【数据结构学习笔记】4.1串的定义、基本操作、存储结构
1.串的定义
-
串,即字符串(String)是由零个或多个字符组成的有限序列。
-
子串:串中任意个连续的字符组成的子序列。
-
主串:包含子串的串。
-
字串在主串中的位置:字符在串中的序号。
-
子串在主串中的位置:子串的第一个字符在主串中的位置。
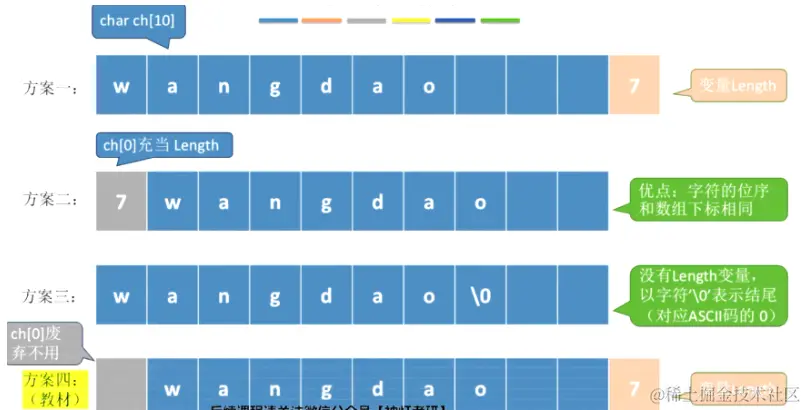
2.串的顺序存储
#define MAXLEN 255
typedef struct{
char ch[MAXLEN];
int length;
}SString;
typedef struct{
char *ch;
int length;
}HString;
HString S;
S.ch=(char *)malloc(MAXLEN * sizeof(char));
S.length=0;
3.串的链式存储
typedef struct StringNode{
char ch;
struct StringNode * next;
}StringNode,* String;

- 一个字符内存为1B,一个指针的内存为4B,导致存储密度低
typedef struct StringNode{
char ch[4];
struct StringNode * next;
}StringNode,* String;

4.基本操作的实现
-
SubString(&Sub,S,pos,len):求子串。用Sub返回串S 的第pos个字符起长度为len的子串。
typedef struct{
char ch[MAXLEN]
int length
}SString
//子串范围越界
if(pos+len-1>S.length)
return false
for(int i=pos
Sub.ch[i-pos+1]=S.ch[i]
Sub.length=len
return true
}
-
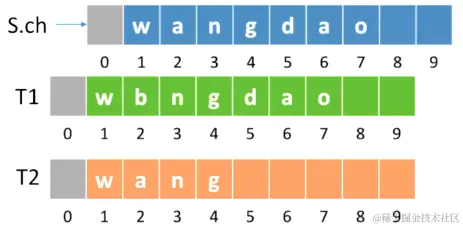
StrCompare(S,T):比较操作。若S>T,则返回值>0;若S=T,则返回值=0;若S<T,则返回值<0
int StrCompare(SString S,SString T){
for(int i=1
if(S.ch[i]!=T.ch[i])
return S.ch[i]-T.ch[i]
}
//扫描过的所有字符都相同,则长度长的串更大
return S.length-T.length
}
-
Index(S,T):定位操作。若主串S中存在与串T值相同的子串,则返回它在主串S中第一次出现的位置;否则函数值为0。
int Index(SString S,SString T){
int i=1,n=StrLength(S),m=StrLength(T);
SString sub; //用于暂存子串
while(i<=n-m+1){
SubString(sub,S,i,m);
if(StrCompare(sub,T)!=0) ++i;
else return i; //返回子串在主串中的位置
}
return 0; //S中不存在与T相等的子串
}
一段段向后遍历。