问题陈述
给出一个单词列表 "WORDLIST",找出最长的完美单词。一个完美的单词是指在'WORDLIST'中所有可能的前缀都存在的单词。
如果在'WORDLIST'中存在一个以上相同长度的完美词,则返回具有最小词典顺序的词。如果对于给定的输入不可能有这样的词,可以返回一个空字符串。
输入
["w", "wo", "wor", "wow", "worm", "work"]
["w", "wo", "wor", "worl","world"]
["a","banana","app","appl","ap","apply","apple"]
输出
"工作"
"世界"
"苹果"
解释
在第一个输入中,"worm "和 "work "都是最长的完美词,因为这两个词的所有前缀都在列表中。但是 "work "在词汇学上要比 "worm "小。所以,正确的输出是 "work"。
在第二个输入中,每个词都是一个完美的词,但 "world "是最长的。所以,正确的输出是 "world"。
在第三个输入中,"a"、"ap"、"app"、"appl"、"apply "和 "apple "是完美字符串。所以,正确的输出是 "apple"。
解决方法
这个问题可以用HashSet和Trie数据结构来有效解决。我们将看到这两种方法。我们将用C++和Java语言编写同样的代码。
方法1:蛮力方法
解决这个问题的蛮力方法是遍历单词列表,对每个单词遍历其字符并获得前缀,然后通过再次遍历单词列表检查这些前缀是否存在于单词列表中。
算法
- 创建一个变量 "LONGEST "来记录最长的单词,并将其初始化为一个空字符串。
- 遍历 "WORDLIST"。
- 创建一个变量 "PREFIX",保存 "CURRENT_WORD "的前缀。
- 对于 "CURRENT_WORD "的字符进行遍历。
- 将 "CURRENT_CHARACTER "加入到 "PREFIX "变量中。
- 检查 "PREFIX "是否存在于 "WORDLIST "中
- 要检查 "WORDLIST "中是否有 "PREFIX"。
- 创建一个标志 "PRESENT",并将其初始化为一个假值
- 遍历 "WORDLIST"。
- 如果 "PREFIX "存在,将 "PRESENT "的值设为真,并中断循环
- 返回 "PRESENT "的值
- 如果 "CURRENT_WORD "的所有前缀都存在于 "WORDLIST "中。
- 如果 "CRRENT_WORD "的大小大于 "LONGEST "的大小,将 "LONGEST "设置为 "CRRENT_WORD"
- 如果 "CURRENT_WORD "的大小等于 "LONGEST "的大小,则将 "LONGEST "的值设置为 "CURRENT_WORD "和 "LONGEST "之间按字母顺序排列的小值。
- 返回 "LONGEST "的值
下面是上述算法的C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool isPresent(vector<string>& words, string str) {
bool present = false;
for(string word: words) {
if(word == str) {
present = true;
break;
}
}
return present;
}
string longestPerfctWord(vector<string> &words) {
string longest = "";
for(auto word: words) {
string prefix = "";
bool allPrefixesPresent = true;
for(auto ch: word) {
prefix.push_back(ch);
if(!isPresent(words, prefix)) {
allPrefixesPresent = false;
break;
}
}
if(allPrefixesPresent) {
if(word.size() > longest.size())
longest = word;
if(word.size() == longest.size())
longest = (word < longest)? word: longest;
}
}
return longest;
}
int main()
{
vector<string> v1 = {"w", "wo", "wor", "wow", "worm", "work"};
vector<string> v2 = {"w","wo","wor","worl","world"};
vector<string> v3 = {"a","banana","app","appl","ap","apply","apple"};
cout << longestPerfctWord(v1) << endl; //output: work
cout << longestPerfctWord(v2) << endl; //output: world
cout << longestPerfctWord(v3) << endl; //output: apple
}
下面是上述算法的Java实现
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public static boolean isPresent(String[] words, String str) {
for(String word: words) {
if(word.equals(str))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static String longestPerfectWord(String[] words) {
String longest = "";
for(String word: words) {
String prefix = "";
boolean allPrefixesPresent = true;
for(int i = 0;i < word.length();++i) {
prefix += Character.toString(word.charAt(i));
if(!isPresent(words, prefix)) {
allPrefixesPresent = false;
break;
}
}
if(allPrefixesPresent) {
if(word.length() > longest.length())
longest = word;
if(word.length() == longest.length())
longest = (word.compareTo(longest) < 0) ? word: longest;
}
}
return longest;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] v1 = {"w", "wo", "wor", "wow", "worm", "work"};
String[] v2 = {"w","wo","wor","worl","world"};
String[] v3 = {"a","banana","app","appl","ap","apply","apple"};
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v1)); //output: work
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v2)); //output: world
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v3)); //output: apple
}
}
时间复杂度。我们可以看到所有的前缀都是为一个词创建的。因此,如果该词的长度为w,那么将创建w个前缀。由于单词列表中有n个单词,Σ**(w)**前缀将被创建。现在,所有的前缀都被搜索到词表中,这需要O(n)时间。这整个过程发生在世界列表中的所有元素上。
因此,时间复杂度=O(n * Σ(w) * n) = O(n2 * Σ(w)),可以近似为O(n3)。
空间复杂度:由于没有额外的空间被用于操作,所以空间复杂度为O(1)。
方法2:使用哈希集
使用HashSet的想法是,它提供了O(1)的查找时间。因此,检查特定的前缀是否存在于词表中的操作不会花费O(n)时间,可以在O(1)时间内完成。
算法
- 创建一个 "HASH_SET "来存储 "WORDLIST",以加快查询速度。
- 创建一个 "LONGEST "来存储最长的完美字符串,并将其初始化为一个空字符串
- 对于 "WORDLIST "中从头到尾的 "CURRENT_STRING",做。
- 将 "CURRENT_STRING "插入 "HASH_SET "中。
- 对于'CURRENT_STRING',从'WORDLIST'的开头到结尾,做。
- 检查 "CURRENT_STRING "是否为完美字符串
- 检查 "CURRENT_STRING "是否完美
- 检查 "CURRENT_STRING "的所有前缀是否存在于 "HAHS_SET "中。
- 如果 "CURRENT_STRING "是完美的,并且该字符串的长度大于 "LONGEST "的长度,则将 "LONGEST "设置为 "CURRENT_STRING"。
- 如果 "CURRENT_STRING "是完美的,并且字符串的长度等于 "LONGEST "的长度,则将 "LONGEST "设置为按字母顺序排列的小字符串。
- 返回 "LONGEST"。
C++实现
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
unordered_set<string> s;
bool isPerfect(string word) {
string prefix = "";
for(char ch: word) {
prefix.push_back(ch);
if(s.find(prefix) == s.end())
return false;
}
return true;
}
string longestPerfectString(vector<string>& words) {
for(auto word: words) {
s.insert(word);
}
string longest = "";
for(auto word: words) {
if(word.size() >= longest.size() && isPerfect(word))
if(word.size() > longest.size() || (word < longest))
longest = word;
}
return longest;
}
int main() {
vector<string> v1 = {"w", "wo", "wor", "wow", "worm", "work"};
vector<string> v2 = {"w","wo","wor","worl","world"};
vector<string> v3 = {"a","banana","app","appl","ap","apply","apple"};
cout << longestPerfectString(v1) << endl; //output: work
cout << longestPerfectString(v2) << endl; //output: world
cout << longestPerfectString(v3) << endl; //output: apple
}
Java实现
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
public static boolean isPerfect(String word) {
int n = word.length();
String s = "";
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i) {
s += Character.toString(word.charAt(i));
if(!set.contains(s))
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static String longestPerfectWord(String[] words) {
for(String word: words) {
set.add(word);
}
String longest = "";
for(String word: words) {
if(word.length() >= longest.length() && isPerfect(word)) {
if(word.length() > longest.length() || (word.compareTo(longest) < 0))
longest = word;
}
}
return longest;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] v1 = {"w", "wo", "wor", "wow", "worm", "work"};
String[] v2 = {"w","wo","wor","worl","world"};
String[] v3 = {"a","banana","app","appl","ap","apply","apple"};
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v1)); //output: work
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v2)); //output: world
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v3)); //output: apple
}
}
时间复杂度。检查每个前缀需要一个线性时间操作。对于一个长度为'W'的单词,前缀的最大长度为'W'。检查集合中最大长度前缀的时间复杂度是O(W)。对于'WORDLIST'中的单词'W',所有可能的前缀都要检查。所以,检查一个词的所有前缀的时间复杂度是O(W^2)。要检查所有单词的前缀,时间复杂度为O(∑Wi2),其中Wi代表 "WORDLIST "中的每个单词。
空间复杂度。为了创建一个词的所有前缀,需要额外的空间。因此,空间复杂度为O(∑Wi2),其中Wi代表 "WORDLIST "中的每个词。
方法3:使用Trie
trie数据结构是一种树状的数据结构,在大多数情况下,它用于在字典中插入和搜索单词。下图给出了一个关于 trie 数据结构的概念。
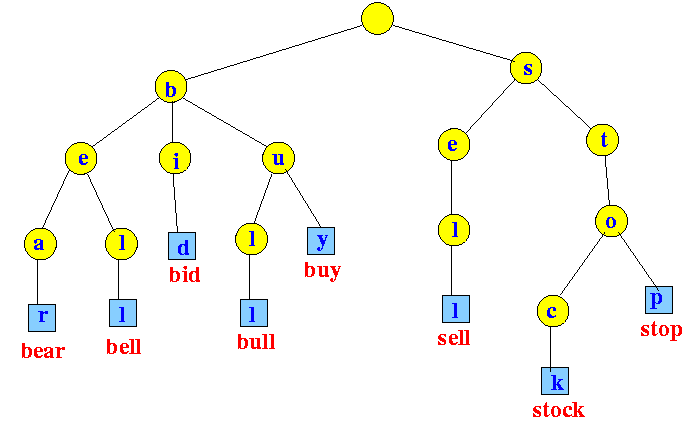
从图中可以看出,Trie数据结构由节点组成,与二叉树的节点不同,它可以引用许多其他节点。
如果我们观察一下,就会发现,如果一个Trie数据结构包含一个词,那么它的所有前缀也都包含在内。
例如,在上图中,最右边插入的词是 "stop",它的所有前缀--"s"、"st"、"sto",也都在 trie 中。
这些前缀可以在线性时间内被搜索到。因此,它非常适用于我们的问题。
算法
- 创建一个 "TRIE "来存储 "WORDLIST "中的单词
- 创建一个变量 "LONGEST",跟踪最长的完美字符串
- 对于 "WORD "从头到尾在 "WORDLIST "中。
- 如果 "WORD "的长度大于 "LONGEST "的长度,并且 "WORD "是一个完美的字符串(为了检查该字符串是否完美,我们将检查所有的前缀是否存在于三角形中)。
- 如果 "WORD "的长度大于 "LONGEST "的长度。
- 将 "LONGEST "设为 "WORD"。
- 如果 "WORD "的长度等于 "LONGEST "的长度,并且 "WORD "在词典上比 "LONGEST "小。
- 将 "LONGEST "设为 "WORD"。
- 如果 "WORD "的长度大于 "LONGEST "的长度。
- 如果 "WORD "的长度大于 "LONGEST "的长度,并且 "WORD "是一个完美的字符串(为了检查该字符串是否完美,我们将检查所有的前缀是否存在于三角形中)。
- 返回 "LONGEST "的值
C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
Node* links[26];
bool end = false;
bool containsKey(char ch) {
return links[ch - 'a'] != nullptr;
}
void put(char ch, Node* node) {
links[ch - 'a'] = node;
}
Node* get(char ch) {
return links[ch - 'a'];
}
void setEnd() {
end = true;
}
bool isEnd() {
return end;
}
};
class Trie {
private:
Node* root;
public:
Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
void insert(string word) {
Node* node = root;
for(auto ch: word) {
if(!node->containsKey(ch))
node->put(ch, new Node());
node = node->get(ch);
}
node->setEnd();
}
void insertAll(vector<string>& words) {
for(auto word: words)
insert(word);
}
bool isPerfect(string word) {
Node* node = root;
for(auto ch: word) {
if(!node->containsKey(ch))
return false;
node = node->get(ch);
if(!node->isEnd())
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
//We are going to implement this method to return the longest perfect string
string longestPerfectString(vector<string>& words) {
Trie* trie = new Trie();
trie->insertAll(words);
string longest = "";
for(auto word: words) {
if(word.size() >= longest.size() && trie->isPerfect(word)) {
if(word.size() > longest.size() || (word < longest))
longest = word;
}
}
return longest;
}
int main()
{
vector<string> v1 = {"w", "wo", "wor", "wow", "worm", "work"};
vector<string> v2 = {"w","wo","wor","worl","world"};
vector<string> v3 = {"a","banana","app","appl","ap","apply","apple"};
cout << longestPerfectString(v1) << endl; //output: work
cout << longestPerfectString(v2) << endl; //output: world
cout << longestPerfectString(v3) << endl; //output: apple
return 0;
}
Java实现
class Node {
private Node links[];
private boolean flag;
public Node() {
this.links = new Node[26];
this.flag = false;
}
public boolean containsKey(char ch) {
return this.links[ch - 'a'] != null;
}
public Node get(char ch) {
return this.links[ch - 'a'];
}
public void put(char ch, Node node) {
this.links[ch - 'a'] = node;
}
public void setEnd() {
this.flag = true;
}
public boolean isEnd() {
return this.flag;
}
}
class Trie {
private Node root;
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
private void insert(String word) {
Node node = root;
for(int i = 0;i < word.length();++i) {
if(!node.containsKey(word.charAt(i))) {
node.put(word.charAt(i), new Node());
}
node = node.get(word.charAt(i));
}
node.setEnd();
}
public void insertAll(String[] words) {
for(String word: words)
insert(word);
}
public boolean isPerfect(String word) {
Node node = root;
int n = word.length();
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i) {
if(node.containsKey(word.charAt(i))) {
node = node.get(word.charAt(i));
if(!node.isEnd())
return false;
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public String getLongestPerfect(String[] arr) {
String longest = "";
for(String word: arr) {
if(word.length() >= longest.length() && isPerfect(word)) {
if(word.length() > longest.length())
longest = word;
if(word.length() == longest.length()) {
if(word.compareTo(longest) < 0)
longest = word;
}
}
}
return longest;
}
}
class Solution {
public static String longestPerfectWord(String[] words) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insertAll(words);
return trie.getLongestPerfect(words);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] v1 = {"w", "wo", "wor", "wow", "worm", "work"};
String[] v2 = {"w","wo","wor","worl","world"};
String[] v3 = {"a","banana","app","appl","ap","apply","apple"};
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v1)); //output: work
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v2)); //output: world
System.out.println(longestPerfectWord(v3)); //output: apple
}
}
时间复杂度::在最坏的情况下,我们可能需要遍历整个 trie 数据结构。trie数据结构包含所有单词的所有字母。所以,这个方法的时间复杂度是O(⅀Wi),其中Wi代表'WORDLIST'中第i个词的长度。
空间复杂度。需要额外的空间来存储Trie数据结构中的所有单词。因此,空间复杂度为O(⅀Wi),其中Wi代表'WORDLIST'中第i个词的长度。
编码愉快
!🤗🤗🤗再见!👋👋👋见