C++中typeid的介绍
在C++中,typeid是一个操作符,用来检索一个对象的运行时或动态类型信息。对象可以是一个变量类型、对象类型或表达式类型。要在程序中使用typeid运算符,需要包括库头。它返回类型为const type_info的l值来表示值的类型。typeid的表达式是一个lvalue表达式(lvalue有程序可以访问的地址。例如,变量名、函数、类成员、联盟等)。它基本上适用于那些不能用所提供的静态信息确定真实类型的对象。
语法
下面给出的是在C++程序中使用typeid的基本语法:
typeid(expression)
或
typeid(type)
其中:
表达式。在这里,整个表达式被作为一个参数传递,以检索其类型的运行时信息。首先对表达式进行评估,然后根据最终结果提供其类型。
类型。在这种情况下,变量或对象被作为一个参数传递,以检索它的动态类型。与表达式参数不同,它不需要进行评估。因此,直接获得信息的类型作为最终结果。
返回值。 它返回一个对象的运行时或动态类型信息,它是一个 const type_info 类型的 lvalue。如果该类型是一个引用类型,它返回引用类型的type_info对象。
typeid在C++中如何工作?
下面给出了一些描述typeid在C++程序中工作的重要观点:
- 如果在typeid运算符中作为参数传递的表达式是基类的,但是对象是基类派生的类型,那么结果是派生类的type_info引用。
- 如果在typeid操作符中作为参数传递的表达式正在解除对一个指针的引用,并且指针的值是空的或者指向一个无效的对象,那么将抛出bad_typeid错误。
- 如果在type expression中传递的表达式既不是一个解除引用的指针,也不是基类的一个对象,它将返回type_info引用作为表达式的静态类型。在这种情况下,引用在评估时被忽略。
- 在我们只需要类信息的情况下,typeid被用来代替dynamic_cast。
- 当我们需要找到与运行时信息的计算相关的表达式类型时,操作符typeid很有用,例如
多态类类型的对象的引用或指针的解除引用。
- 操作数typeid不能应用于不完整的类型。因此,如果对象正在构建或销毁,那么它返回正在构建或销毁的类的std::type_info。
C++中typeid的例子
下面给出了一些例子,说明typeid在程序中的应用。
例子#1
获取简单对象(如int、float、char)的typeid并比较其类型
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i, j;
float f;
char c, *d;
double e;
//Getting the type using the typeid operator and passing the variables
const type_info& ti1 = typeid(i);
const type_info& ti2 = typeid(j);
const type_info& ti3 = typeid(f);
const type_info& ti4 = typeid(c);
const type_info& ti5 = typeid(d);
const type_info& ti6 = typeid(e);
const type_info& ti7 = typeid(*d);
// Printing the types of the variables of different data type on the console
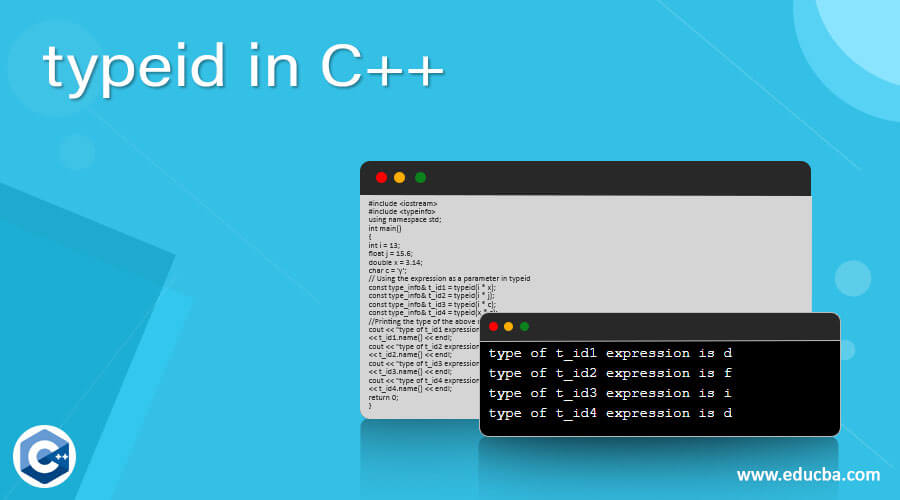
cout << ti1.name() << endl;
cout << ti2.name() << endl;
cout << ti3.name() << endl;
cout << ti4.name() << endl;
cout << ti5.name() << endl;
cout << ti6.name() << endl;
cout << ti7.name() << endl;
//making comparisons in the types retrieved above
if (ti1 == ti2)
{
cout<< "Both i and j are of same type " << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Both i and j are of different types" << endl;
}
if(ti5== ti7)
{
cout << "Both pointer and its address are of same type" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Both pointer and its address are of different types" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
例#2
使用typeid操作符获得多态和非多态基类的对象类型
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
//using polymorphic base class B1
class B1 {
public:
virtual void fun() {}
};
//using non-polymorphic base class B2
class B2 {};
class D1 : public B1 {};
class D2 : public B2 {};
using namespace std;
//main function
int main() {
D1* d1 = new D1;
B1* b1 = d1;
D2* d2 = new D2;
B2* b2 = d2;
//Printing the type of above class objects on the console
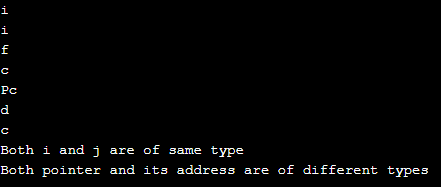
cout << typeid( d1 ).name() << endl;
cout << typeid( b1 ).name() << endl;
cout << typeid( *d1 ).name() << endl;
cout << typeid( *b1 ).name() << endl;
cout << typeid( d2 ).name() << endl;
cout << typeid( b2 ).name() << endl;
cout << typeid( *d2 ).name() << endl;
cout << typeid( *b2 ).name() << endl;
}
输出
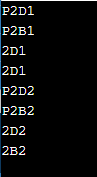
例#3
通过对typeid运算符中作为参数使用的表达式的评估来获取类型。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 13;
float j = 15.6;
double x = 3.14;
char c = 'y';
// Using the expression as a parameter in typeid
const type_info& t_id1 = typeid(i * x);
const type_info& t_id2 = typeid(i * j);
const type_info& t_id3 = typeid(i * c);
const type_info& t_id4 = typeid(x * c);
//Printing the type of the above calculated expressions on the console
cout << "type of t_id1 expression is "
<< t_id1.name() << endl;
cout << "type of t_id2 expression is "
<< t_id2.name() << endl;
cout << "type of t_id3 expression is "
<< t_id3.name() << endl;
cout << "type of t_id4 expression is "
<< t_id4.name() << endl;
return 0;
}
输出

在这种方式下,typeid是通过传递表达式的类型作为typeid运算符的参数来计算的。在简单数据类型的情况下,如int、float、double等,typeid的结果不需要任何计算,而在表达式的情况下,表达式首先被评估,然后它们的类型才会产生。
总结
上面的描述清楚地解释了什么是C++中的typeid,以及它是如何用来查找对象的动态类型的。typeid的返回类型取决于要计算的对象的类型。它抛出了许多错误,导致了意外的输出。因此,在程序中使用这个操作符之前,需要对它有一个很好的理解。