在这篇文章中,我们解释了Trie的自下而上遍历的算法方法。
内容表
- 什么是Trie?
- 什么是Trie的自下而上遍历?
- 算法
- 代码方法
- 复杂度
什么是Trie?
Trie是一种特殊的数据结构,用于以有效的方式存储数据(一般来说,我们存储字符串)。它类似于树。它是一个n次方树,其中每个分支由n个组件组成。它也被称为前缀树或数字树。它由节点和边组成。它是一种索引结构,经常用于信息检索和组织。
它被用于字典中(存储、删除、搜索),寻找前缀字符串。它是一种有序的数据结构。
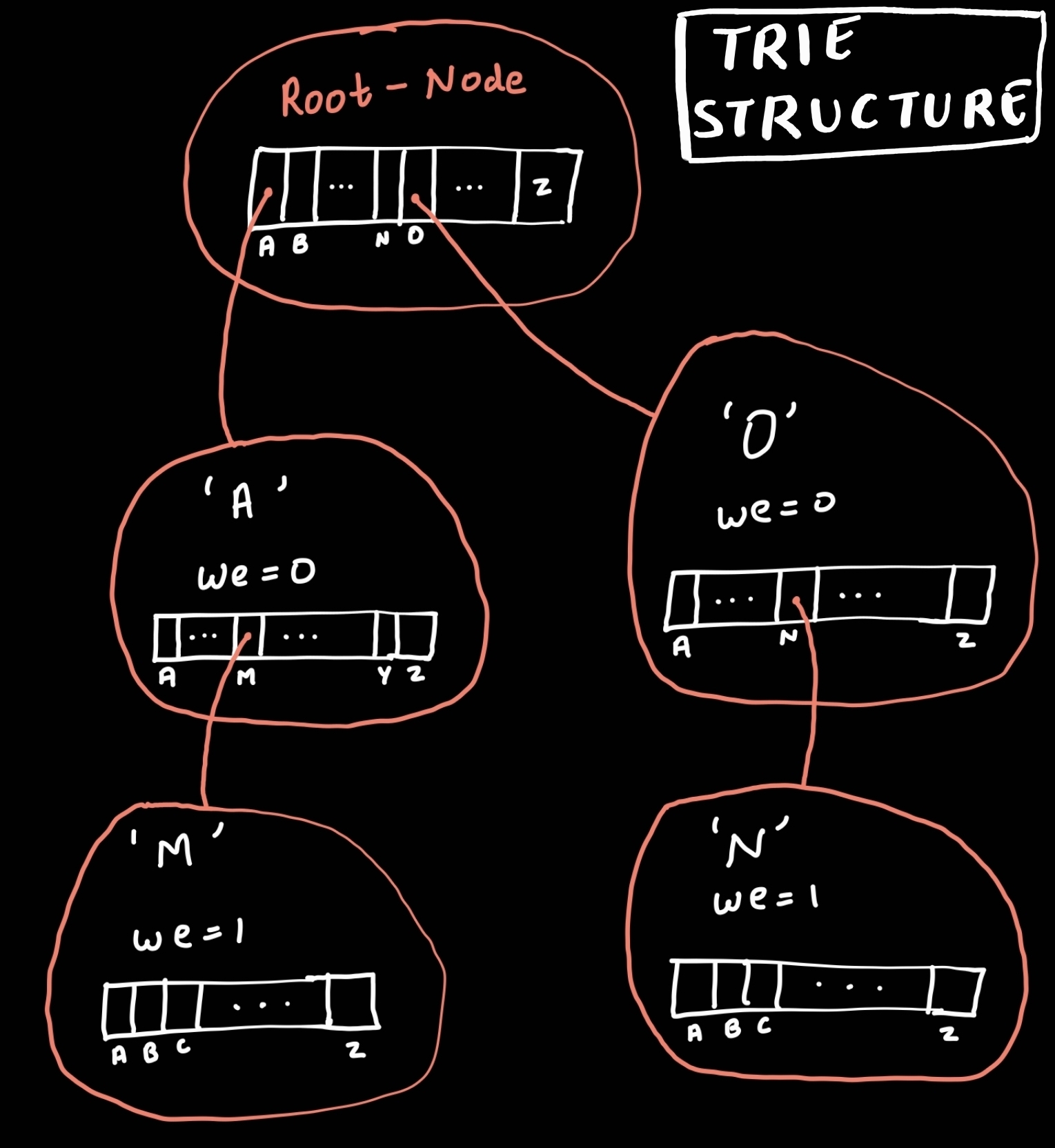
Trie数据结构的结构
struct trie-node{
trie-node *child[26]; //26 because english have 26 alphabets
//child will have 26 values
bool we; //"we" stands for end of word
};
- "我们 "将告诉你这个字母是否是单词的结尾?
- 对于单词的最后一个字母,"我们 "将有1(1)或True,其余的字母有0(0)或False。
- trie的数据结构如下图所示
三元组的自下而上的遍历
三元组自下而上的遍历是一种以从下到上的方式打印字母的方法。这是一个递归法。
例如。让我们把{ cat, coa, bat, bar, on }存储在Trie中。Trie看起来就像下面给出的那样:
Trie:
Root-Node
/ | \
b c o
| / \ |
a a o n
/ \ | |
r t t a
现在,在打印时,我们将首先以自下而上的方式打印最左边的子树,然后以自下而上的方式打印第二个最左边的子树,然后以同样的方式打印第三个最左边的子树,最后到最右边的子树。
在自下而上中,我们从树的底部字母开始打印到顶部的字母。因此,输出将是:
Output: r, t, a, b, t, a, a, o, c, n, o
trie的自下而上的遍历类似于树的后序遍历。
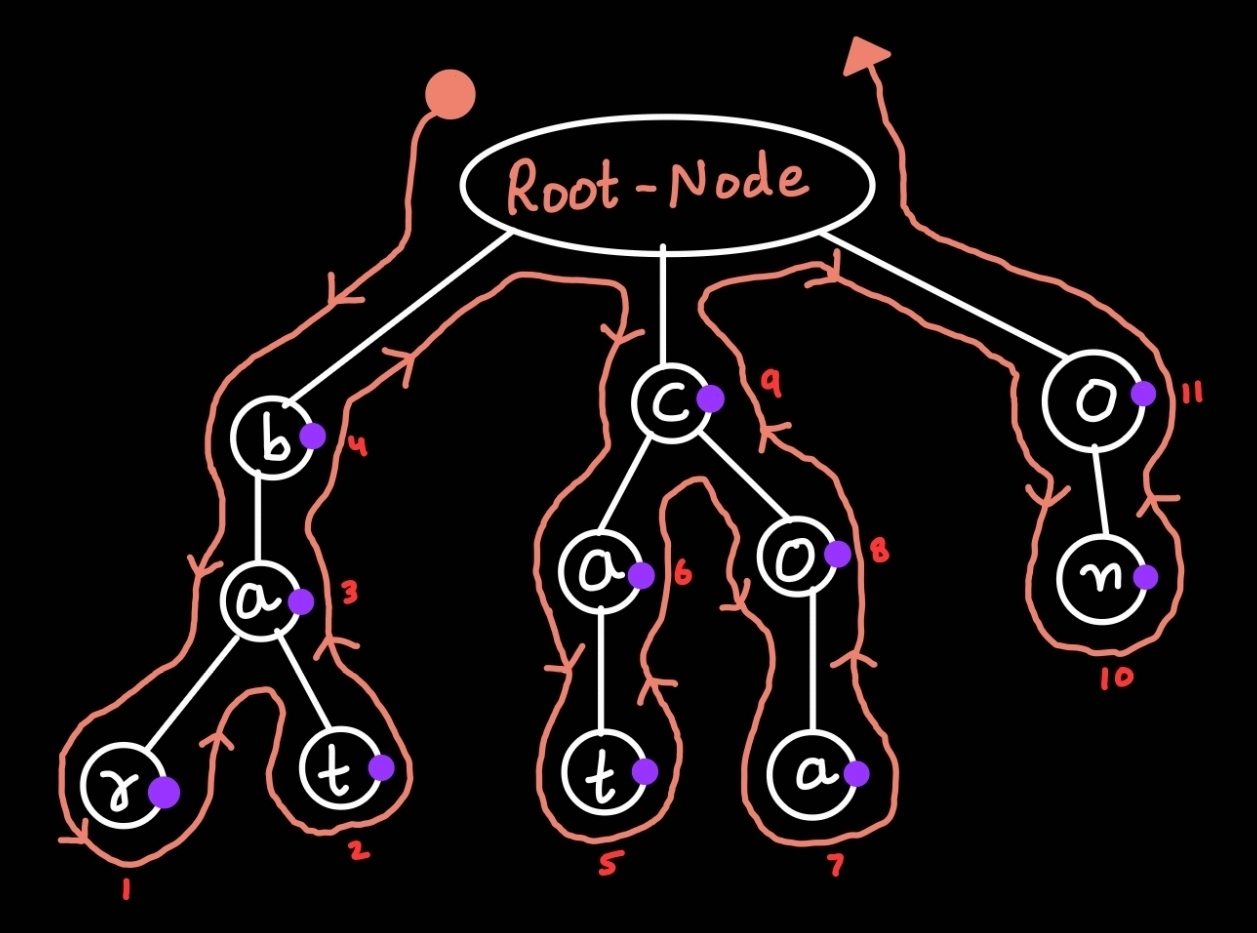
这棵树的后序输出是。{ r, t, a, b, t, a, a, o, c, n, o }
算法
开始B-print。
- 我们以递归方式从上到下移动。
- 如果(头是NULL),则返回。
- 如果(头是NOT-NULL),则递归移动到下一个节点(子节点)。
- 我们一直往下走,直到找不到包含 "我们=1 "值的节点,因为其中的字母表将是这个词的最后一个字母表。
- 当我们返回时打印节点的值/字母表。
结束B-print。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/*------------Structure of trie-node-------------*/
struct T_node {
bool we;
T_node *child[26];
T_node() //To create new node
{
we = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
child[i] = NULL; //Initializing all child value to null
}
}
};
class trie {
public:
T_node *root;
trie() //Constructor
{
root = new T_node();
}
void insert(string ); //Fuction to insert
void b_print(T_node *); //Function to print in Bottom-up manner
};
/*-------------Function to insert the string--------------*/
void trie::insert(string data) {
T_node *head = root; //assigning root to head
int length = data.size(); //length of word
int in= 0; //"in" is for index for child[]
int h = 0; //'h' is for height or level of tree
while (h < length) {
in = data[h] - 'a';
if (head->child[in] == NULL) {
head->child[in] = new T_node();
}
head = head->child[in];
h++;
}
if (head != NULL) {
//assign the "we" true which represent the end of word
head->we = true;
}
}
/*-----------B-print Function to print data--------------*/
void trie::b_print(T_node *head) {
if (head == NULL)
return;
int i = 0;
while (i <= 25) {
if (head->child[i] != NULL && head->we != true) {
b_print(head->child[i]); //Recursive call
cout <<" "<< (char)(i + 97); //To print alphabet
}
i++;
}
}
/*--------------Driver Function--------------*/
int main() {
trie t1; //"t1" is the Object of trie
/*
Root-Node
/ | \
b c o
| / \ |
a a o n
/ \ | |
r t t a
*/
t1.insert("cat");
t1.insert("coa");
t1.insert("bar");
t1.insert("bat");
t1.insert("on");
t1.b_print(t1.root);
return 0;
}
Output: r t a b t a a o c n o
复杂度
时间效率取决于 trie 数据结构,并且取决于用户输入的关键词字符串。
时间复杂性。O(K),其中'K'是给定词的总长度(大约)。因为,程序将通过 trie 中的每一个节点来打印,例如:
如果给定的词是 {cat, rat, hat, set}
"cat "的长度=3
"rat
"的长度=3 "
hat "的长度
=3
"set "的长度=3
那么K = (3 + 3 + 3 + 3)
K = 12
空间复杂性:O(K),其中 "K "代表三角形中的字母数量。因为程序会去打印三角形中的每一个节点。