在散列中,有散列函数将键映射到一些值。 但这些散列函数可能导致碰撞,即两个或多个键被映射到相同的值。 链式散列 可以避免这种碰撞。
这个想法是使hashtable的每个单元格都指向具有相同散列函数值的记录的LinkedList。
Java中的散列
Java散列 是一种用于将值映射到键的技术,这使得只需输入键就能轻松检索到值。 在Java中使用HASHING的主要优点是,它可以降低任何程序的时间复杂度,即使是比较重要的侧给,也可以使基本操作的执行时间保持不变。
但散列函数的主要问题是它会导致碰撞,因为两个或多个键可以指向相同的值。 如果你想避免这种连锁,主要使用散列。 所以,要在散列表中插入一个值,主要要求是用公式计算的散列索引。
Hashindex: key%number_of_items
让我们用Java来实现散列,有以下几种方式。
使用哈希表实现散列
请看下面的代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Hashing1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Hashtable<Integer, String> hm = new Hashtable<Integer, String>();
hm.put(1, "App");
hm.put(12, "Dividend");
hm.put(15, "Best place to learn");
hm.put(3, "Java");
System.out.println(hm);
}
}
请看输出:
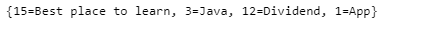
上面使用的方法是同步的散列方式。
使用hashmap实现散列
请看下面的代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Hashing2 {
static void createHashMap(int arr[]) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> hmap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
Integer c = hmap.get(arr[i]);
if (hmap.get(arr[i]) == null) {
hmap.put(arr[i], 1);
} else {
hmap.put(arr[i], ++c);
}
}
System.out.println(hmap);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 11, 35, 6, 11, 4, 6, 12 };
createHashMap(arr);
}
}
请看输出:

上面的方法是用非同步的方式来实现散列。
在这里,我们通过将元素作为键和值作为频率,从数组中创建了一个哈希图。
使用LinkedHashMap实现散列
请看下面的程序:
import java.util.*;
public class BasicLinkedHashMap {
public static void main(String a[]) {
LinkedHashMap<String, String> lhm = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
lhm.put("one", "AppDividend.Com");
lhm.put("two", "https://appdividend.com/amp/category/java-tutorials/");
System.out.println("Value for key 'one' is: " + lhm.get("one"));
System.out.println("Size of the map: " + lhm.size());
System.out.println("Is map empty? " + lhm.isEmpty());
System.out.println("Contains key 'two'? " + lhm.containsKey("two"));
System.out.println("delete element 'one': " + lhm.remove("one"));
System.out.println(lhm);
}
}
请看输出结果:
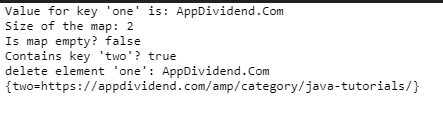
上述方法与HashMap类似,但唯一的优点是它能保持元素的顺序。
使用ConcurrentHashMap实现散列
请看下面的程序:
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ConcurrentHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String> m = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String>();
m.put(100, "C++");
m.put(101, "Is");
m.put(102, "Always");
m.put(103, "Best");
System.out.println("ConcurentHashMap: " + m);
m.putIfAbsent(101, "C++");
System.out.println("\nConcurentHashMap: " + m);
m.remove(102, "Always");
System.out.println("\nConcurentHashMap: " + m);
m.replace(100, "C++", "Java");
System.out.println("\nConcurentHashMap: " + m);
}
}
请看下面的输出:

上面的方法与哈希图类似。不同的是,它是同步的,而且速度更快,因为使用了多个锁。
使用HashSet实现散列
请看下面的程序:
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> h = new HashSet<String>();
h.add("India");
h.add("Australia");
h.add("South Africa");
h.add("India");
System.out.println(h);
System.out.println("Does HashSet contains India or not:" + h.contains("India"));
h.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("List after removing Australia:" + h);
System.out.println("Traversing the list:");
Iterator<String> i = h.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
请看输出:

上面使用的方法与HashMap类似。唯一的区别是,HashSet只维护键,而不是对。
使用LinkedHashSet实现散列
请看下面的程序:
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<String> linkedset = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
linkedset.add("A");
linkedset.add("B");
linkedset.add("C");
linkedset.add("D");
// This will not add new element as A already exists
linkedset.add("A");
linkedset.add("E");
System.out.println("Size of LinkedHashSet = " + linkedset.size());
System.out.println("Original LinkedHashSet:" + linkedset);
linkedset.remove("D");
System.out.println("Trying to Remove Z which is not " + "present: " + linkedset.remove("Z"));
System.out.println("Checking if A is present=" + linkedset.contains("A"));
System.out.println("Updated LinkedHashSet: " + linkedset);
}
}
请看输出结果:

上面的方法与LinkedHashMap相似。不同的是,它只维护键,而不是对。
本教程就到此为止。