("33"));
System.out.println(s.substring(20));
System.out.println(s.substring(5,12));
System.out.println(s.substring(5,12).trim());
}
}
StringBuffer类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| append(Object s) | StringBuffer | 在字符串末尾追加字符串 s |
| insert(int offsetm,Object s) | StringBuffer | 在 offsetm 的位置插入字符串 s |
| length() | int | 确定 StringBuffer 对象的长度 |
| setCharAt(int pos,char ch) | void | 使用 ch 指定的新值设置 pos 指定的位置上的字符 |
| toString() | String | 转换为字符串形式 |
| reverse() | StringBuffer | 反转字符串 |
| delete(int start, int end) | StringBuffer | 删除调用对象中从 start 位置开始直到 end 指定的索引(end-1)位置的字符序列 |
| replace(int start, int end, String s) | StringBuffer | 使用一组字符替换另一组字符。将用替换字符串从 start 指定的位置开始替换,直到 end 指定的位置结束 |
public class StringBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer("faith");
s.append(" love");
s.insert(5, " hope");
System.out.println(s.length());
s.setCharAt(10, '&');
System.out.println(s.toString());
System.out.println(s.reverse());
s.delete(4, 4);
s.replace(4, 5, " and ");
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
}
Math类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| sin(double numvalue) | double | 计算角 numvalue 的正弦值 |
| cos(double numvalue) | double | 计算角 numvalue 的余弦值 |
| tan(double numvalue) | double | 计算角 numvalue 的正切值 |
| acos(double numvalue) | double | 计算 numvalue 的反余弦 |
| asin(double numvalue) | double | 计算 numvalue 的反正弦 |
| atan(double numvalue) | double | 计算 numvalue 的反正切 |
| pow(double a, double b) | double | 计算 a 的 b 次方 |
| sqrt(double numvalue) | double | 计算给定值的正平方根 |
| abs(int numvalue) | int 计算 int | 类型值 numvalue 的绝对值,也接收 long、float 和 double 类型的参数 |
| ceil(double numvalue) | double | 返回大于等于 numvalue 的最小整数值 |
| floor(double numvalue) | double | 返回小于等于 numvalue 的最大整数值 |
| max(int a, int b) | int | 返回 int 型 a 和 b 中的较大值,也接收 long、float 和 double 类型的参数 |
| min(int a, int b) | int | 返回 a 和 b 中的较小值,也可接受 long、float 和 double 类型的参数 |
| rint(double numvalue) | double | 返回最接近 numvalue 的整数值 |
| round(T arg) | arg 为 double 时返回 long,为 float 时返回 int | 返回最接近 arg 的整数值 |
| random() | double | 返回带正号的 double 值,该值大于等于 0.0 且小于 1.0 |
public class MathTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.sin(Math.PI/6));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.PI/6));
System.out.println(Math.tan(Math.PI/6));
System.out.println(Math.acos(Math.PI/6));
System.out.println(Math.asin(Math.PI/6));
System.out.println(Math.atan(Math.PI/6));
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3));
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(9));
System.out.println(Math.abs(-1));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(9.5));
System.out.println(Math.rint(9.4));
System.out.println(Math.floor(9.4));
System.out.println(Math.max(3, 7));
System.out.println(Math.min(3, 7));
System.out.println(Math.rint(0.7));
System.out.println(Math.random());
}
}
Class类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| getClass() | Class | 返回当前对象的 Class 对象 |
| forName(String className) | Class | 返回当前对象的 Class 对象 |
| .class | Class | 返回当前对象的 Class 对象 |
| .TYPE | Class | 获取相对应的基本数据类型的 Class 实例 |
public class ClassTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
String s = new String();// class java.lang.String
System.out.println(s.getClass());
System.out.println(s.getClass().forName("java.lang.String"));// class java.lang.String
System.out.println(Integer.class);// class java.lang.Integer
System.out.println(Integer.TYPE);// int
}
}
Object类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| equals(Objectobj) | boolean | 将当前对象实例与给定的对象进行比较,检查它们是否相等 |
| finalize() throws Throwable | void | 当垃圾回收器确定不存在对象的更多引用时,由对象的垃圾回收器调用此方法。通常被子类重写 |
| getClass() | Class | 返回当前对象的 Class 对象 |
| toString() | String | 返回此对象的字符串表示 |
| wait() throws InterruptedException | void | 在其他线程调用此对象的 notify() 方法或 notifyAll() 方法前,使当前线程进入等待状态 |
public class ObjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object a = new Object();
Object b = new Object();
System.out.println(a.equals(b));
System.out.println(a.getClass());
System.out.println(a.toString());
}
}
日期
import java.util.*
public class DateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
String strDate, strTime = ""
Date objDate = new Date()
System.out.println(objDate)
long time = objDate.getTime()
System.out.println(time)
strDate = objDate.toString()
strTime = strDate.substring(11,(strDate.length() - 4))
System.out.println(strTime.substring(0,8))
}
}
代码示例
import java.util.*;
import java.text.*;
public class CalendarTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.add(Calendar.HOUR, 2);
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1);
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
}
}
代码示例
import java.util.*
import java.text.*
public class CalendarTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
DateFormat fdate = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
String str =fdate.format(new Date())
System.out.println(str)
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
calendar.setTime(new Date())
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR))
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1)
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE))
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR))
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH))
calendar.add(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, 3)
System.out.println(calendar.getTime())
str = (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SS")).format(calendar.getTime())
System.out.println(str)
calendar.setTime(new Date())
str = (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SS")).format(calendar.getTime())
System.out.println(str)
Calendar calendarNew = Calendar.getInstance()
calendarNew.add(Calendar.HOUR, -5)
System.out.println(calendarNew.compareTo(calendar))
calendarNew.add(Calendar.HOUR, +7)
System.out.println(calendarNew.compareTo(calendar))
calendarNew.add(Calendar.HOUR, -2)
str = (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SS")).format(calendarNew.getTime())
System.out.println(str)
str = (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SS")).format(calendar.getTime())
System.out.println(str)
System.out.println(calendarNew.compareTo(calendar))
}
}
代码示例
Random 类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|
| nextInt() | int | 产生一个整型随机数 |
| nextLong() | long | 产生一个 long 型随机数 |
| nextFloat() | float | 产生一个 Float 型随机数 |
| nextDouble() | double | 产生一个 Double 型随机数 |
| nextGaussian () | double | 产生一个 double 型的 Gaussian 随机数 |
import java.util.*;
public class RandomTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r = new Random();
System.out.println(r.nextInt());
System.out.println(r.nextLong());
System.out.println(r.nextFloat());
System.out.println(r.nextDouble());
System.out.println(r.nextGaussian());
}
}
Thread 类
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|
| run () | 为线程指明了它要完成的任务 |
| start () | 启动线程 |
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Thread2());
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class Thread1 extends Thread{
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){
System.out.println("Hello! This is " + i);
}
}
}
class Thread2 implements Runnable {
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
System.out.println("Thanks. There is " + i);
}
}
}