在bash编程中,有三种类型的循环被使用。While循环是其中之一。和其他循环一样,while循环也是用来做重复性的工作。本文通过使用不同的例子来说明如何在bash脚本中使用while循环。
while 循环的语法:
while [ condition ]
do
commands
done
while循环的开始和结束块是由bash脚本中的do和done 关键字定义的。终止条件是在循环的开始部分定义的。打开文本编辑器写一个bash脚本,测试下面的while循环例子。
例1: 迭代循环的固定次数
创建一个名为while1.sh的bash文件,内容如下。这里,循环将迭代5次,并在每次迭代中打印计数器的值。
#!/bin/bash
# Initialize the counter
n=1
# Iterate the loop for 5 times
while [ $n -le 5 ]
do
# Print the value of n in each iteration
echo "Running $n time"
# Increment the value of n by 1
(( n++ ))
done
输出:
执行上述脚本后,将出现以下输出。

例2: 使用break语句进行有条件退出
break语句是用来根据特定的条件提前退出循环的。创建一个名为while2.sh的bash文件,代码如下。这里,循环被定义为迭代10次,但当计数器的值为6时,迭代将被停止。
#!/bin/bash
# Initialize the counter
n=1
# Iterate the loop for 10 times
while [ $n -le 10 ]
do
# Check the value of n
if [ $n == 6 ]
then
echo "terminated"
break
fi
# Print the current value of n
echo "Position: $n"
# Increment the value of n by 1
(( n++ ))
done
输出
执行上述脚本后,将出现以下输出。

例3: 使用continue语句来省略特定的步骤
创建一个名为while3.sh的bash文件,代码如下。在这个例子中,循环将迭代5次,但它不会打印所有5个位置。当循环迭代到第3次时, continue语句将被执行, 循环将进入下一次迭代, 而不打印第3个位置的文本。
#!/bin/bash
# Initialize the counter
n=0
# Iterate the loop for 5 times
while [ $n -le 5 ]
do
# Increment the value of n by 1
(( n++ ))
# Check the value of n
if [ $n == 3 ]
then
continue
fi
# Print the current value of n
echo "Position: $n"
done
输出
执行上述脚本后会出现以下输出。

例4: 读取带有选项的命令行参数
创建一个名为while4.sh的bash文件,代码如下。这里,循环被用来读取带有选项的命令行参数。如果三个参数值通过了有效的选项,该脚本将在执行后打印格式化的参数值。
#!/bin/bash
# Read the command-line arguments values with option using loop
while getopts n:a:e: OPT
do
case "${OPT}"
in
n) name=${OPTARG};;
a) address=${OPTARG};;
e) email=${OPTARG};;
*) echo "Invalid option"
exit 1;;
esac
done
# Print the argument values
printf "Name:$name\nAddress:$address\nEmail:$email\n"
输出
执行上述脚本后会出现以下输出。

例5:逐行读取文件
用下面的代码创建一个名为while5.sh的bash文件。这里,文件名将在执行时的第一个命令行参数中给出。如果该文件存在,那么该文件的内容将通过循环逐行打印;否则,将打印出一条错误信息。
#!/bin/bash
# Check the command-line argument value is given or not
if [ $# -gt 0 ]; then
# Assign the filename from comand-line argument value
filename=$1
# Read file line by line
while read line; do
# Print each line
echo $line
done < $filename
else
# Print message if no argument is provided
echo "Argument value is missing."
fi
输出
在执行完上面的脚本后会出现下面的输出。

例6: 将内容写进一个文件
用下面的代码创建一个名为while6.sh的bash文件。这里,文件名将从用户那里获取,文本内容将被写入其中。用户在输入文件的内容后,必须键入Ctrl+D。
#! /bin/bash
echo -n "Enter the filename to create: "
# Take the filename that will be created
read filename
# Read the content of the file from the terminal
while read line
do
echo $line >> $filename
done
输出
在执行上述脚本后,将出现以下输出。

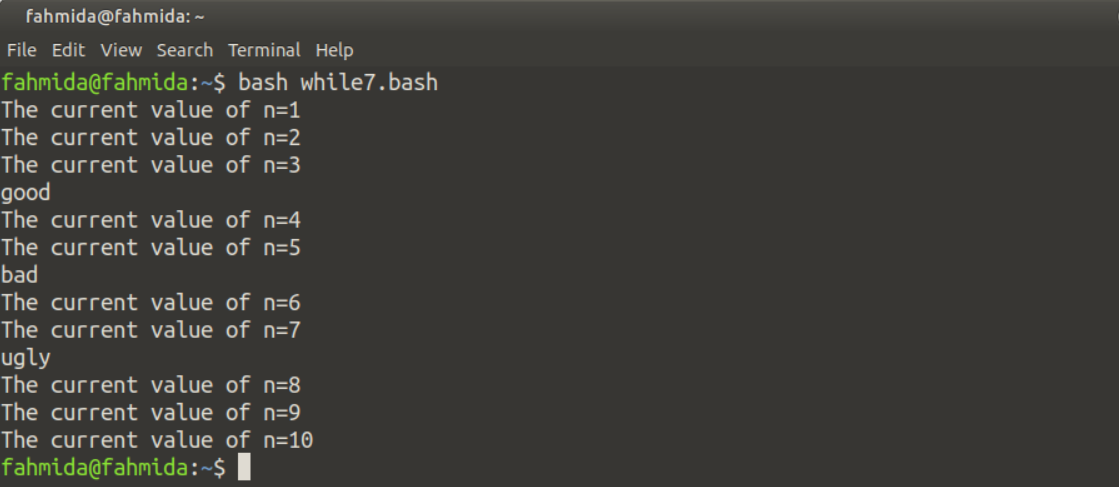
例7:创建一个无限循环
有时,出于各种编程目的,需要声明一个无限循环。创建一个名为while7.sh的bash文件,测试无限循环的代码。在这个例子中,没有为该循环设置终止条件。这种类型的循环被称为无限循环。这里,一个exit语句被用来从无限循环中退出。所以,这个循环将被迭代10次,当迭代值等于10时,退出语句将被执行以退出无限循环。
#!/bin/bash
# Initialize the counter
n=1
# Declare an infinite loop
while :
do
printf "The current value of n=$n\n"
if [ $n == 3 ]
then
echo "good"
elif [ $n == 5 ]
then
echo "bad"
elif [ $n == 7 ]
then
echo "ugly"
elif [ $n == 10 ]
then
exit 0
fi
# Increment the value of n by 1
((n++))
done
# Take the filename that will be created
read filename
# Read the content of the file from the terminal
while read line
do
echo $line >> $filename
done
输出
在执行上述脚本后,将出现以下输出。
例8:使用C语言的while循环
创建一个名为while8.sh的bash文件,代码如下。这里,while循环已经以C风格的格式声明,它将通过将计数器的值增加10来迭代5次。
#!/bin/bash
# Initialize the counter
n=5
# Define the while in C-style
while((n <= 50))
do
echo $n
# Increment counter by 10
((n=n+10))
done
输出
在执行上述脚本后,将出现以下输出。

总结
在本教程中,通过使用多个例子解释了while循环的不同用途。我希望bash用户在练习了这些例子之后,能够在他们的脚本中正确使用这个循环。