ReetrantLock
- ReentrantLock支持可重入
- 基于AQS实现,支持公平锁与非公平锁
- 支持锁中断
其中提供了两种构造方法
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
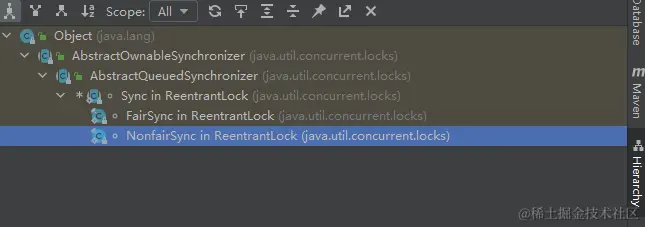
- Sync类继承自
AQS,并有两个实现类FairSync、NonfairSync,分别是ReentrantLock的公平和非公平实现
公平锁的实现
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
...
}
- 其中 acquire 方法中调用了 tryAcquire 方法
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
非公平锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
...
}
- 其中 acquire 是AQS的方法,其中调用了 tryAcquire 方法
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
------------------------------------------------
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
公平锁和非公平锁的差异实现
- 公平锁和非公平锁的本质就是在获取锁的时候,是否在乎有其它线程在排队就直接去获取锁。
- 在公平锁的实现中,加入了队列,由于队列先进先出的特性,去实现了公平锁
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
- 其中非公平锁的lock直接去修改state的值,尝试获取锁,没有管是不是有别的线程在排队
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
- 其中 tryAcquire 方法里少了判断阻塞的逻辑 方法名 hasQueuedPredecessors
如有错误请指正,谢谢