Java中的分页简介
Java分页概念用于在第一页、第二页、第三页、第四页等页面之间移动。按钮或链接。分页的主要目的是通过点击链接或按钮在内容之间立即移动。Java分页有多个链接或按钮提供给第一页、第二页、第三页、第四页等。在Java中创建第一页、第二页、第三页、第四页等按钮;我们有Servlets来实现这一点。
什么是Bootstrap Pager?
Java分页的概念是通过使用第一页、第二页、第三页、第四页等,按钮或更多的链接或按钮,根据客户的要求,顺利地访问内容。
为什么我们要使用JavaScript分页?
以下是我们使用JavaScript分页的原因。
实时场景
让我们以亚马逊网站或Flipkart网站为例,显示他们数据库中的可用产品。假设他们有100万种产品。如果他们试图在同一时间显示所有的产品,客户必须等待更多的时间,比如一天,才能看到所有的产品列表。
我们应该如何处理这种情况?
- 我们可以通过使用链接按钮列表的方式,一次向他们展示50到100个项目,而不是一次显示所有的项目。
- 如果顾客对前50到100个产品不满意,那么他就会转到下一个50到100个产品,如此循环。这个概念被称为分页。
创建分页项目的步骤
- 创建任何带有setter和getters的类,用于向列表中添加值。
- 为分页逻辑创建Servlet类。
- 创建一个类将列表中的值添加到任何数据库中,以便在输出视图页面上看到这些值。
注意: 这里使用的是MySQL数据库;请确保你必须在你的电脑上安装MySQL服务器。使用mysql-connector-java.jar文件来处理MySQL数据库代码。
4.4.创建一个HTML视图页面用于查看分页。
语法
Servlet语法
//create a setter and getter class
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
private float salary;
//setters and getters
}
//for pagination logic in servlet class
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriterOut=response.getWriter();
String stringPageNumber=request.getParameter("page");
int paginationPageID=Integer.parseInt(stringPageNumber);
int toalCount=pageNumbers;
if(paginationPageID==1){}
else{
paginationPageID=paginationPageID-1;
paginationPageID=paginationPageID*toalCount+1;
}
}
//database connection for getting customer values
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection con=null;
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test","root","root");
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
return con;
}
//view output html page
<body>
<div class="a">
<a href="PaginationServlet?page=1">View Customer Details</a>
</div>
</body>
在Java中分页的例子
上面提到的每个步骤我们都作为一个单独的例子,以便更好地理解。一旦你完成了所有的例子,你的项目结构必须像Eclipse中的下面这样;否则,可能无法工作。
创建一个动态网页项目,并添加以下所有的例子,就像下面这样。
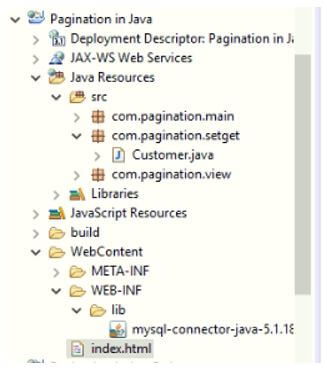
注意: 使用Apache Tomcat服务器7.0。
例子 #1
创建客户类。
Java代码:Customer.java
package com.pagination.setget;
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
private float salary;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public float getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(float salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
例子 #2
为分页逻辑创建servlet类。
Java Servlet代码: Pagination.java
package com.pagination.view;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.pagination.main.Pagination;
import com.pagination.setget.*;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
@WebServlet("/PaginationServlet")
public class ViewPagination extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
httpServletResponse.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriterOut=httpServletResponse.getWriter();
String stringPageNumber=httpServletRequest.getParameter("page");
int paginationPageID=Integer.parseInt(stringPageNumber);
int toalCount=5;
if(paginationPageID==1){}
else{
paginationPageID=paginationPageID-1;
paginationPageID=paginationPageID*toalCount+1;
}
List<Customer> customerList=Pagination.getRecords(paginationPageID,toalCount);
printWriterOut.print("<h2 style='color:green;text-align:center'>Introduction to Servlet Pagination</h2>");
printWriterOut.print("<h3 style='color:blue;text-align:center'>Customer Details in Table Format</h3>");
printWriterOut.print("<h1 style='color:brown'>We are in Page number=>"+stringPageNumber+"</h1>");
printWriterOut.print("<table style='color:navy' border='2' cellpadding='4' width='80%'>");
printWriterOut.print("<tr><th>Customer ID</th><th>Customer Name</th><th>Customer Salary</th>");
for(Customer customer:customerList){
printWriterOut.print("<tr><td>"+customer.getId()+"</td><td>"+customer.getName()+"</td><td>"+customer.getSalary()+"</td></tr>");
}
printWriterOut.print("</table>");
printWriterOut.print("<a href='PaginationServlet?page=1'>First Page||</a> ");
printWriterOut.print("<a href='PaginationServlet?page=2'>Second Page||</a> ");
printWriterOut.print("<a href='PaginationServlet?page=3'>Third Page||</a> ");
printWriterOut.print("<a href='PaginationServlet?page=4'>Fourth Page||</a> ");
printWriterOut.print("<a href='PaginationServlet?page=5'>Fifth Page</a> ");
printWriterOut.close();
}
}
例子#3
创建MySQL数据库代码,用于保存列表值。
Java代码:MySQLPagination.java
package com.pagination.main;
import com.pagination.setget.*;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Pagination {
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection=null;
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
connection=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test","root","root");
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
return connection;
}
public static List<Customer> getRecords(int start,int total){
List<Customer> list=new ArrayList<Customer>();
try{
Connection connection=getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement("select * from customer limit "+(start-1)+","+total);
ResultSet rs=preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Customer customer=new Customer();
customer.setId(rs.getInt(1));
customer.setName(rs.getString(2));
customer.setSalary(rs.getFloat(3));
list.add(customer);
}
connection.close();
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
return list;
}
}
例子 #4
HTML代码:ViewPagination.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Pagination</title>
<style type="text/css">
.a {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<a href="PaginationServlet?page=1">View Customer Details</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
输出:
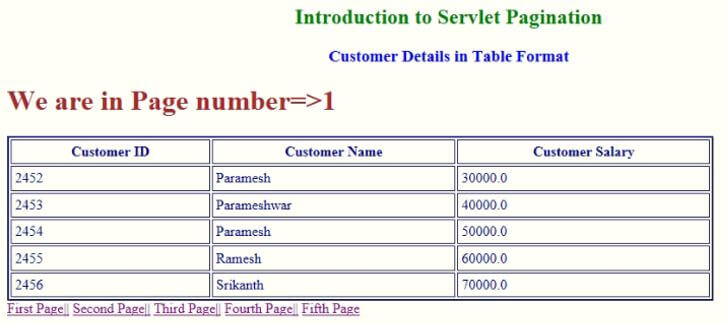
解释一下:
- 在第一个例子中,我们已经创建了一个Customer setter和getter类。
- 在第二个例子中,我们创建了Pagination servlet类来添加分页逻辑。
- 在第三个例子中,我们创建了一个MySQL数据库,用于添加列表值以显示在分页视图中。
- 在第四个例子中,我们通过使用一个HTML页面创建了一个视图页面。
结论 - Java中的分页
Java中的分页是通过使用按钮或链接立即在各页之间移动。Java中的分页可以通过Servlet和HTML y使用MySQL jar文件完成。